
Concept explainers
a)
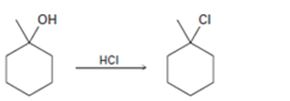
Interpretation:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30
Concept introduction:
Alcohols get protonated in the presence of strong acids. The protonated intermediate will lose a molecule of water to yield a carbocation. The nucleophilic attack by the halide ion will lead to the formation of the alkyl halide.
To propose:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HCl involving two cationic intermediates.
b)
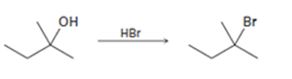
Interpretation:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HBr involving two cationic intermediates is to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols get protonated in the presence of strong acids. The protonated intermediate will lose a molecule of water to yield a carbocation. The nucleophilic attack by the halide ion will lead to the formation of the alkyl halide.
To propose:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HBr involving two cationic intermediates.
c)
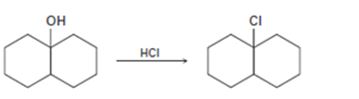
Interpretation:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HCl involving two cationic intermediates is to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols get protonated in the presence of strong acids. The protonated intermediate will lose a molecule of water to yield a carbocation. The nucleophilic attack by the halide ion will lead to the formation of the alkyl halide.
To propose:
The complete mechanism for the conversion of 30 alcohol given to 30 alkyl halide by treating with HCl involving two cationic intermediates.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction converting an alcohol into an alkyl halide. If chirality is important to the reaction include it.arrow_forwardWrite, in words three different reactions we can use to make an alcohol.arrow_forwardDraw the reduction mechanism for the reduction of the aldehyde.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the reaction of XeF4 with H2O? Group of answer choices H2XeF2 H2XeF4 XeO3 H2XeOarrow_forwardWhile noble gas exerts the strongest London (dispersion) forces on neighboring atoms? Group of answer choices Xe Ar Kr Nearrow_forwardWhich of the following elements is corrosive to your skin due to that element breaking down C=C bonds? Group of answer choices fluorine iodine bromine chlorinearrow_forward
