
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
A structure for the alcohol with molecular formula C9H12O and the following spectral data is to be proposed.
1HNMR: 0.88 δ (triplet,Rel.area=3.00); 1.80 δ (quintet, Rel.area=2.00); 2.32 δ (Rel.area=1.00); 4.54 δ (triplet, Rel.area=1.00); 7.24 δ (Rel.area=5.00).
Concept introduction:
In 1HNMR spectrum, the alcoholic proton absorption occurs in the range 3.4 δ - 4.5 δ while that of phenolic proton occur in the range 3.0 to 8.0. The
The absorption due to 10 alkyl group (CH3) is seen around 0.7 δ - 1.3 δ, that due to a 20 alkyl group (CH2) is seen around 1.2 δ - 1.6 δ while that due to 30 alkyl group (CH) is seen around 1.4 δ - 1.8 δ The multiplicity of a signal gives an idea about the protons present in the adjacent carbons.
To propose:
A structure for the alcohol with molecular formula C9H12O and the following spectral data is to be proposed.
1HNMR: 0.88 δ (triplet,Rel.area=3.00); 1.80 δ (quintet, Rel.area=2.00); 2.32 δ (Rel.area=1.00); 4.54 δ (triplet, Rel.area=1.00); 7.24 δ (Rel.area=5.00).
b)
C8H10O2
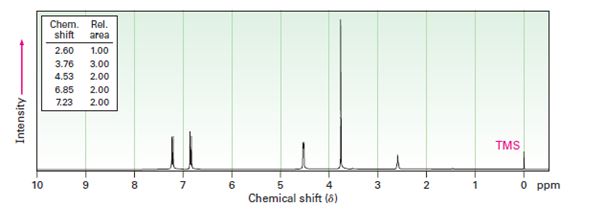
Interpretation:
A structure for the alcohol with molecular formula C8H10O2 and the following spectral data is to be proposed.
IR: 3500 cm-1,
1HNMR: 2.60 δ (Rel.area=1.00); 3.76 δ (Rel.area=3.00); 4.53 δ (Rel.area=2.00); 6.85 δ (Rel.area=2.00); 7.23 δ (Rel.area=2.00).
Concept introduction:
In 1HNMR spectrum, the alcoholic proton absorption occurs in the range 3.4 δ - 4.5 δ while that of phenolic proton occur in the range 3.0 to 8.0. The aromatic protons give a broad peak in the range 6.5 δ - 8.0 δ, the benzylic protons normally absorb in the region 2.3 δ - 3.0 δ.
To propose:
A structure for the alcohol with molecular formula C8H10O2 and the following spectral data is to be proposed.
1HNMR: 2.60 δ (Rel.area=1.00); 3.76 δ (Rel.area=3.00); 4.53 δ (Rel.area=2.00); 6.85 δ (Rel.area=2.00); 7.23 δ (Rel.area=2.00).
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Answerarrow_forward2. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. CH3 Ph OEt هد Ph CH3 Hint: the species on the left is an ynolate, which behaves a lot like an enolate.arrow_forwardb. CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C an unexpected product, containing a single 9- membered ring the expected product, containing two fused rings H3C-I (H3C)2CuLi an enolatearrow_forward
- b. H3C CH3 1. 2. H3O+ H3C MgBr H3Carrow_forwardPredict the major products of this reaction: excess H+ NaOH ? A Note that the first reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the first reactant than the second. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privarrow_forward1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forward
- Predict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forwardWhat is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation? CH3 HH DH CH3arrow_forwardΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forward
- How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

