
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the organic compound formed by elimination from an alcohol needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In a substitution reaction, one
Explanation of Solution
Alcohol undergoes elimination reaction to form
For example:
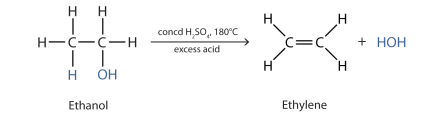
In the above reaction, ethanol reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to form alkene and water.
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the organic compound formed by addition of hydrogen chloride to an alkene needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In a substitution reaction, one functional group is replaced by other functional group. In addition reaction, two reactants simply add to form a single product. In condensation reaction, addition of two reactants takes place after removal of water molecule. The elimination reaction results when removal of two substituent groups takes place from a molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The addition reaction of hydrogen chloride to alkene results in the formation of
For example:
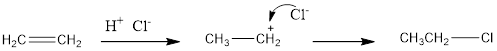
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the organic compound formed by addition of water to an alkene needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In a substitution reaction, one functional group is replaced by other functional group. In addition reaction, two reactants simply add to form a single product. In condensation reaction, addition of two reactants takes place after removal of water molecule. The elimination reaction results when removal of two substituent groups takes place from a molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of water to alkene in the presence of an acid results in the formation of an alcohol. This is known as hydration of an alkene.
For example:
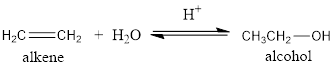
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the organic compound formed by substitution of a hydroxyl group for a halogen atom needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In a substitution reaction, one functional group is replaced by other functional group. In addition reaction, two reactants simply add to form a single product. In condensation reaction, addition of two reactants takes place after removal of water molecule. The elimination reaction results when removal of two substituent groups takes place from a molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The substitution of hydroxyl group for a halogen atom results in the formation of an alkyl halide from an alcohol. This results in the formation of water molecule as a byproduct.
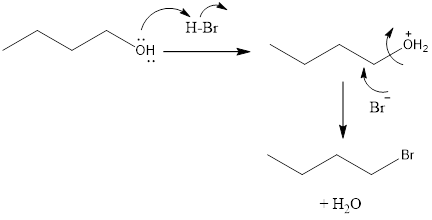
Chapter 22 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- A partir de Aluminio y Co(NO3)2ꞏ6H2O, indicar las reacciones a realizar para obtener Azul de Thenard (Al2CoO4).arrow_forwardTo obtain Thenard Blue (Al2CoO4), the following reaction is correct (performed in an oven):Al(OH)3 + Co(OH)2 → Al2CoO4 + 4 H2Oarrow_forwardProblem 38 can u explain and solve thanks april 24arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





