
(a)
Interpretation:
The geometrical structure of
Concept introduction:
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
According to VSEPR theory,
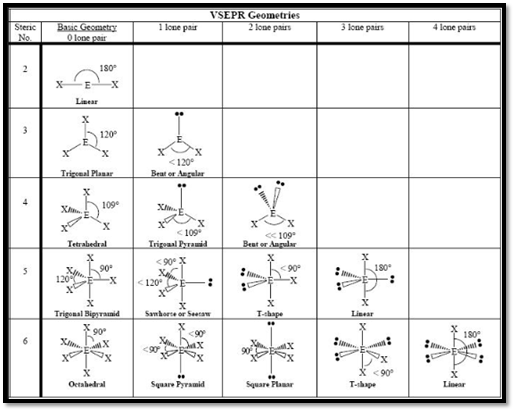
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The geometrical structure of
Concept introduction:
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
According to VSEPR theory,

Figure 1
(c)
Interpretation:
The geometrical structure of
Concept introduction:
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
According to VSEPR theory,

Figure 1
(d)
Interpretation:
The geometrical structure of
Concept introduction:
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then the tends to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
According to VSEPR theory,

Figure 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





