
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between
(a)
Answer to Problem 17.136EP
Nitrogen-containing compound that is required was,
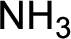
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
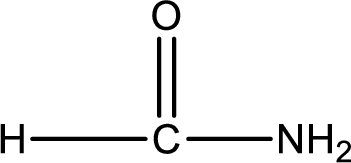
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The nitrogen-containing compound can be identified as shown below,
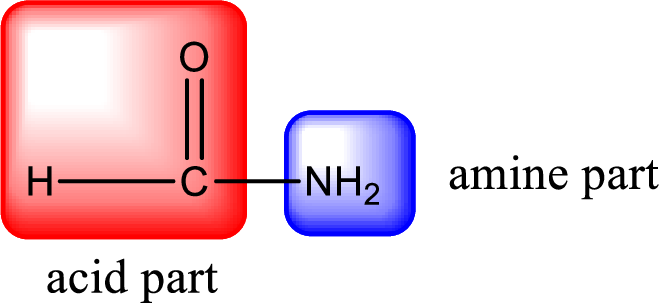
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
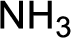
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between amine and carboxylic acid. In this reaction, the
(b)
Answer to Problem 17.136EP
Nitrogen-containing compound that is required was,
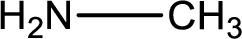
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
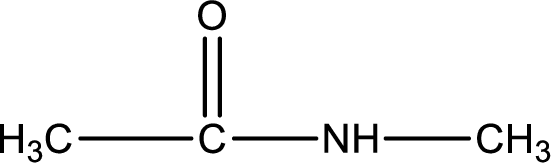
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The nitrogen-containing compound can be identified as shown below,
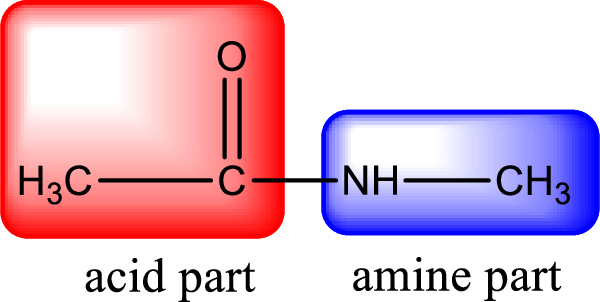
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
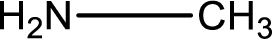
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between amine and carboxylic acid. In this reaction, the
(c)
Answer to Problem 17.136EP
Nitrogen-containing compound that is required was,
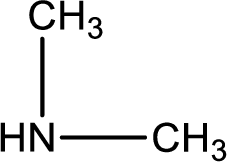
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
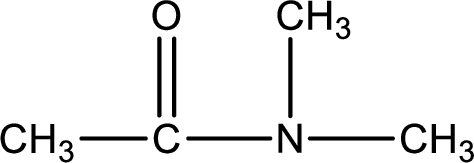
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The nitrogen-containing compound can be identified as shown below,
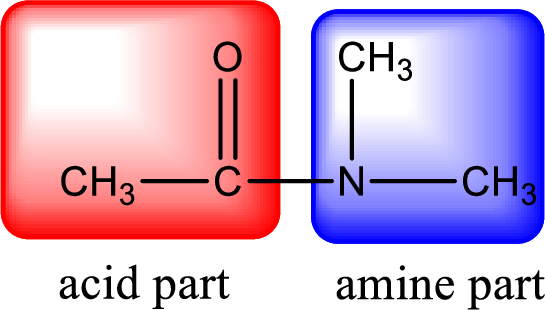
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
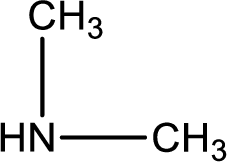
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound as product through amidification has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are synthesized using amidification reaction. This involves a reaction between amine and carboxylic acid. In this reaction, the
(d)
Answer to Problem 17.136EP
Nitrogen-containing compound that is required was,
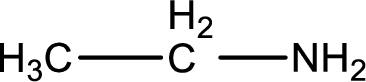
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is,
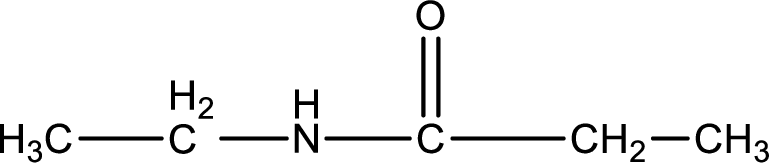
As the nitrogen atom present in the above amide has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it, the amide is a primary amide. Primary amide is produced by the reaction of ammonia with carboxylic acid. The nitrogen-containing compound can be identified as shown below,
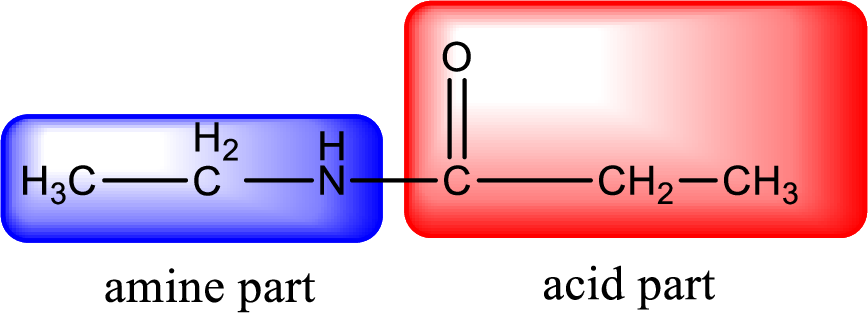
Hydrogen atom has to be added to the amine part and
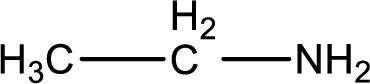
Structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is required to produce the given compound is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- please help with synthesisarrow_forward10. Stereochemistry. Assign R/S stereochemistry for the chiral center indicated on the following compound. In order to recieve full credit, you MUST SHOW YOUR WORK! H₂N CI OH CI カー 11. () Stereochemistry. Draw all possible stereoisomers of the following compound. Assign R/S configurations for all stereoisomers and indicate the relationship between each as enantiomer, diastereomer, or meso. NH2 H HNH, -18arrow_forwardb) 8. Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur Please explain your rational using 10 words or less not likely to occur • The double bond is still in the Same position + Likely to oc occur WHY? -3 H3C Brave Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less. CI 2 -cobs ?? MUST INDICATE H -2 -2 Br EQ Cl OR AT Br H& most stable WHY? - 4arrow_forward
- CH 12 Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided. NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below -4 NOT HOH OH 3 Conformer A: Br OH A Samo Br H 04 Br H H3 CH₂ H anti stagere Br CH clipsed H Brott H IV H MISSING 2 -2 B C D E F X 6 Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY: 13. (1 structure LOWEST ENERGY: Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry when applicable. a) ८८ 2 "Br {t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa Parent name (noname) 4 Bromo Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane # -2 -2arrow_forwardin the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forward
- Molecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forwardIndicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


