
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The formal charge on each atom has to be determined and structure of lower energy has to be identified.

Concept Introduction:
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Here,
Lowest energy structure is the one that has zero or nearly zero formal charge.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation as follows:
For structure 1:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Similarly for other Lewis structure, substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Hence formal charge on each structure is illustrated below:

Since the former has less formal charges on maximum number of atoms so I is lower in energy than II therefore I represents structure of lowest energy.
(b)
Interpretation:
The formal charge on each atom has to be determined and structure of lower energy has to be identified.
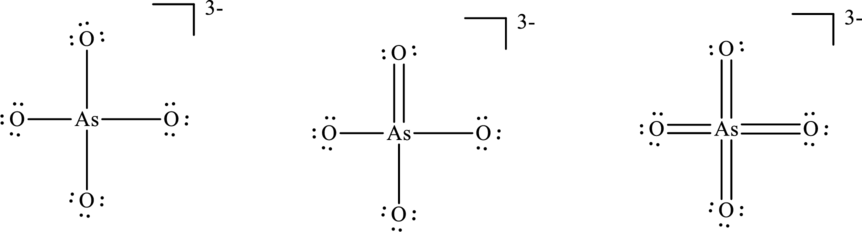
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation as follows:
For structure I:
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 5 for
For structure II:
Similarly for second Lewis structure, substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 5 for
For structure III:
Similarly for third Lewis structure, substitute 6 for
Substitute 5 for
Hence formal charge in the two structures is illustrated below.
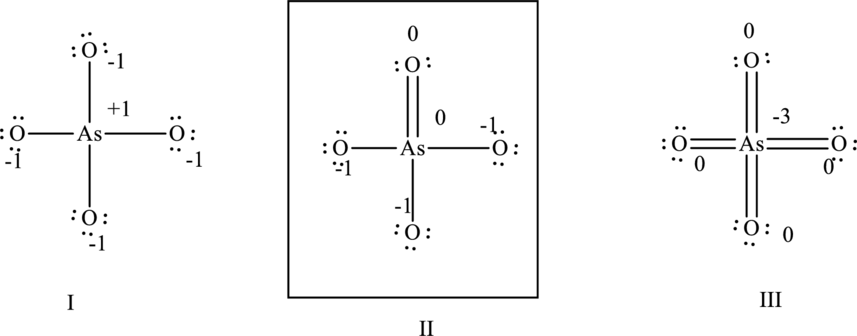
Since the II has a
(b)
Interpretation:
The formal charge on each atom has to be determined and structure of lower energy has to be identified.
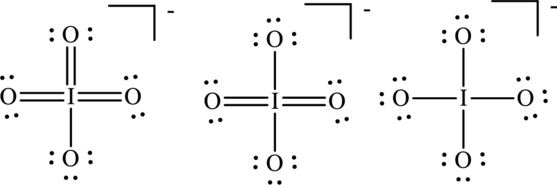
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation as follows:
For Lewis structureI, substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 7 for
For Lewis structure II,
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 7 for
For Lewis structure III, substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 7 for
Hence formal charge in the three structures is illustrated below:
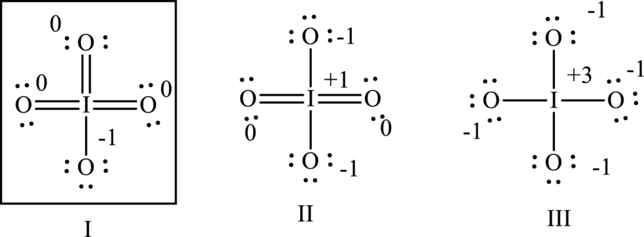
Since I has zero formal charges on central electronegative iodine atom compared to other cases with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight
- Problem 3. Provide a mechanism for the following transformation: H₂SO A Me. Me Me Me Mearrow_forwardYou are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: xi 1. ☑ 2. H₂O хе i Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. There is no reagent that will make this synthesis work without complications. : ☐ S ☐arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forward
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C-C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 CI MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No G टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. དྲ。 ✗MgBr ? O CI Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new C-C bond? Yes No • ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No × : ☐ Xarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: OH NaBH4 H ? CH3OH Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : Sarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LIAIHA 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : ☐arrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C - C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 tu ? ? OH Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No C $ ©arrow_forwardAs the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C-C bond as its major product: 1. MgCl ? 2. H₂O* If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new CC bond. G marrow_forward
- Including activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M NH4 Ksp Hg2Br2 = 5.6×10-23.arrow_forwardgive example for the following(by equation) a. Converting a water insoluble compound to a soluble one. b. Diazotization reaction form diazonium salt c. coupling reaction of a diazonium salt d. indacator properties of MO e. Diazotization ( diazonium salt of bromobenzene)arrow_forward2-Propanone and ethyllithium are mixed and subsequently acid hydrolyzed. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





