
Concept explainers
The common thermal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process requires the cycling of reagents through three distinct temperatures for denaturation (90 − 94°C), annealing (50 − 55°C), and extension (72°C). In continuous-flow PCR reactors, the temperatures of the three thermal zones are maintained as fixed while the reagents are cycled continuously through these zones. These temperature variations induce significant variations in the fluid density, which under appropriate conditions can be used to generate fluid motion. The figure depicts a thermosiphon-based PCR device. The closed loop is filled with PCR reagents. The plan of the loop is inclined at an angle α with respect to the vertical. The loop is surrounded by three heaters and coolers that maintain different temperatures.
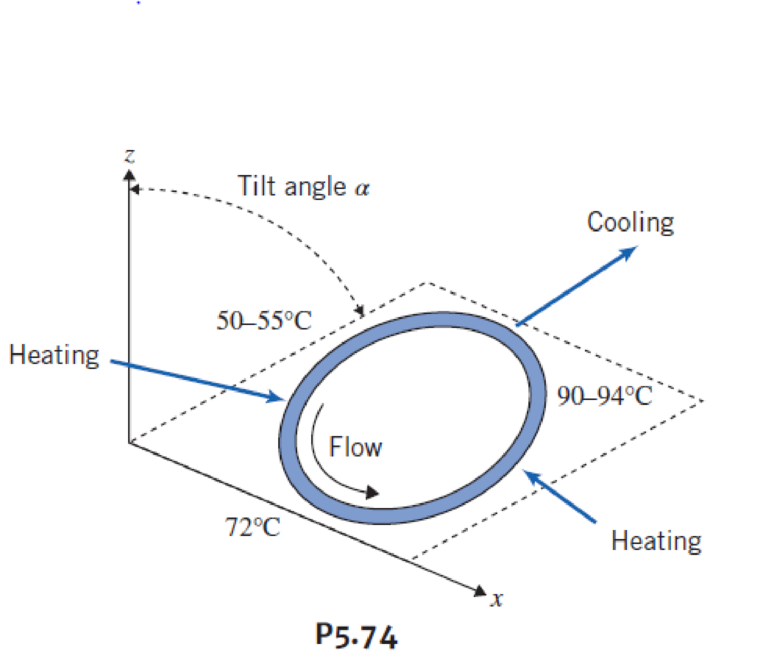
- (a) Explain why the fluid automatically circulates in the closed loop in the counterclockwise direction.
- (b) What is the effect of the angle α on the fluid velocity?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
- For Heat transfer through cylinder tube wall, the temperature is to be a linear function of r (radius) of the tube. Select one: O True O False The conductivity of H20 in solid form (ice) is higher than that of H20 in liquid form (water). Select one: O True O False F, (Correction factor for temperature in some heat exchangers) should be 1.0 or greater than 1.0 in some cases. Select one: O True Falsearrow_forwardNote:- • Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. • Answer completely. • You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardWaste heat from the first washing cycle of a dishwasher will be stored in PCM (latent heat:200 J/g) to be utilized in preheating of the second washing cycle with a flow rate of 3 L/min for 15 min. How much PCM in kg is needed to increase the temperature of the second washing cycle by 5 °C? (water density=1 kg/L, C₂= 4,18 kJ/kg °C). Assume PCM is totally melted during storage and frozen during recovery. O a. 2.3 kg O b. 1.9 kg O c. 4.7 kg O d. 5.7 kgarrow_forward
- In any heat exchanger, the log mean temperature difference "could" be the same as the mean "average" temperature difference of both ends of the heat exchanger, depending on the temperature profile within that heat exchanger along heat exchanger tubes. Select one: OTrue O False At very low pressures (vacuum), the thermal conductivity of gases approaches zero. Select one: O True O Falsearrow_forwardB/A boiling channel receives a thermal power of 6000 kw. If subcooled water at 275 °C enters the channel at a flow rate of 15 kg/s what is the void fraction at the channel outlet where the slip ratio is 1.687 and pressure is 68 bar. Given data: At 68 bar: h=1256 KJ/Kg, hg-1518 KJ/Kg, V-1.344*10-³ m³/Kg, V-28.27*10³ m³/Kgarrow_forwardThe liquid food is flowed through an uninsulated pipe at 90 ° C. The product flow rate is 0.3 kg / s and has a density of 1000 kg / m³, specific heat 4 kJ / (kg K), a viscosity of 8 x 10-6 Pa s, and a thermal conductivity of 0.55 W / (m) K). Assume that the change in viscosity is negligible. The internal diameter of the pipe is 30 mm with a thickness of 3 mm made of stainless steel (k = 15 W / [m ° C]). The outside temperature is 15 ° C. If the outer convective heat transfer coefficient is 18 W / (m² K), calculate the heat loss at steady state per meter pipe length. a. Find the convection coefficient in pipe = W / m² ° C. b. Calculate heat loss per meter pipe length = wattsarrow_forward
- Pressurized water (pin = 10 bar, Tin =110◦C) enters the bottom of an L = 12m long vertical tube of diameter D = 110 mm at a mass flow rate of m =1.5kg/s . The tube is located inside a combustion chamber, resulting in heat transfer to the tube. Superheated steam exits the top of the tube at pout = 7 bar, Tout = 600◦C. Determine the change in the rate at which the following quantities enter and exit the tube: (a) the combined thermal and flow work, (b) the mechanical energy, and (c) the total energy of the water. Also, (d) determine the heat transfer rate, Q˙. Hint: Relevant properties may be obtained from a thermodynamics text.arrow_forwardA group of students were tasked to compare the coefficient of performance of the freezer after observing how effective it operates after it converts a certain amount of water to ice in 6 hours. They were able to construct the table shown below. Compute the actual and ideal COP for both freezers Panasonic White Westinghouse 0.08 hp Power rating 42 W Mass of water 15 kg 20.5 kg Latent heat of solidification 80 cal/g 80 cal/g Interior temperature Exterior temperature 0.9- - 10°C 31'C 20°Carrow_forwardA steam trap is a device to purge steam condensate from a system without venting uncondensed steam. In one of the crudest trap types, the condensate collects and raises a float attached to a drain plug. Whenthe float reaches a certain level, it “pulls the plug,” opening the drain valve and allowing the liquid to discharge. The float then drops down to its original position and the valve closes, preventing uncondensed steam from escaping.(a) Suppose saturated steam at 25 bar is used to heat 100 kg/min of an oil from 135°C to 185°C. Heat must be transferred to the oil at a rate of 1:00 x 10 4 kJ/min to accomplish this task. The steam condenses on the exterior of a bundle of tubes through which the oil is flowing. Condensate collectsin the bottom of the exchanger and exits through a steam trap set to discharge when 1200 g of liquid is collected. How often does the trap discharge?(b) Especially when periodic maintenance checks are not performed, steam traps often fail to close completely…arrow_forward
- Please show your solution on a paper with measures of units in every process. The actual velocity of gas entering in a chimney is 8 m/s. The gas temperature is 25°C with a gas constant of 0.287 kJ/kg-K. Determine the gas pressure for a mass of a gas is 50,000 kg/hr and chimney diameter of 1.39 m.arrow_forwardVelocity of a gas When a hot gas exits a cylindrical smoke- stack, its velocity varies throughout a circular cross section of the smokestack, with the gas near the center of the cross section having a greater velocity than the gas near the perime- ter. This phenomenon can be described by the formula V = Vmas where Vmax is the maximum velocity of the gas, ro is the radius of the smokestack, and V is the velocity of the gas at a distance r from the center of the circular cross section. Solve this formula for r.arrow_forward2 m^3/min of a light oil are to be heated from 20C to 100C (with zero vaporization) in an exchanger using 250 kPa steam of 90% quality. The heat losses to the surrounding air have been estimated to be 5% of the heat transferred from the condensing steam to the oil. If the steam condensate leaves at its saturation point, what mass of steam perhour will be used in the exchanger? For light oil, Specific gravity= 0.88Specific heat= 2.00 kJ/kg-KFor steam at 250 kPa,Saturated liquid: hf= 535.49 kJ/kgvf=0.001067 m^3/kgSaturated vapor: hg= 2716.8 kJ/kgvg= 0.7188 m^3/kgarrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
