
(a)
Interpretation: The electron dot structure of HOOH needs to be drawn. Also, the polar covalent bonds need to be identified by assigning partial positive and negative charges on atoms.
Concept Introduction: A covalent bond can be polar if the two atoms bonded together have electronegativity differences. Here, an atom with more electronegativity has a partial negative charge, and an atom with less electronegativity has a partial positive charge.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is HOOH. Here, oxygen atoms are bonded together with one hydrogen atom. The number of valence electrons in an oxygen atom is 6 and that in the hydrogen atom is 1; thus, the total number of valence electrons will be:
The arrangement of electrons around an atom can be represented as follows:
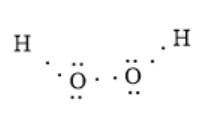
In the above molecule, the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atom. Thus, the oxygen atom will have a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atom will have a partial positive charge. This is represented as follows:
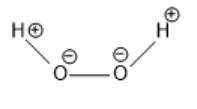
(b)
Interpretation: The electron dot structure of BrCl needs to be drawn. Also, the polar covalent bonds need to be identified by assigning partial positive and negative charges on atoms.
Concept Introduction: A covalent bond can be polar if the two atoms bonded together have electronegativity differences. Here, the atom with more electronegativity has a partial negative charge, and the atom with less electronegativity has a partial positive charge.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is BrCl. Here, Br and Cl are bonded via a single covalent bond. There are 7 valence electrons on Br and Cl atoms. Thus, the total number of valence electrons in the molecule will be:
The arrangement of electrons around the atom in the molecule can be represented as follows:
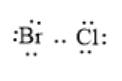
In the above molecule, the Cl atom is more electronegative than the Br atom. Thus, the Cl atom will have a partial negative charge and the Br atom will have a partial positive charge. This can be represented as follows:
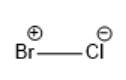
(c)
Interpretation: The electron dot structure of HBr needs to be drawn. Also, the polar covalent bonds need to be identified by assigning partial positive and negative charges on atoms.
Concept Introduction: A covalent bond can be polar if the two atoms bonded together have electronegativity differences. Here, the atom with more electronegativity has a partial negative charge, and the atom with less electronegativity has a partial positive charge.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is HBr. Here, H and Br are bonded via a single covalent bond. There are 7 valence electrons in the Br atom and 1 valence electron in the H atom. Thus, the total number of valence electrons in a molecule will be:
The arrangement of electrons around an atom in the molecule can be represented as follows:
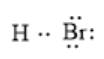
In the molecule, the Br atom is more electronegative than the H atom thus, there will be a partial negative charge on Br and a partial positive charge on the H atom. This can be represented as follows:
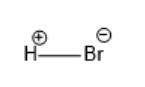
(d)
Interpretation: The electron dot structure of
Concept Introduction: A covalent bond can be polar if the two atoms bonded together have electronegativity differences. Here, the atom with more electronegativity has a partial negative charge, and the atom with less electronegativity has a partial positive charge.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
The arrangement of electrons around atoms in the molecule can be represented as follows:
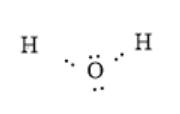
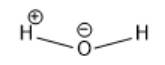
In the above molecule, the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atom. Thus, the oxygen atom will have a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atom will have a partial positive charge. This is represented as follows:
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





