
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure, VSEPR formula, bond angle, and molecular shape for
Concept Introduction:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model predicts shape by inclusion of bond angles and most distant arrangement of atoms that leads to minimum repulsion. For the molecules that have no lone pairs around the central atom the bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement is decided by the table as follows:
In order to determine the shape the steps to be followed are indicated as follows:
- 1. Lewis structure of molecule should be written.
- 2. The type electron arrangement around the central atom should be identified around the central atom. This essentially refers to determination of bond pairs and unshared or lone pairs around central atoms.
- 3. Then bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement that can maximize the distance of electron pairs about central atom determines the shape.
For molecules that have lone pairs around central atom, lone pairs influence shape, because there are no atoms at the positions occupied by these lone pairs. The key rule that governs the molecular shape, in this case, is the extent of lone –lone pair repulsions are far greater than lone bond pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsions. The table that summarized the molecular shapes possible for various combinations of bonded and lone pairs are given as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E.16E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 15 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
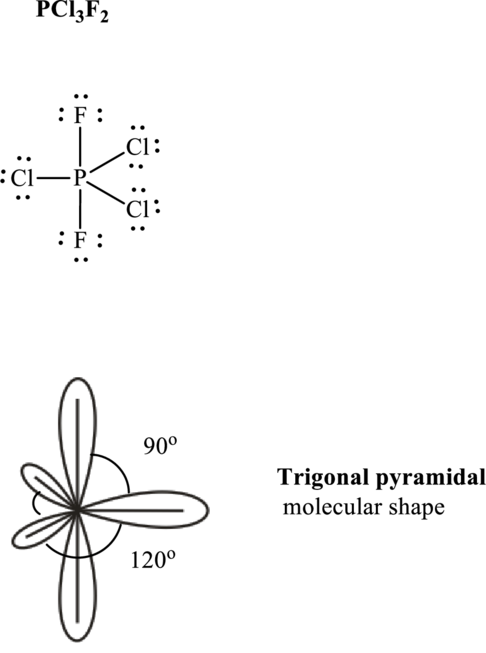
It is evident that
One lone pair is localized on equatorial positions so as to minimize lone pair–bond pair repulsions in accordance with VSPER model. This leads see-saw shape for
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and each unique atom attached by X and
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure, VSEPR formula, bond angle, and molecular shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 2E.16E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 12 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
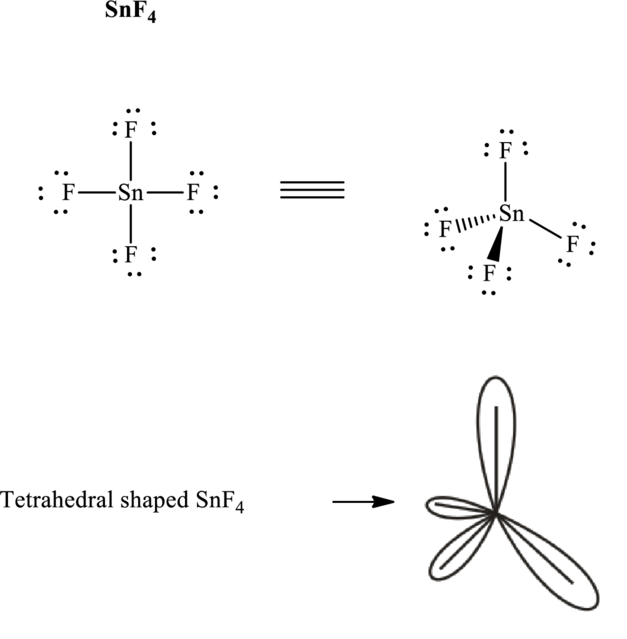
It is evident that
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bon pairs by X, then for any tetrahedral species with no one pairs the VSEPR formula is predicted to be
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure, VSEPR formula, bond angle, and molecular shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.16E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on atom along with two negative charges in
The skeleton structure in
These 18 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs on each fluorine atom to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
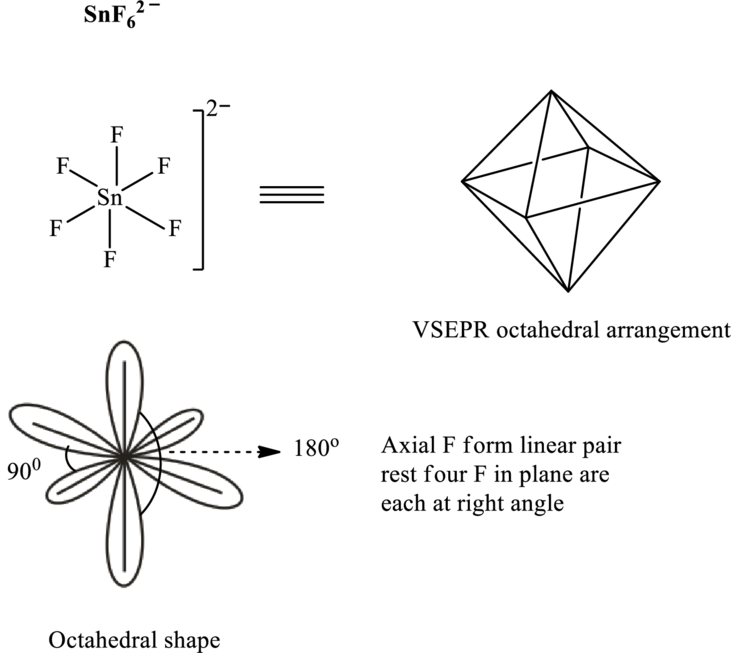
It is evident that in
(d)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure, VSEPR formula, bond angle and molecular shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E.16E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each fluorine and central iodine in
The skeleton structure in
These 16 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the fluorine atoms and one on central iodine to satisfy respective octet. Hence, the Lewis structure
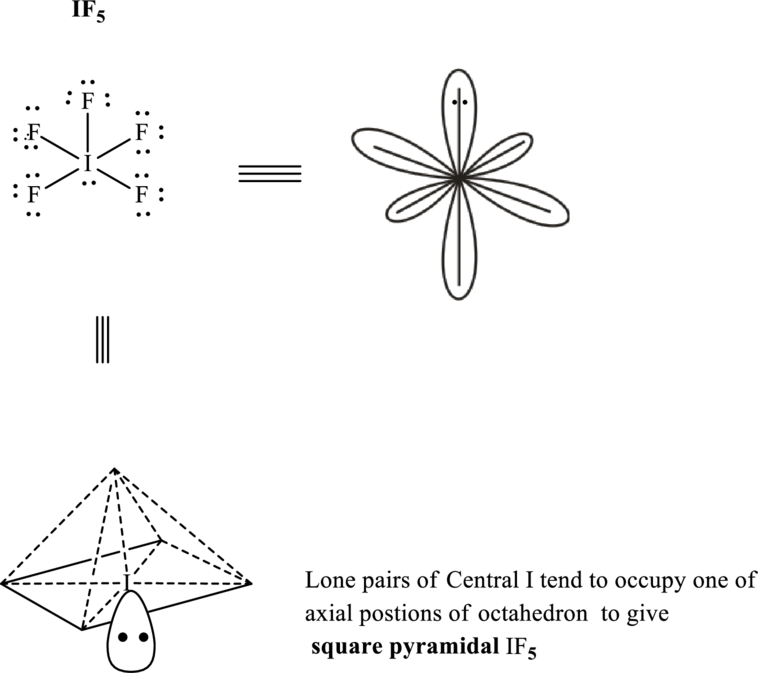
It is evident that in
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any square planar species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
(e)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure, VSEPR formula, bond angle and molecular shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Answer to Problem 2E.16E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on atom in
Thus, Lewis structure in
These 12 electron pairs are allotted as either lone pairs or multiple bonds with
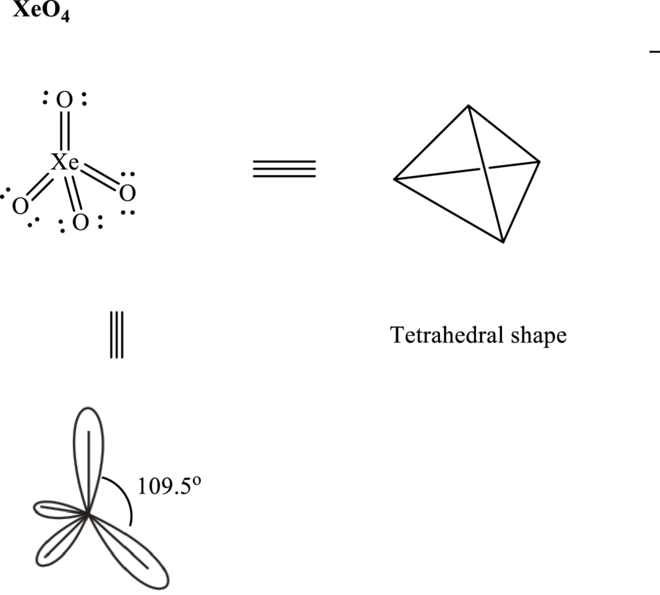
It is evident that in
So
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any tetrahedral species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight
- Please help me with number 5 using my data and graph. I think I might have number 3 and 4 but if possible please check me. Thanks in advance!arrow_forwarddict the major products of this organic reaction. C Explanation Check 90 + 1.0₂ 3 2. (CH3)2S Click and drag f drawing a stru © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. • 22 4 5 7 8 Y W E R S F H Bilarrow_forwardcan someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all the curly arrows and 2. Draw the GPNA molecule and identify the phenylalanine portion. 3. Draw L-phenylalanine with the correct stereochemistryarrow_forward
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardPredict the major products of both organic reactions. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. esc esc Explanation Check 2 : + + X H₁₂O + Х ง WW E R Y qab Ccaps lock shift $ P X Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil T FR F18 9 G t K L Z X V B N M control opption command command T C darrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrohalogenation of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for caps lock Explanation Check 2 W E R + X 5 HCI Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil Y F G H K L ZZ X C V B N M control opption command F10 F10 command 4 BA Ar Carrow_forward
- I don't understand why the amide on the top left, with the R attached to one side, doesn't get substituted with OH to form a carboxylic acid. And if only one can be substituted, why did it choose the amide it chose rather than the other amide?arrow_forwardesc Draw the Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. Explanation Check BBB + X 0 1. Hg (OAc)2, H₂O 2. Na BH 5 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bl P 豆 28 2 28 N 9 W E R T Y A S aps lock G H K L Z X C V B N M T central H command #e commandarrow_forwardC A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. (X) This transformation can't be done in one step. + Tarrow_forward
- く Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. Explanation Check OH + + ✓ 2 H₂SO 4 O xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forwardDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Parrow_forwardPredicting edict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. + No reaction. Explanation Check HO Na O H xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Iarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning


