
(a)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, the compound with high regioselective ability towards addition of
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as
The product of electrophilic addition reaction obtained by addition of electrophile to
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Chemical reaction involves bond making and breaking of two or more reactants in order to attain products from the reactants.
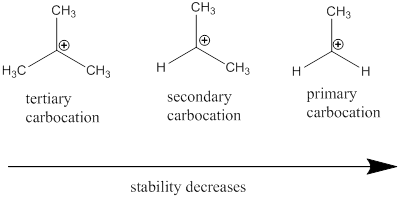
Cation: The positively charged chemical species is referred as cation.
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
(b)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, the compound with high regioselective ability towards addition of
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
The product of electrophilic addition reaction obtained by addition of electrophile to
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Chemical reaction involves bond making and breaking of two or more reactants in order to attain products from the reactants.
Cation: The positively charged chemical species is referred as cation.
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





