
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism of 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde to compound A has to be shown.
(b)
Interpretation:
The reagent and experiment condition is to be given for the conversion of A to B.
Concept introduction:
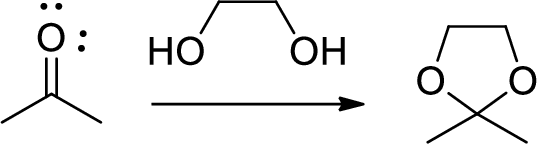
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the conversion of B to C is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an aldehyde or a ketone gets converted to
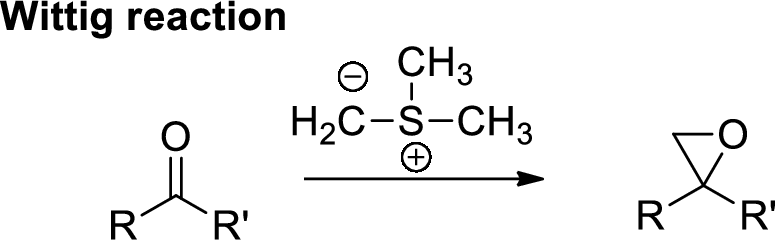
(d)
Interpretation:
The reagent and experiment condition is to be given for the conversion of C to D.
Concept introduction:
(e)
Interpretation:
The reagent and experiment condition is to be given for the conversion of D to albuterol.
Concept introduction:
Diol is to protect the ketone and aldehyde (carbonyl group). In this reaction acetone is protected as acetal by using ethylene glycol.
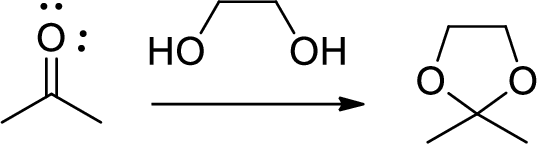
(f)
Interpretation:
The possible stereoisomer’s has to be shown if the product is chiral.
Concept introduction:
Chiral:
A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule. Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer: A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: F structure Br LL Br Br الحمد name ☐ ☐arrow_forwardDraw an appropriate reactant on the left-hand side of this organic reaction. Also, if any additional major products will be formed, add them to the right-hand side of the reaction. + + Х ง C 1. MCPBA Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. NaOH, H₂O Explanation Check OI... OH ol OH 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardCalculate the atomic packing factor of quartz, knowing that the number of Si atoms per cm3 is 2.66·1022 and that the atomic radii of silicon and oxygen are, respectively, 0.038 and 0.117 nm.arrow_forward
- 3. a. Use the periodic table to add up the molecular weight of thionyl chloride (SOCl2) and show your work. b. The actual value obtained for the molecular ion on a high resolution mass spectrometer is 117.9041. Explain the discrepancy. c. Show the calculations that correctly result in the exact mass of 117.9041 for SOC₁₂. Use Table 11.2 or Appendix E in your calculations.arrow_forward6. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B₂2+ B22+, B2, C22, B22- and N22+ Molecular Orbital Diagram B2 C22- B22- N22+ Which molecule is paramagnetic?arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- EXERCISES: Complete the following exercises. You must show all work to receive full credit. 1. How many molecular orbitals can be built from the valence shell orbitals in O2? 2. Give the ground state electron configuration (e.g., 02s² 0*2s² П 2p²) for these molecules and deduce its bond order. Ground State Configuration Bond Order H2+ 02 N2arrow_forward7. Draw the Lewis structures and molecular orbital diagrams for CO and NO. What are their bond orders? Are the molecular orbital diagrams similar to their Lewis structures? Explain. CO Lewis Structure NO Lewis Structure CO Bond Order NO Bond Order CO Molecular Orbital Diagram NO Molecular Orbital Diagramarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structure of 4-ethyl-1,2,4-trifluoro-2-methyloctane.arrow_forward5. The existence of compounds of the noble gases was once a great surprise and stimulated a great deal of theoretical work. Label the molecular orbital diagram for XeF (include atom chemical symbol, atomic orbitals, and molecular orbitals) and deduce its ground state electron configuration. Is XeF likely to have a shorter bond length than XeF+? XeF XeF+ Bond Orderarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
