
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Why benzene fails to react under the given reaction conditions has to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Radical reaction: It is reacting to electron octet of valence shell.
A radical can break a bond in another molecular and abstract a partner with an electron, giving substitution in the original molecule.
A radical can added to an
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 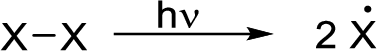
Chain propagation: 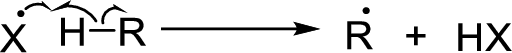
Chain termination:
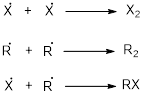
It is a change in enthalpy of a hemolysis reaction at absolute zero where a molecule is broken down into two free radicals.
(b)
Interpretation:
Why the bond dissociation enthalpy of a
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization: It is the mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals suitable for the paring of electrons to from chemical bonds in valance bond theory.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please draw by handarrow_forward3. Predict the major product and give a mechanism for the following reactions: (CH3)3COH/H₂SO4 a) b) NC CH₂O c) LOCH, (CH3)3COH/H2SO4 H,SO -OHarrow_forwardIndicate if the aldehyde shown reacts with the provided nucleophiles in acid or base conditions. a NaBH4 be Li eli -NH2 P(Ph3) f KCN g OH excess h CH3OH i NaCHCCH3arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardPolar solutes are most likely to dissolve into _____, and _____ are most likely to dissolve into nonpolar solvents. A. nonpolar solutes; polar solvents B. nonpolar solvents; polar solvents C. polar solvents; nonpolar solutes D. polar solutes; nonpolar solventsarrow_forwardDeducing the Peactants Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Xarrow_forward
- Draw all 8 stereoisomers, circling each pair of enantiomer(s)/ mirror image compound(s)arrow_forwardBookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help Chemical Formula - Aktiv Che X + → C 11 a app.aktiv.com Google Chrome isn't your default browser Set as default Question 12 of 16 Q Fri Feb 2 Verify it's you New Chrome availabl- Write the balanced molecular chemical equation for the reaction in aqueous solution for mercury(I) nitrate and chromium(VI) sulfate. If no reaction occurs, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. 3 Hg(NO3)2(aq) + Cг2(SO4)3(aq) → 3 Hg₂SO (s) + 2 Cr(NO3), (aq) ean Ui mate co ence an climate bility inc ulnerabili women, main critic CLIMATE-INI ernational + 10 O 2 W FEB 1 + 4- 3- 2- 2 2 ( 3 4 NS 28 2 ty 56 + 2+ 3+ 4+ 7 8 9 0 5 (s) (1) Ch O 8 9 (g) (aq) Hg NR CI Cr x H₂O A 80 Q A DII A F2 F3 FA F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 #3 EA $ do 50 % 6 CO & 7 E R T Y U 8 ( 9 0 F10 34 F11 川 F12 Subr + delete 0 { P }arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction n the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. >arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Some important notes: A ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardif the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
