
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.SE, Problem 54AP
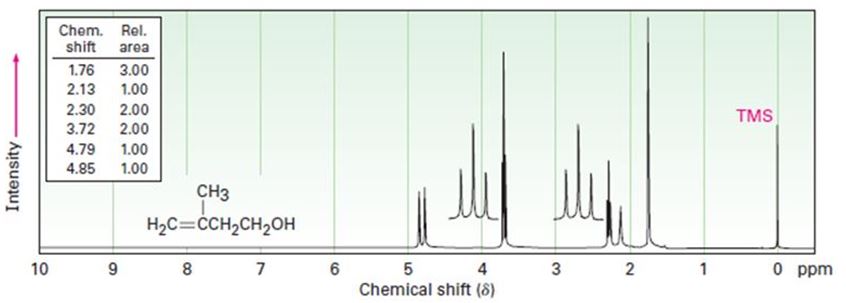
The 1HNMR spectrum shown is that of 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol. Assign all the observed resonance peaks to specific protons, and account for the splitting patterns.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please predict the products for each of the
following reactions.
Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov
vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry
(syn- vs anti- or both).
If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please
draw all the enantiomers.
Hint: In this case you must choose the best
answer to demonstrate the stereochemistry of
H2 addition.
1.03
2. (CH3)2S
BIZ
CH₂OH
2. DMS
KMnO4, NaOH
ΖΗ
Pd or Pt (catalyst)
HBr
20 1
HBr
ROOR (peroxide)
HO
H-SO
HC
12 11 10
BH, THE
2. H2O2, NaOH
Brz
cold
HI
19
18
17
16
MCPBA
15
14
13
A
Br
H₂O
BH3⚫THF
Brz
EtOH
Pd or Ni (catalyst)
D₂ (deuterium)
1. Os04
2. H2O2
CH3CO3H
(peroxyacid)
1. MCPBA
2. H₂O*
H
B
+
H
H
H
"H
C
H
H
D
Explain how Beer’s Law can be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide examples.
Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis.
Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Provide examples.
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 17.1 - Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 17.2 - The following data for isomeric four-carbon...Ch. 17.2 - Rank the following substances in order of...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 17.4 - What reagent would you use to accomplish each of...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 17.5 - Prob. 9PCh. 17.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 17.5 - Use the reaction of a Grignard reagent with a...Ch. 17.6 - How would you carry out the following...Ch. 17.6 - What products(s) would you expect from dehydration...Ch. 17.7 - What alcohols would give the following products on...Ch. 17.7 - What products would you expect from oxidation of...Ch. 17.8 - TMS ethers can be removed by treatment with...Ch. 17.9 - Show the mechanism for the reaction of...Ch. 17.11 - Prob. 18PCh. 17.11 - When the 1HNMR spectrum of an alcohol is run in...Ch. 17.SE - Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:Ch. 17.SE - Draw the structure of the carbonyl compound(s)...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 22VCCh. 17.SE - Prob. 23VCCh. 17.SE - Name and assign R or S stereochemistry to the...Ch. 17.SE - Evidence for the intermediate carbocations in the...Ch. 17.SE - Acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2,...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 27MPCh. 17.SE - Treatment of the following epoxide with aqueous...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 29MPCh. 17.SE - Prob. 30MPCh. 17.SE - Identify the type of substitution mechanism (SN1,...Ch. 17.SE - The conversion of 3 alcohols into alkenes under...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 33MPCh. 17.SE - The trimethylsilyl (TMS) protecting group is one...Ch. 17.SE - When the alcohol below is treated with POCI3 and...Ch. 17.SE - Phenols generally have lower pKa’s than...Ch. 17.SE - Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:Ch. 17.SE - Draw and name the eight isomeric alcohols with...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 39APCh. 17.SE - Named bombykol, the sex pheromone secreted by the...Ch. 17.SE - Carvacrol is a naturally occurring substance...Ch. 17.SE - What Grignard reagent and what carbonyl compound...Ch. 17.SE - What carbonyl compounds would you reduce to...Ch. 17.SE - What carbonyl compounds might you start with to...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 45APCh. 17.SE - What products would you obtain from reaction of...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 47APCh. 17.SE - How would you prepare the following compounds from...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 49APCh. 17.SE - What products would you expect to obtain from...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 51APCh. 17.SE - Propose structures for alcohols that have the...Ch. 17.SE - Propose a structure consistent with the following...Ch. 17.SE - The 1HNMR spectrum shown is that of...Ch. 17.SE - A compound of unknown structure gave the following...Ch. 17.SE - Propose a structure for a compound C15H24O that...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 57APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 58APCh. 17.SE - Rank the following substituted phenols in order of...Ch. 17.SE - Benzvl chloride can be converted into benzaldehvde...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 61APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 62APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 63APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 64APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 65APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 66APCh. 17.SE - Dehydration of trans-2-methylcyclopentanol with...Ch. 17.SE - 2, 3-Dimethyl-2, 3-butanediol has the common name...Ch. 17.SE - As a rule, axial alcohols oxidize somewhat faster...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 70APCh. 17.SE - A problem often encountered in the oxidation of...Ch. 17.SE - Identify the reagents a-f in the Following scheme:Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 73APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 74APCh. 17.SE - Compound A, C8H10O, has the IR and 1H NMR spectra...Ch. 17.SE - Prob. 76APCh. 17.SE - Prob. 77AP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forwardBriefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Gibbs model and the Gibbs absorption equation.arrow_forward
- Briefly state the electrocapillary equation for ideally polarized electrodes.arrow_forwardWhat is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forward
- The molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
NMR Spectroscopy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SBir5wUS3Bo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY