
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: As a hybrid of five contributing structures the given molecule has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Kekule structures:
The double bonds of an
The Kekule structure for benzene ring:
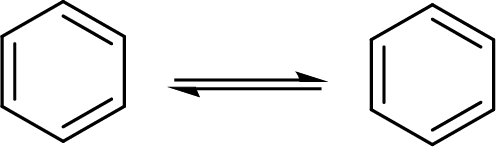
The back and forth shift of the double bonds in between these two forms is shown here:
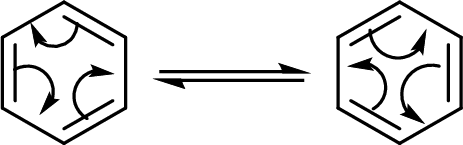
(b)
Interpretation: As a hybrid of five contributing structures the given molecule has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Kekule structures:
The double bonds of an aromatic ring shift back and forth very rapidly. The resulted forms or structures cannot be separated and stay in equilibrium. Those structures are known as Kekule structures.
The Kekule structure for benzene ring:
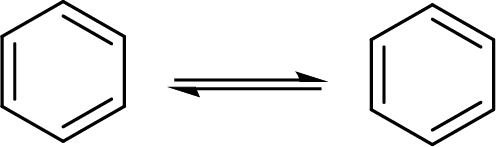
The back and forth shift of the double bonds in between these two forms is shown here:
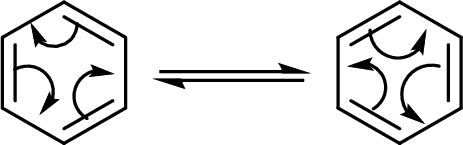
(c)
Interpretation: As a hybrid of five contributing structures the given molecule has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Kekule structures:
The double bonds of an aromatic ring shift back and forth very rapidly. The resulted forms or structures cannot be separated and stay in equilibrium. Those structures are known as Kekule structures.
The Kekule structure for benzene ring:
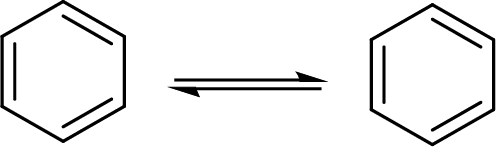
The back and forth shift of the double bonds in between these two forms is shown here:
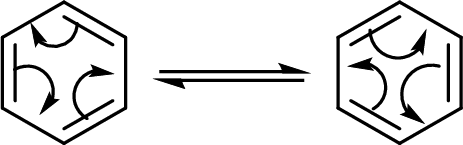
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





