
Concept explainers
Devise a synthesis of each compound using
a.
![]() e.
e.![]()
(a)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
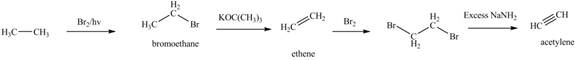
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
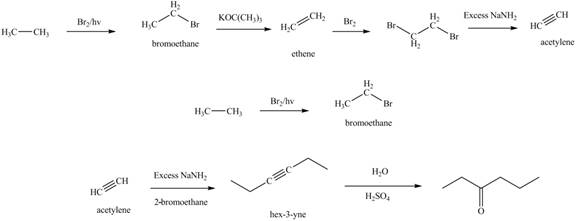
The synthesis of acetylene
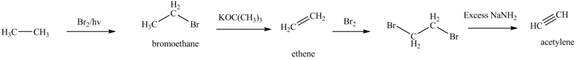
Figure 1
The synthesis of given compound from
(b)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
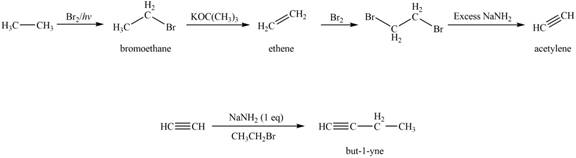
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of acetylene
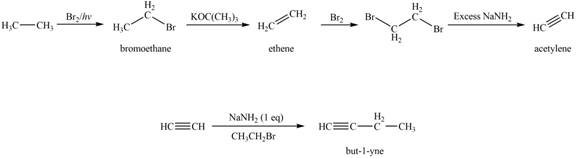
Figure 2
The synthesis of given compound from
(c)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
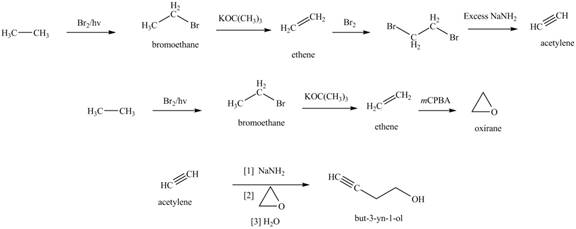
Explanation of Solution
The epoxidation of ethene, which is obtained from ethane, in the presence of m-chloroperbenzoic acid
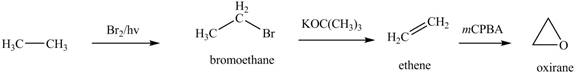
Figure 3
The synthesis of acetylene is shown in Figure 1. Acetylene undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with oxirane in the presence of base to yield desired product as shown in Figure 4.
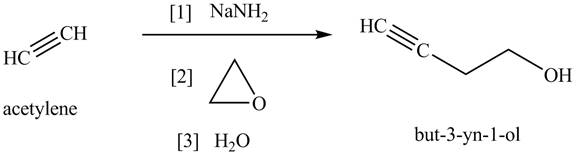
Figure 4
The synthesis of given compound from
(d)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
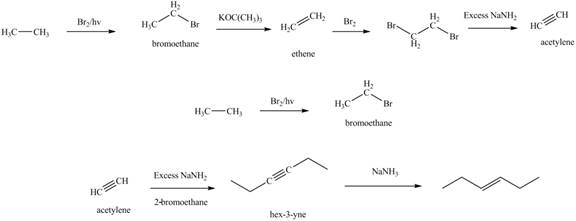
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of acetylene and bromoethane is shown in Figure 1. Acetylene undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with two molecules of bromoethane to form symmetrical alkyne. The triple bond of symmetrical alkyne is reduced to double bond on reaction with
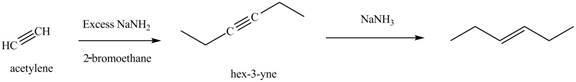
Figure 5
The synthesis of given compound from
(e)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of acetylene and bromoethane is shown in Figure 1. Acetylene undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with two molecules of bromoethane to form symmetrical alkyne. The symmetrical alkyne converts into ketone on reaction with
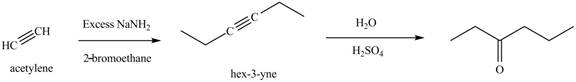
Figure 6
The synthesis of given compound from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Nonearrow_forward16. Consider the probability distribution p(x) = ax", 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 for a positive integer n. A. Derive an expression for the constant a, to normalize p(x). B. Compute the average (x) as a function of n. C. Compute σ2 = (x²) - (x)², the variance of x, as a function of n.arrow_forward451. Use the diffusion model from lecture that showed the likelihood of mixing occurring in a lattice model with eight lattice sites: Case Left Right A B C Permeable Barrier → and show that with 2V lattice sites on each side of the permeable barrier and a total of 2V white particles and 2V black particles, that perfect de-mixing (all one color on each side of the barrier) becomes increasingly unlikely as V increases.arrow_forward
- 46. Consider an ideal gas that occupies 2.50 dm³ at a pressure of 3.00 bar. If the gas is compressed isothermally at a constant external pressure so that the final volume is 0.500 dm³, calculate the smallest value Rest can have. Calculate the work involved using this value of Rext.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward2010. Suppose that a 10 kg mass of iron at 20 C is dropped from a heigh of 100 meters. What is the kinetics energy of the mass just before it hits the ground, assuming no air resistance? What is its speed? What would be the final temperature of the mass if all the kinetic energy at impact is transformed into internal energy? The molar heat capacity of iron is Cpp = 25.1J mol-¹ K-1 and the gravitational acceleration constant is 9.8 m s¯² |arrow_forward
- ell last during 7. Write the isotopes and their % abundance of isotopes of i) Cl ii) Br 8. Circle all the molecules that show Molecular ion peak as an odd number? c) NH2CH2CH2NH2 d) C6H5NH2 a) CH³CN b) CH3OHarrow_forwardCalsulate specific heat Dissolution of NaOH ก ง ง Mass of water in cup Final temp. of water + NaOH Initial temp. of water AT Water AH Dissolution NaOH - "CaicuraORT. AH (NaOH)=-AH( 30g (water) 29.0°C 210°C 8°C (82) 100 3.. =1003.20 Conjosarrow_forwardPlease provide throrough analysis to apply into further problems.arrow_forward
- Molecular ion peak: the peak corresponding to the intact morecure (with a positive charge) 4. What would the base peak and Molecular ion peaks when isobutane is subjected to Mass spectrometry? Draw the structures and write the molecular weights of the fragments. 5. Circle most stable cation a) tert-butyl cation b) Isopropyl cation c) Ethyl cation. d)Methyl cationarrow_forwardHow many arrangements are there of 15 indistinguishable lattice gas particles distributed on: a.V = 15 sites b.V = 16 sites c.V = 20 sitesarrow_forwardFor which element is the 3d subshell higher in energy than that 4s subshell? Group of answer choices Zr Ca V Niarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





