
a)
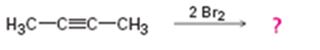
Interpretation:
Assuming that halogens add to
Concept introduction:
Alkynes when treated with one equivalent of a halogen yield a dihaloalkene as the product. They react with two equivalents of the halogens to yield a tetrahaloalkane derivative. In the first step of the addition reaction the nucleophilic attack of the π electrons of the double/triple bond in alkene/alkyne on a halogen results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. In the second step the halide ion attacks the cyclic halonium ion to yield the product.
To propose:
A mechanism and to predict the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Br2 adds to 2-butyne assuming that bromine adds to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes.
b)
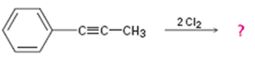
Interpretation:
Assuming that halogens add to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes, a mechanism is to be proposed and the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Cl2 adds to 1-phenylpropyne is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes when treated with one equivalent of a halogen yield a dihaloalkene as the product. They react with two equivalents of the reagents to yield a tetrahaloalkane as the product. In the first step of the addition reaction, the nucleophilic attack of the π electrons of the double/triple bond in alkene/alkyne on a halogen results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. In the second step the halide ion attacks the cyclic halonium ion to yield the product.
To propose:
A mechanism and to predict the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Cl2 adds to 1-phenylpropyne assuming that chlorine adds to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes.
c)
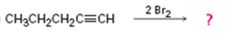
Interpretation:
Assuming that halogens add to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes, a mechanism is to be proposed and the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Br2 adds to 1-pentyne is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes when treated with one equivalent of a halogen yield a dihaloalkene as the product. They react with two equivalents of the reagents to yield a tetrahaloalkane as the product. In the first step of the addition reaction the nucleophilic attack of the π electrons of the double/triple bond in alkene/alkyne on a halogen results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. In the second step the halide ion attacks the cyclic halonium ion to yield the product.
To propose:
A mechanism and to predict the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Br2 adds to 1-pentyne assuming that bromine adds to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please provide with answer, steps and explanation of ideas to solve.arrow_forwardUsing what we have learned in CHEM 2310 and up through class on 1/31, propose a series of reaction steps to achieve the transformation below. Be sure to show all reagents and intermediates for full credit. You do not need to draw mechanism arrows, but you do need to include charges where appropriate. If you do not put your group name, you will get half credit at most. ? Brarrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the formation of 2-bromovanillin using bromonium ion as the reactive electrophile.arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole




