
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of carbinoxamine has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (
Grignard reagent is reaction with carbonyl compound such as
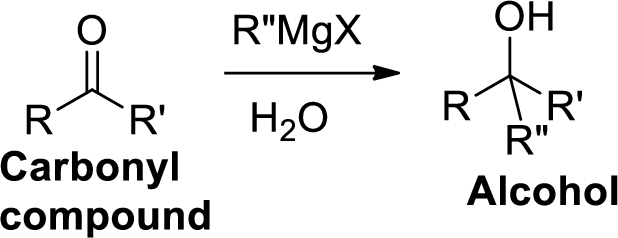
(b)
Interpretation:
The chirality of Carbinoxamine is to be identified and the possible stereoisomers has to be identified in the given synthesis.
Concept introduction:
Chiral:
A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule.
Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer:
A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers:
Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers:
A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers:
A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture:
A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


