
Concept explainers
A tank contains water (20°C) at an initial depth y0 = 1 m. The tank diameter is D = 250 mm and a tube of diameter d = 3 mm and length L = 4 m is attached to the bottom of the tank. For laminar flow a reasonable model for the water level over time is
Using Euler methods with time steps of 12 min and 6 min:
- (a) Estimate the water depth after 120 min, and compute the errors compared to the exact solution
- (b) Plot the Euler and exact results.
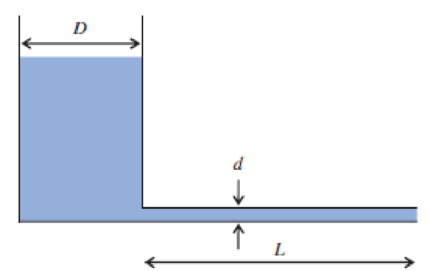
P5.75
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
- In a wind tunnel lab, the pitot tube is located at the height of 2 m, the measured static pressure P=1.0 Pa, total pressure P₁-88 Pa, if we assume the flow in the test section follow the profile of exponential function with a-0.22. Please calculated the wind velocity at the height of 1m. p=1.22kg/m³. (continued 1) Measured pressures at points A, B and C as follows: P-25 Pa, P=-55 Pa, P=-43 Pa, please calculate the wind pressure coefficients based on the reference wind velocity pressure at 1 m. A Carrow_forwardThe volume flow in a water pipe is 9000 m°/h. The pipe length is 80 m, the pipe diameter 1 m. The material data of water are a density of 1000 kg/m? and kinematic viscosity v=10® m7s. A steel pipe with roughness 0.05 mm is used. Determine the pressure drop in the pipe.arrow_forwardA constant-thickness film of viscous liquid (SG = 0.8, μ = 0.5 Pa-s) flows down an inclined plate an angle of 10⁰ as shown in the figure The velocity profile is given by the equation, u(y) = Cy(2h — y). If the value of his 5 cm, what is the value of the maximum velocity in m/s? NOTE: The pressure does not vary along the flow direction. u(y) Answer:arrow_forward
- Problem (3) Find the rate of change of h(t) (mm/s) if water is the fluid at all locations. Use V₁ = 7.1 m/s and Q = 1000 L/min. m₂ = 10 kg/s 4 cm dia. V₁ Answer: 120 cm h(t) 8arrow_forwardWater flows past a flat plate that has a length L = 5 m and a width w = 2 m, as shown in Figure Q4. The shear stress at the wall is given by Tw= μ du dy. When the flow is laminar the shear stress at the wall is given by the equation: Tw = 0.0644 pU 2 8 x Where p = 1000 kg/m3 is the water density and U∞ = 5 m/s is the velocity of the water. The height of the boundary layer is 5, and can be approximated by 8(x) = 5√ ux pU* The viscosity of water is μ = 1 mPa.s. a) Estimate the drag force on the plate. You may use the expression FD = | TwdA b) When the flow becomes turbulent, we can approximate the velocity gradient at the wall as constant, au ay = A. If the total drag force is 300 N, find A. c) When the fluid is heated to 900C, the density drops slightly and the viscosity decreases a lot, and engineers observe that the equation, Tw = 0.0644pU 2 6 x, becomes less accurate. Explain why this might occur (1-2 sentences). d) In order to visually examine a turbulent boundary layer, engineers…arrow_forwardAt t = 0 the tank shown in fig. is full up to top level, write the differential equation for the function of depth with respect to time. Tank 2 m 2 m conical 1 m 1 m cylinder r = 0.05 m Choose T or F F Case 1: y> 1 case 2: y< 1 m boundary condition at t=tm ,y=1 TI(1)2 dy/dt =0 -cd* t *( 0.05)2 * (2gy)1/2 I(y+1)2 dy/dt =o - cd* n *( 0.05)2 * (2gy)1/2arrow_forward
- Q2/ A fluid containing (water, oil, sand) flowing through the tube and open to the atmosphere as shown in the figure below.. Note that p°- 1.013*105 Pa Calculate the absolute pressure (Pa). Density: Pwater = 1000 kg/m Pail = 800 kg/m Pand = 200 kg/m P. h3=12 cm hg al2cm oIL Pa h25 cm ng = 6 cm %3D Sand waterarrow_forwardWater flows through a venturi as shown in the figure at a flow rate of Q=49.7 L/s. The inlet and throat diameters of the venturi meter are (D = 3.0 cm and d = 2.5 cm) respectively. The height of water column in the manometers L, and L, are 65 and 53 cm respectively. What is the experimental dynamic head at the throat-{section2} (in m)? LI L3 D 2 d (3arrow_forwardFind the horizontal and vertical forces to hold stationary the nozzle shown in the figure below. The fluid flowing through it is 10 °C liquid water; A₁ = 1.2 m², A₂ = 0.300 m², V₁ = 15 m/s, p2 = Patm and p₁ = Patm + 75 kPa. Neglect effects of gravity. Fx= i Fy= i A1 P1 KN kN Fy ZA A2, P2 = Patm Fx 45° Patmarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





