
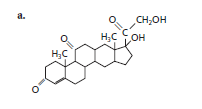
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the following structure is classified as fatty acid, triglyceride, phospholipid, sterioid or wax should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The molecules which contains hydrocarbons and not soluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents is known as lipid.
Lipids are classified as:
Triglycerides, Phospholipids and, Steroids and Waxes.
The building blocks of fat in our bodies and in food are known as fatty acids. Fatty acid consists of
The given structure is classified as steroid as it contains multiple cyclic rings.
Fatty acid consists of carboxylic acid with long aliphatic chain which can be saturated or unsaturated. Generally, fatty acids exist as: phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesteryl esters. These are important structural components for cells.
Fats and oils consist of molecules known as triglycerides (contain ester bonds).
The given structure is:
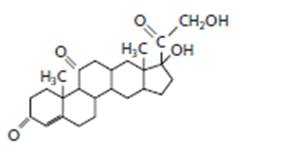
The skeleton of given structure is similar to steroid as it contains many cyclic structures. General structure of steroid contains 17 carbon atoms which are linked with each other in four fused rings, three rings contains six carbon atoms that is cyclohexane rings and one is five membered ring that is cyclopentane.
Thus, in the given structure, four cyclohexane rings are fused and one five membered ring that is cyclopentane is present along with a
Hence, the given structure is classified as steroid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the following structure is classified as fatty acid, triglyceride, phospholipid, sterioid or wax should be determined.
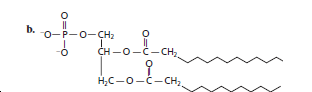
Concept introduction:
The molecules which contains hydrocarbons and not soluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents is known as lipid.
Lipids are classified as:
Triglycerides, Phospholipids and, Steroids and Waxes
The building blocks of fat in our bodies and in food are known as fatty acids. Fatty acid consists of carboxylic acid with long aliphatic chain which can be saturated or unsaturated.
The given structure is classified as phospholipid as it contains a phosphate group, diglyceride and two straight chains of carbon atoms.
Fatty acid consists of carboxylic acid with long aliphatic chain which can be saturated or unsaturated. Generally, fatty acids exist as: phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesteryl esters. These are important structural components for cells.
Fats and oils consist of molecules known as triglycerides (contain ester bonds).
The given structure is:
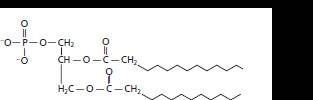
The skeleton of given structure is similar to phospholipids. General structure of phospholipids contains a glycerol molecule(s), phosphate group and two fatty acids.
Thus, in the given structure, two fatty acids are present that are two straight chains of carbon atoms along with a phosphate group and two glyceride group that is diglyceride.
Hence, the given structure is classified as phospholipid.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at 4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer. The H O HỌC—C—0—CH, CH, 2 A ethyl acetate H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm Check OA B OC ch B C Save For Later Submit Ass © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |arrow_forwardHow many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. O ✓ No additional Hs to color in top molecule ง No additional Hs to color in bottom…arrow_forwardin the kinetics experiment, what were the values calculated? Select all that apply.a) equilibrium constantb) pHc) order of reactiond) rate contstantarrow_forward
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





