
(a)
Interpretation:
Starch should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Starch is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is starch.
Starch consists of many units of monosaccharide as it is a
Thus, starch is classified as polysaccharide.
(b)
Interpretation:
Glucose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Glucose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is glucose.
Glucose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule. Glucose is obtained by the photosynthesis process and also found in plants.
The structure is:
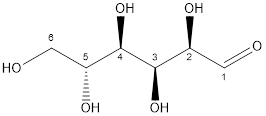
Thus, glucose is classified as monosaccharide.
(c)
Interpretation:
Sucrose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Sucrose is classified as disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is sucrose.
Sucrose consists of two units of monosaccharide. One fructose unit and glucose unit combined with each other by glycosidic bond to form sucrose.
The structure is:
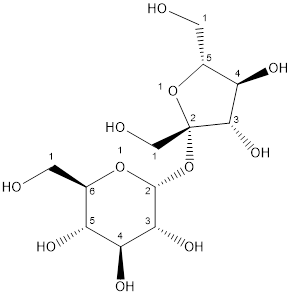
Thus, sucrose is classified as disaccharide.
(d)
Interpretation:
Ribose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Ribose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is ribose.
Ribose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule. Ribose consists of an
The structure is:
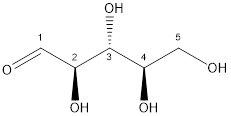
Thus, ribose is classified as monosaccharide.
(e)
Interpretation:
Cellulose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Cellulose is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is cellulose.
Cellulose consists of many units of monosaccharide or sugar as it is a polymeric carbohydrate which consists of various sugar units linked with glycosidic bonds.
Thus, cellulose is classified as polysaccharide.
(f)
Interpretation:
Glycogen should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Glycogen is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is glycogen.
Glycogen consists of many units of monosaccharide or sugar as it is a polymeric carbohydrate which consists of various sugar units linked with glycosidic bonds.
Thus, glycogen is classified as polysaccharide.
(g)
Interpretation:
Fructose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Fructose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is fructose.
Fructose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule.
The structure is:
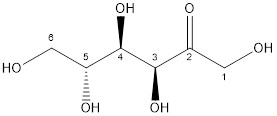
Thus, fructose is classified as monosaccharide.
(h)
Interpretation:
Lactose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Lactose is classified as disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is lactose.
Lactose consists of two units of monosaccharide or sugar. One galactose unit and glucose unit combined with each other by glycosidic bond to form sucrose.
The structure is:
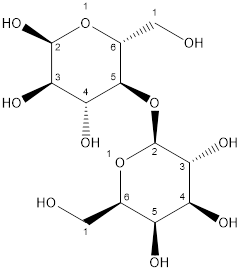
Thus, lactose is classified as disaccharide.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- (3 pts) Silver metal adopts a fcc unit cell structure and has an atomic radius of 144 pm. Fromthis information, calculate the density of silver. Show all work.arrow_forward4. (3 pts) From the information below, determine the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2. Show all work. AH/(kJ mol-¹) Sublimation of Mg(s) +148 lonization of Mg(g) +2187 to Mg2+(g) Vaporization of Br₂(1) +31 Dissociation of Br,(g) +193 Electron gain by Br(g) -331 Formation of MgBr₂(s) -524arrow_forward1. (4 pts-2 pts each part) Consider the crystal structures of NaCl, ZnS, and CsCl (not necessarily shown in this order). a. For one of the three compounds, justify that the unit cell is consistent with stoichiometry of the compound. b. In each of the crystal structures, the cations reside in certain holes in the anions' packing structures. For each compound, what type of holes are occupied by the cations and explain why those particular types of holes are preferred.arrow_forward
- (2 pts) What do you expect to happen in a Na2O crystal if a Cl− ion replaces one of the O2−ions in the lattice?arrow_forward(2 pts) WSe2 is an ionic compound semiconductor that can be made to be p-type or n-type.What must happen to the chemical composition for it to be p-type? What must happen tothe chemical composition for it to be n-type?arrow_forward8. (2 pts) Silicon semiconductors have a bandgap of 1.11 eV. What is the longest photon wavelength that can promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band in a silicon-based photovoltaic solar cell? Show all work. E = hv = hc/λ h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js c = 3.00 x 108 m/s 1 eV 1.602 x 10-19 Jarrow_forward
- A solution containing 100.0 mL of 0.155 M EDTA buffered to pH 10.00 was titrated with 100.0 mL of 0.0152 M Hg(ClO4)2 in a cell: calomel electrode (saturated)//titration solution/Hg(l) Given the formation constant of Hg(EDTA)2-, logKf= 21.5, and alphaY4-=0.30, find out the cell voltage E. Hg2+(aq) + 2e- = Hg(l) E0= 0.852 V E' (calomel electrode, saturated KCl) = 0.241 Varrow_forwardFrom the following reduction potentials I2 (s) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V I2 (aq) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.620 V I3- (aq) + 2e- = 3I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V a) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (aq) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). b) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (s) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). c) Calculate the solubility of I2 (s) in water.arrow_forward2. (3 pts) Consider the unit cell for the spinel compound, CrFe204. How many total particles are in the unit cell? Also, show how the number of particles and their positions are consistent with the CrFe204 stoichiometry - this may or may not be reflected by the particle colors in the diagram. (HINT: In the diagram, the blue particle is in an interior position while each red particle is either in a corner or face position.)arrow_forward
- From the following potentials, calculate the activity of Cl- in saturated KCl. E0 (calomel electrode)= 0.268 V E (calomel electrode, saturated KCl)= 0.241 Varrow_forwardCalculate the voltage of each of the following cells. a) Fe(s)/Fe2+ (1.55 x 10-2 M)//Cu2+ (6.55 x 10-3 M)/Cu(s) b) Pt, H2 (0.255 bar)/HCl (4.55 x 10-4 M), AgCl (sat'd)/Ag Fe2+ +2e- = Fe E0= -0.44 V Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu E0= 0.337 V Ag+ + e- = Ag E0= 0.799 V AgCl(s) + e- = Ag(s) + Cl- E0= 0.222 V 2H+ + 2e- = H2 E0= 0.000 Varrow_forwardA solution contains 0.097 M Ce3+, 1.55x10-3 M Ce4+, 1.55x10-3 M Mn2+, 0.097 M MnO4-, and 1.00 M HClO4 (F= 9.649 x 104 C/mol). a) Write a balanced net reaction that can occur between species in this solution. b) Calculate deltaG0 and K for the reaction. c) Calculate E and deltaG for the conditions given. Ce4+ + e- = Ce3+ E0= 1.70 V MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- = Mn2+ + 4H2O E0= 1.507 Varrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





