
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be classified as primary amine, secondary amine, tertiary amine or quaternary salt.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering
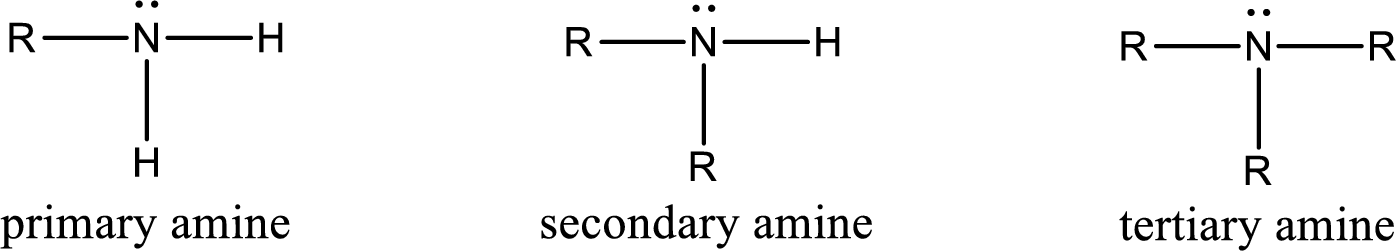
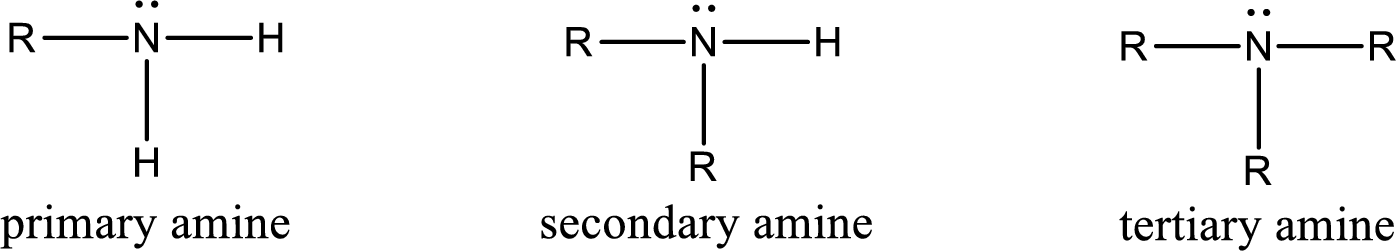
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
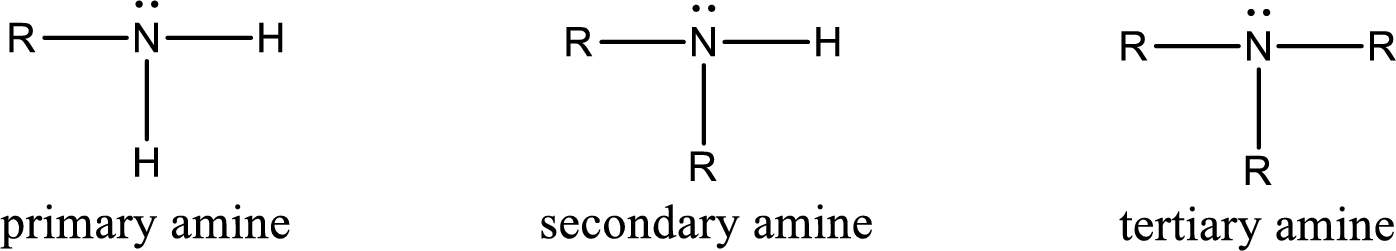
Quaternary ammonium salt is the one that has four carbon atoms attached to the nitrogen atom. This is formed by the reaction of tertiary amine with alkyl halide in presence of a strong base.
(a)
Answer to Problem 17.63EP
Organic product is a primary amine.
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is,

The reactants given in the above reaction are ammonia, propyl chloride. Sodium hydroxide is a reagent that is used for basic condition in this case. As the reaction between ammonia and propyl chloride gives propylamine as the product, this is an alkylation reaction. The complete reaction can be given as,
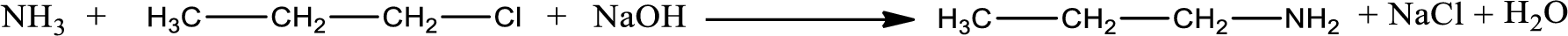
The organic product formed is propylamine. Considering the nitrogen atom in propylamine, it is bonded to one carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms. Hence, it is a primary amine.
The organic product formed in the given reaction is classified.
(b)
Interpretation:
Organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be classified as primary amine, secondary amine, tertiary amine or quaternary salt.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering amines, the alkylating agent that is used is alkyl halides. Alkylation is done under basic conditions. The general equations for amines alkylation process is,
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
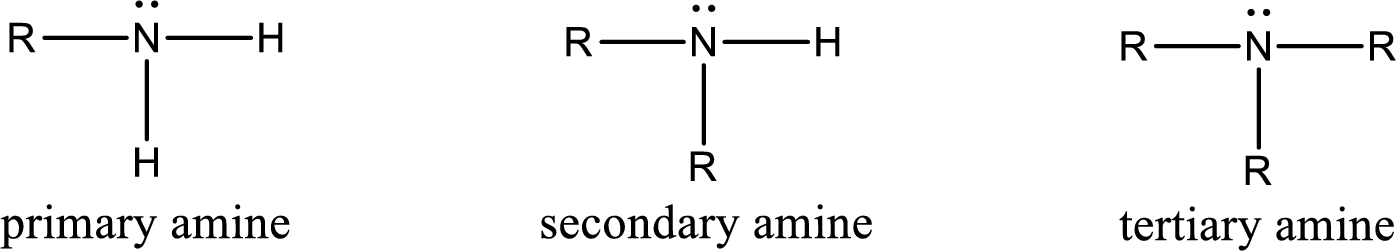
Quaternary ammonium salt is the one that has four carbon atoms attached to the nitrogen atom. This is formed by the reaction of tertiary amine with alkyl halide in presence of a strong base.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17.63EP
Organic product is a tertiary amine.
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is,
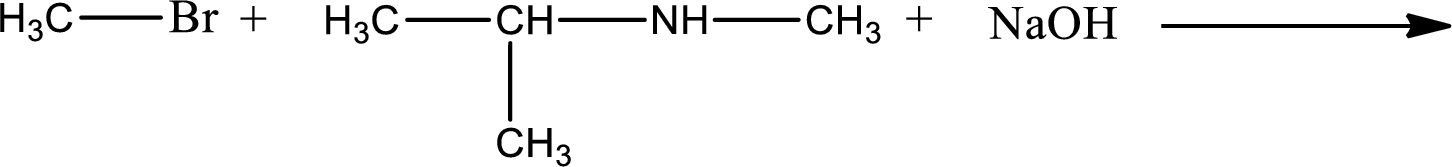
The reactants given in the above reaction are isopropylmethylamine, methyl bromide. Sodium hydroxide is a reagent that is used for basic condition in this case. As the reaction between isopropylmethylamine and methyl bromide gives isopropyldimethylamine as the product, this is an alkylation reaction. The complete reaction can be given as,
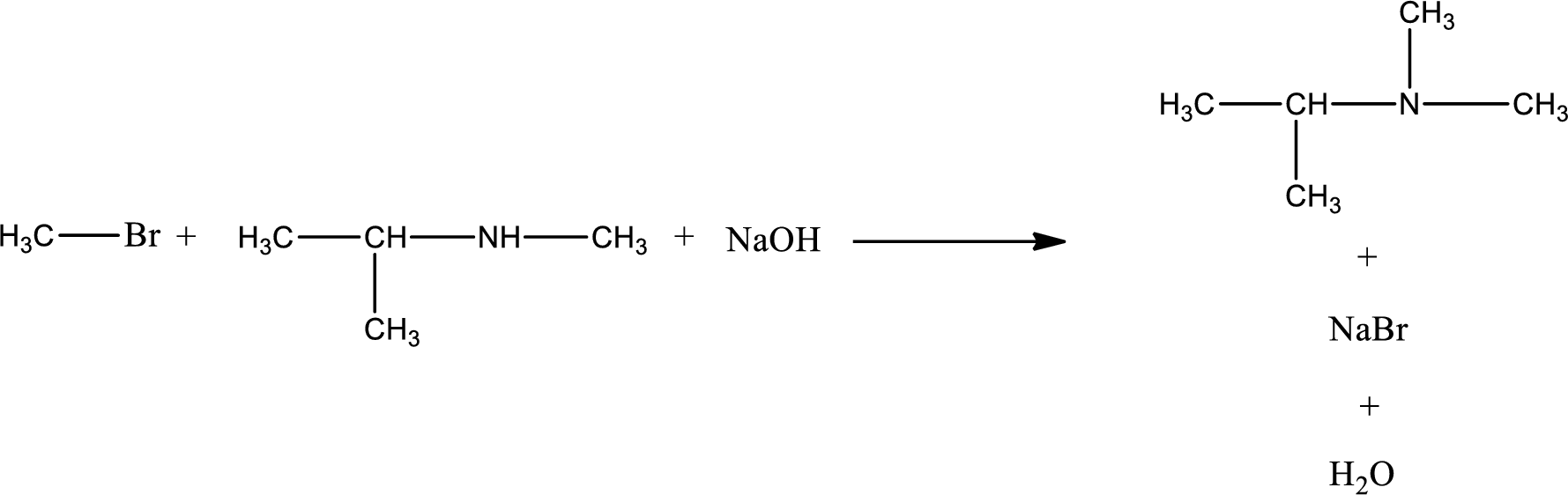
The organic product that is formed has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to three carbon atoms. Hence, it is a tertiary amine.
The organic product formed in the given reaction is classified.
(c)
Interpretation:
Organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be classified as primary amine, secondary amine, tertiary amine or quaternary salt.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering amines, the alkylating agent that is used is alkyl halides. Alkylation is done under basic conditions. The general equations for amines alkylation process is,
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
Quaternary ammonium salt is the one that has four carbon atoms attached to the nitrogen atom. This is formed by the reaction of tertiary amine with alkyl halide in presence of a strong base.
(c)
Answer to Problem 17.63EP
Organic product is a secondary amine.
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is,
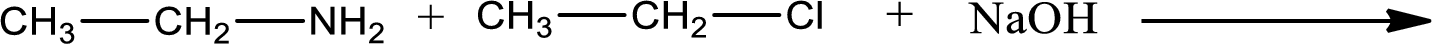
The reactants given in the above reaction are ethylamine, ethyl chloride. Sodium hydroxide is a reagent that is used for basic condition in this case. As the reaction between ethylamine and ethyl chloride gives diethylamine as the product, this is an alkylation reaction. The complete reaction can be given as,
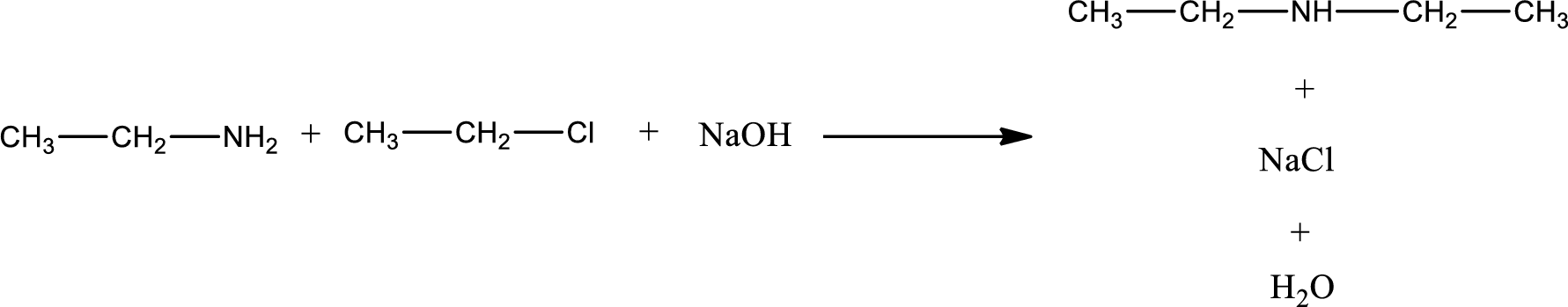
The organic product obtained has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom. Hence, it is a secondary amine.
The organic product formed in the given reaction is classified.
(d)
Interpretation:
Organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be classified as primary amine, secondary amine, tertiary amine or quaternary salt.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering amines, the alkylating agent that is used is alkyl halides. Alkylation is done under basic conditions. The general equations for amines alkylation process is,
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
Quaternary ammonium salt is the one that has four carbon atoms attached to the nitrogen atom. This is formed by the reaction of tertiary amine with alkyl halide in presence of a strong base.
(d)
Answer to Problem 17.63EP
Organic product is a primary amine.
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is,
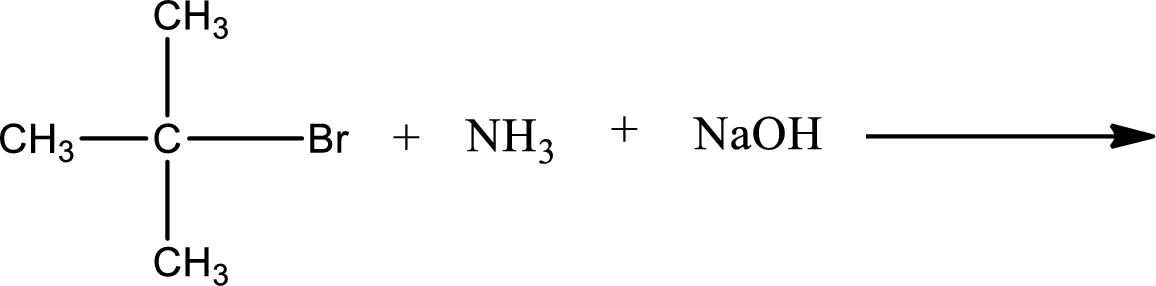
The reactants given in the above reaction are ammonia, tert-butyl bromide. Sodium hydroxide is a reagent that is used for basic condition in this case. As the reaction between ammonia and tert-butyl bromide gives tert-butylamine as the product, this is an alkylation reaction. The complete reaction can be shown as,
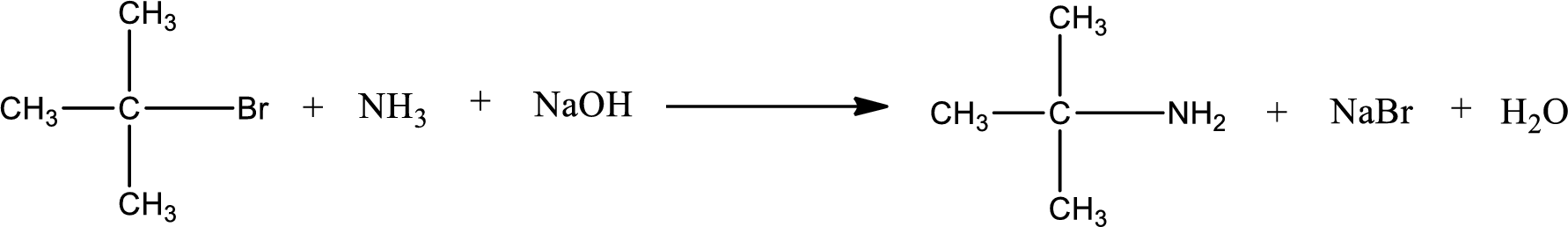
The organic product formed has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to one carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms. Hence, it is a primary amine.
The organic product formed in the given reaction is classified.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



