
a)
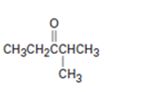
Interpretation:
The name of the ketone shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
To give:
The name of the ketone shown.
b)
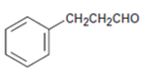
Interpretation:
The name of the aldehyde shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
To give:
The name of the aldehyde shown.
c)
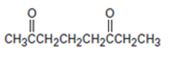
Interpretation:
The name of the diketone shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To give:
The name of the diketone shown.
d)
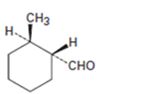
Interpretation:
The name of the aldehyde shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic aldehydes in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To give:
The name of the aldehyde shown.
e)
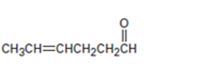
Interpretation:
The name of the aldehyde shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the –CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic aldehydes in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To give:
The name of the aldehyde shown.
f)
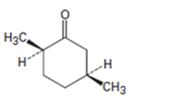
Interpretation:
The name of the ketone shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. For alicyclic ketones the number of carbons in the ring determines the parent name. The numbering starts from the carbonyl carbon and the numbering is done such a way that other functional groups and/or substituents get the lowest possible number.
To give:
The name of the ketone shown.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward

 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





