
Name the following compounds and ions.
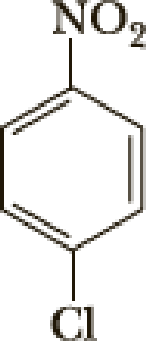
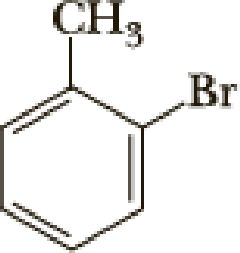

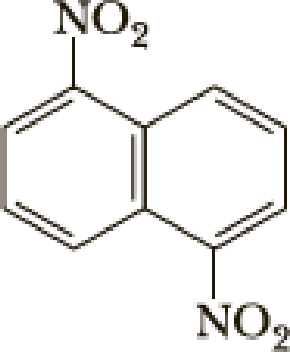
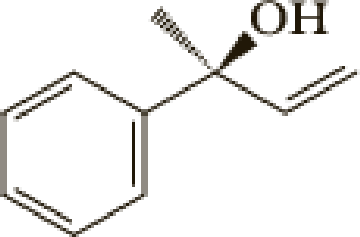

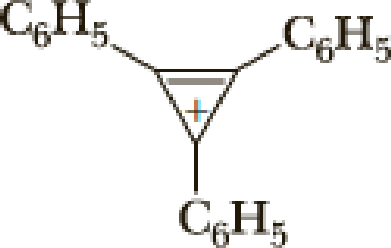
(a)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
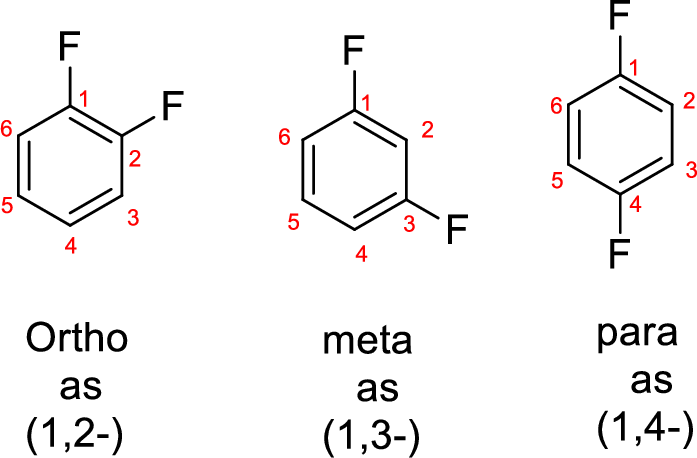
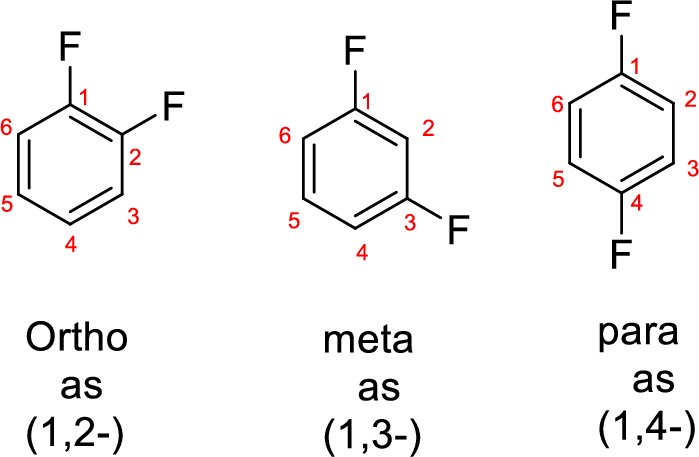
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
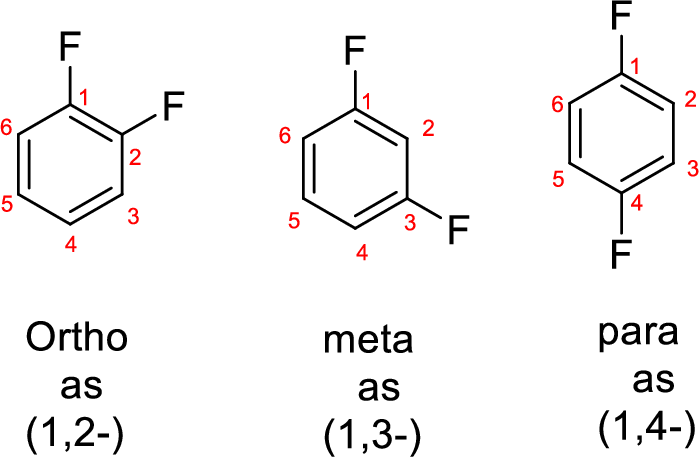
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
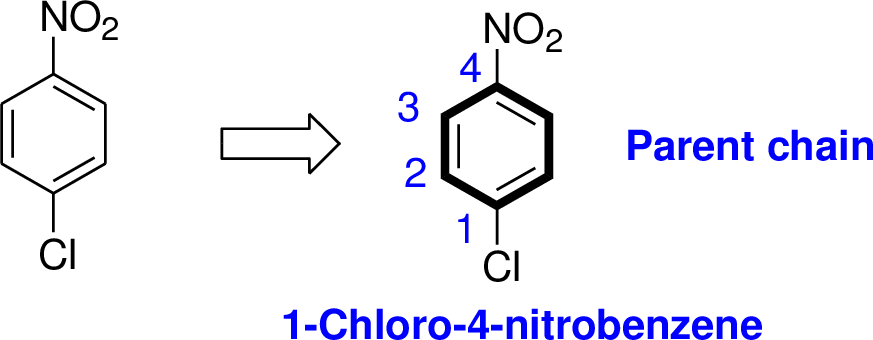
The parent name of the compound is benzene, in the given structure the first carbon is bonded with chlorine
(b)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
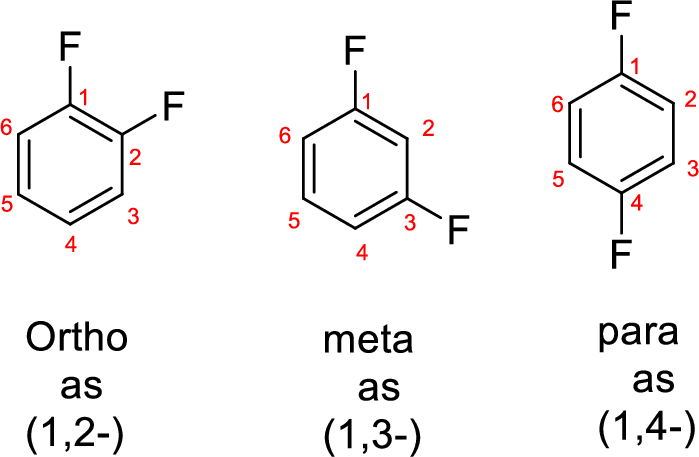
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
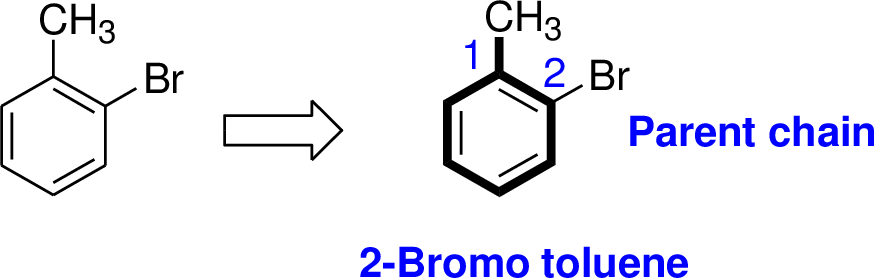
The parent name of the compound is benzene. Benzene is attached with methyl group is called toluene. In the given structure the second carbon is bonded with bromine
(c)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
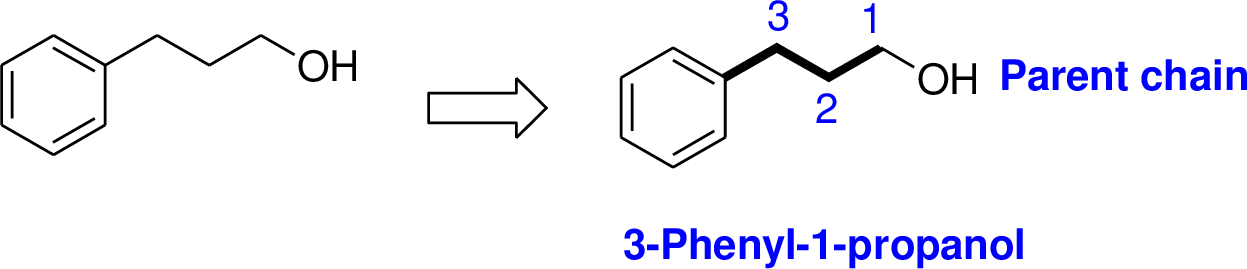
The number of carbon in parent chain is three, hence the parent hydrocarbon is propane. The functional group of the given molecule is alcohol therefore the suffix “-ane” is replaced with “-ol” indicating the presence of alcohol. In the given structure the first carbon is bonded with alcohol
(d)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
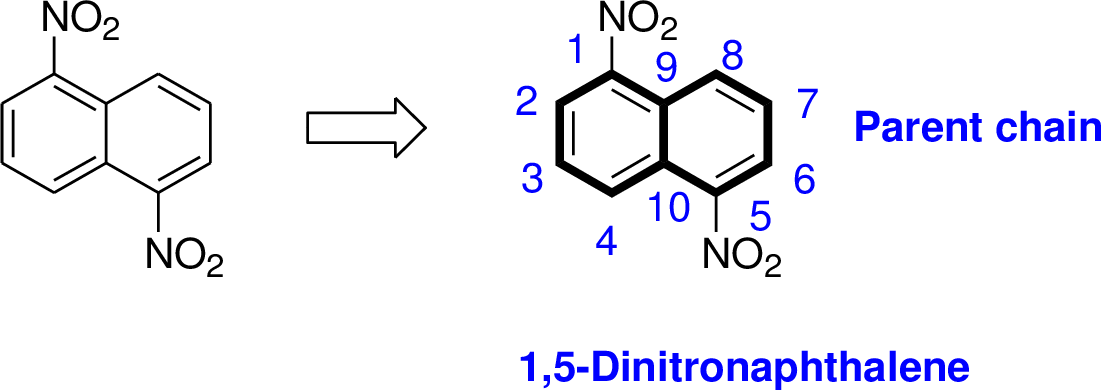
The parent name of the compound is naphthalene, in the given structure the first carbon and fifth carbon is bonded with nitro group
(e)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
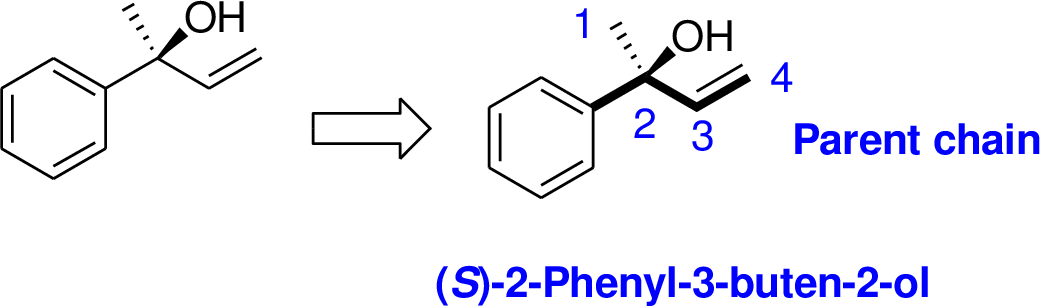
The number of carbon in parent chain is four, hence the parent hydrocarbon is butane. The functional group of the given molecule is alcohol therefore the suffix “-ane” is replaced with “-ol” indicating the presence of alcohol. In the given structure the second carbon is bonded with alcohol
(f)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
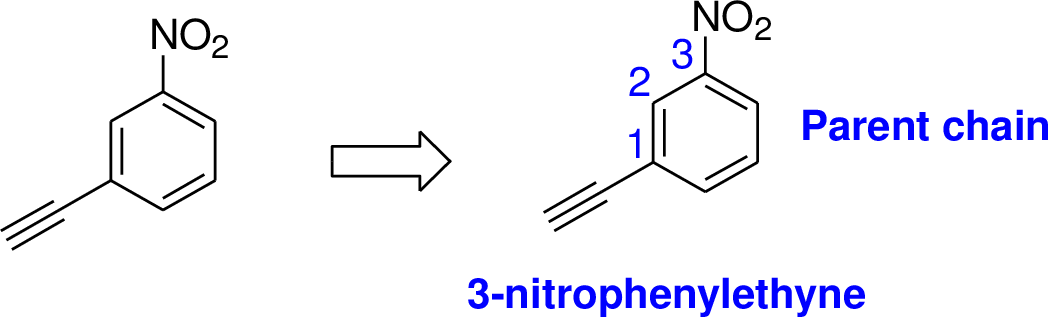
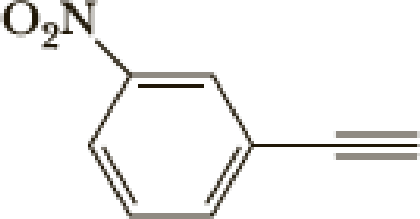
The parent name of the compound is ethyne, in the given structure the first carbon is bonded nitrobenzene (in that third carbon is bonded with nitro group) therefore the name of the compound is 3-nitrophenylethyne.
(g)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
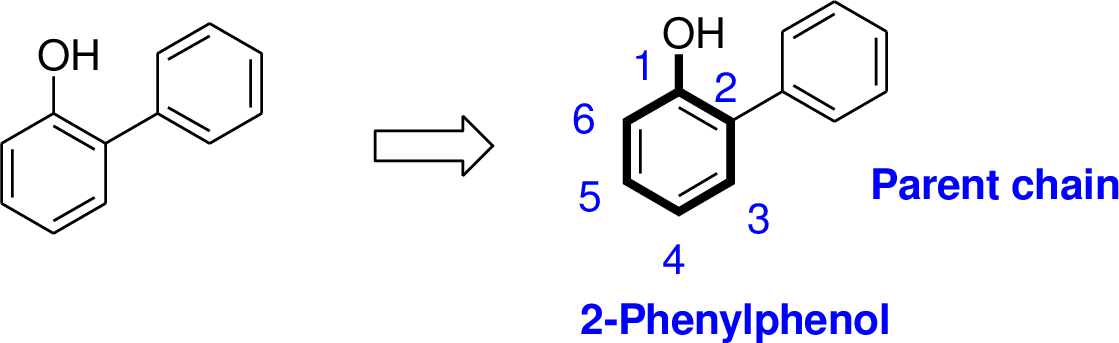
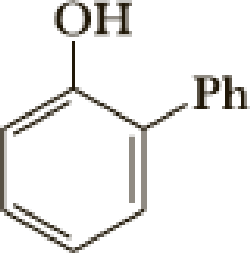
The parent name of the compound is phenol (hydroxyl group is attached with benzene). Benzene is attached with second carbon of phenol moiety. Therefore the name of the compound is 2-Phenylphenol.
(h)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aromatic compounds:
- The parent compound of aromatic compound is Benzene.
- The substituent groups attached to the parent is identified. A substituent group contains group of atoms attached to the carbon atom of the aromatic ring.
- While numbering the parent, the location of the second group relative to the first substituent uses prefixes like o-ortho (1,2-), m-meta (1,3-), and p-para (1,4) in disubstituted aromatic ring.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
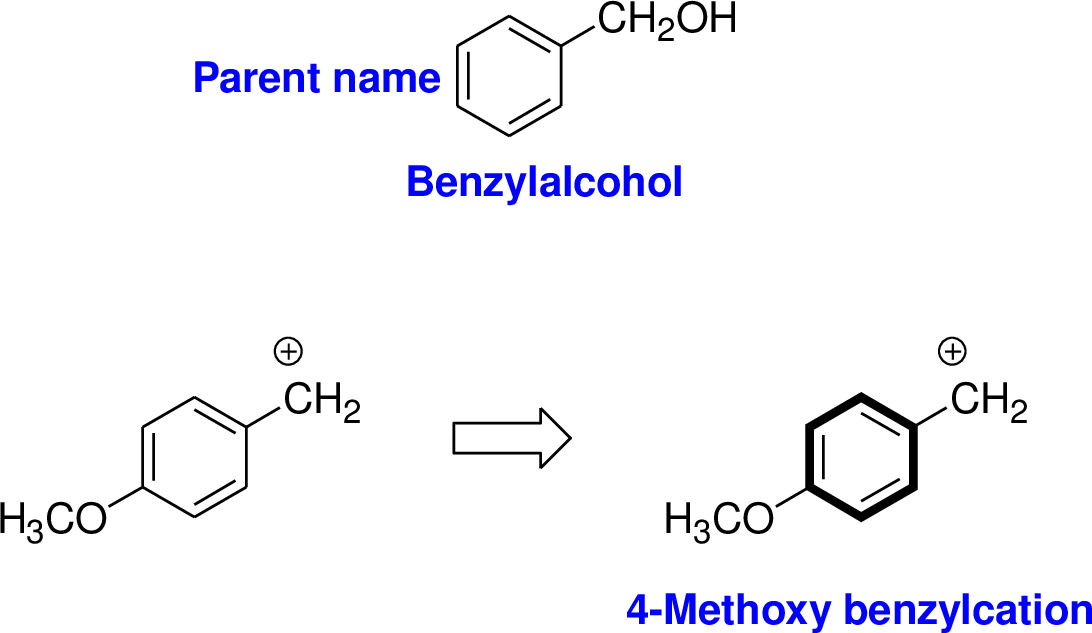
The parent name of the compound is benzyl alcohol, the structure of benzyl alcohol is shown above. Methoxy group is attached with fourth carbon of benzyl moiety and it has positive charge, positive charge is called as cation. Therefore the name of the compound is 4-methoxybenzyl cation.
(i)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
Concept introduction for IUPAC:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:
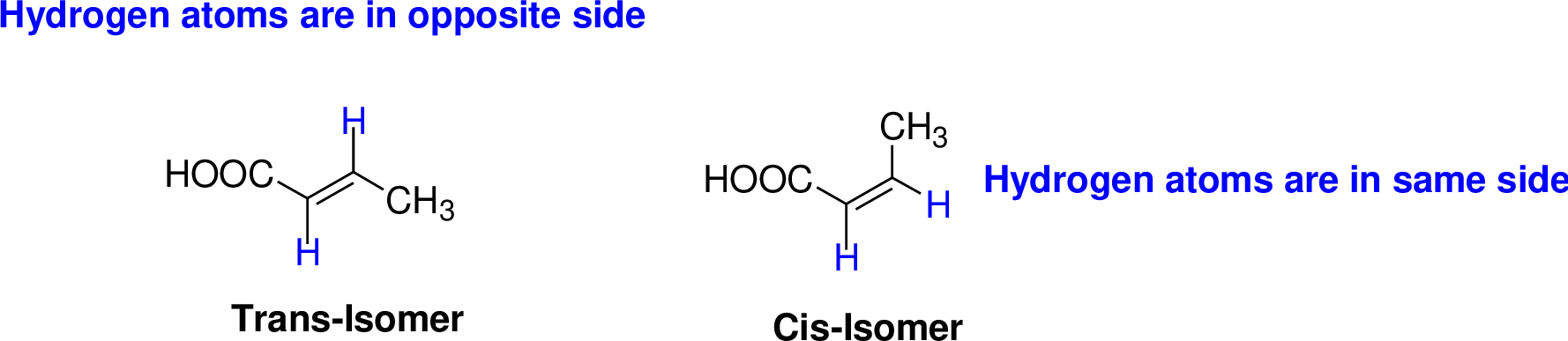
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
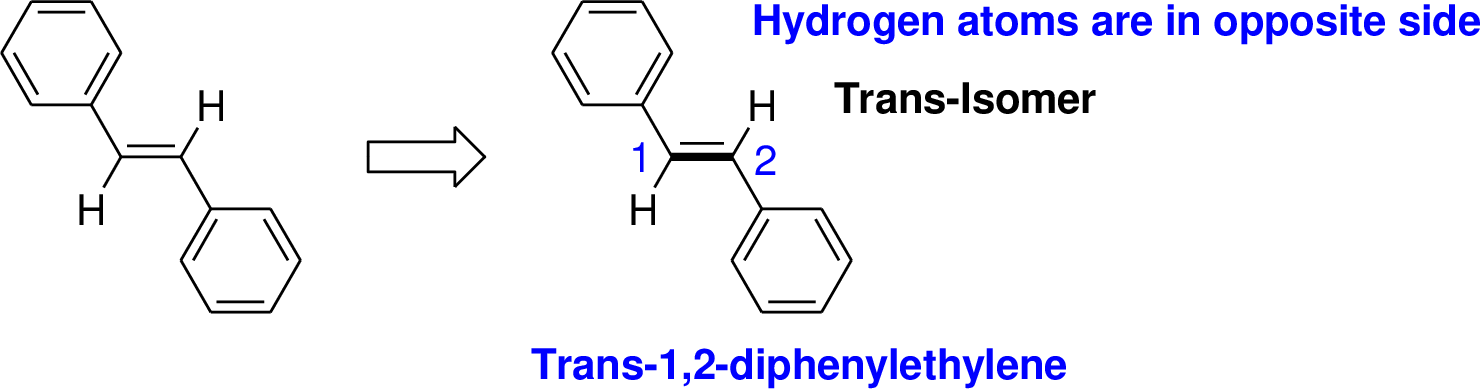
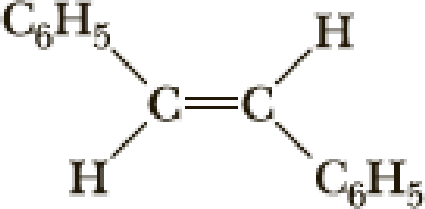
The parent name of the compound is ethylene (two carbon chain with double bond). Two phenyl group is attached with ethylene at first and second carbon, two hydrogen atom is bonded in opposite direction therefore it is trans. Therefore the name of the compound is 1, 2-Diphenylethylene.
(j)
Interpretation:
The name has to be given for the organic compound.
Concept introduction:
Concept introduction for IUPAC:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
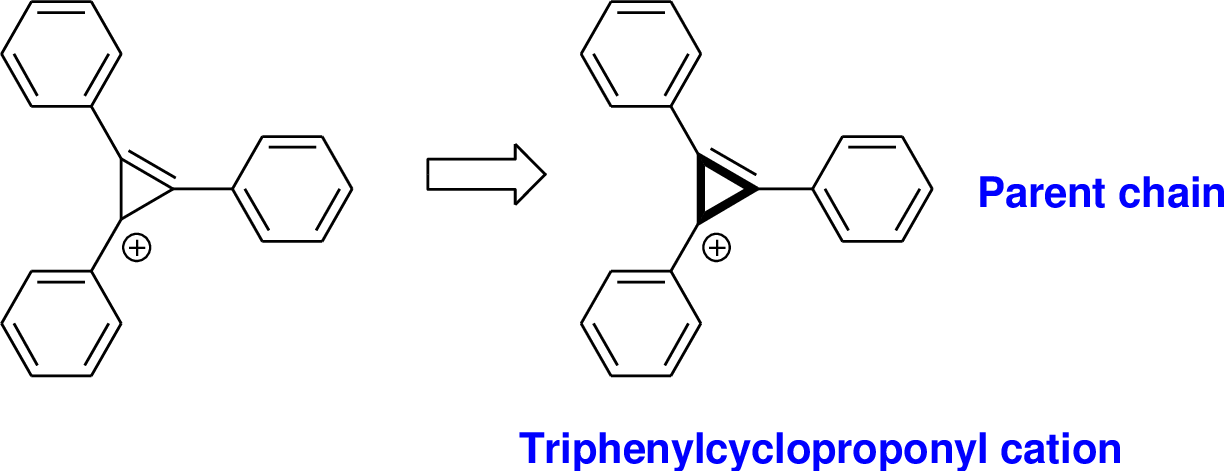
The parent name of the compound is cyclopropane, and it has double bond, it has positive charge, positive charge is called as cation. Three phenyl group is bonded with three different carbon atom Therefore the name of the compound is triphenylcyclopropenyl cation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forward
- Given the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forwardAt 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. State the difference between E and E0.arrow_forward
- In an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery notation. Is that correct?arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery. Is that correct?arrow_forwardCalculate the free energy of formation of 1 mol of Cu in cells where the electrolyte is 1 mol dm-3 Cu2+ in sulfate solution, pH 0. E° for the Cu2+/Cu pair in this medium is +142 mV versus ENH.Assume the anodic reaction is oxygen evolution.Data: EH2 = -0.059 pH (V) and EO2 = 1.230 - 0.059 pH (V); 2.3RT/F = 0.059 Varrow_forward
- If the normal potential for the Fe(III)/Fe(II) pair in acid at zero pH is 524 mV Hg/Hg2Cl2 . The potential of the saturated calomel reference electrode is +246 mV versus the NHE. Calculate E0 vs NHE.arrow_forwardGiven the galvanic cell whose scheme is: (-) Zn/Zn2+ ⋮⋮ Ag+/Ag (+). If we know the normal potentials E°(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76V and E°(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799 V. Indicate the electrodes that are the anode and the cathode and calculate the E0battery.arrow_forwardIndicate the functions that salt bridges have in batteries.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





