
(a)
Interpretation:
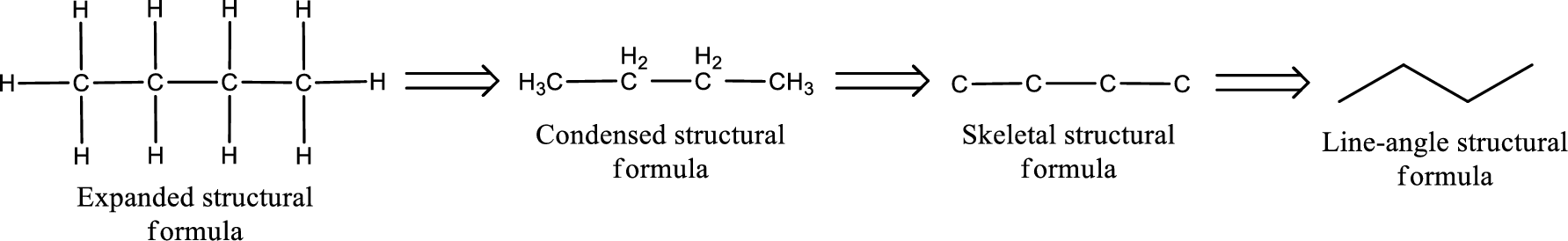
Structural formula for the given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the given aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(b)
Interpretation:
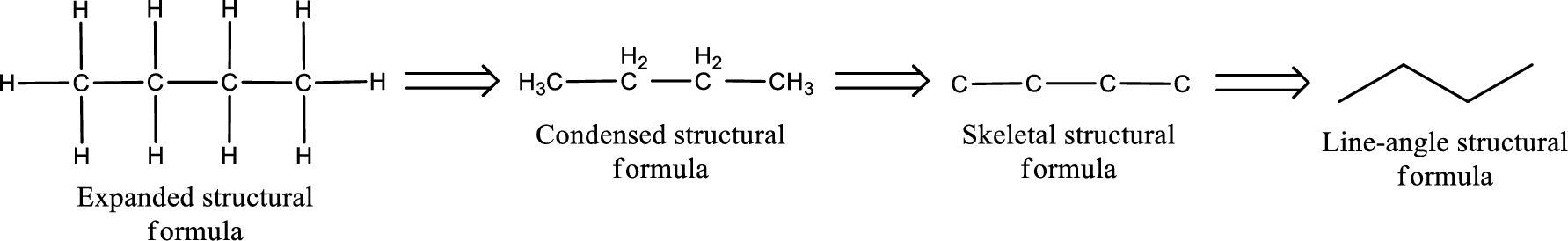
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the given aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(c)
Interpretation:
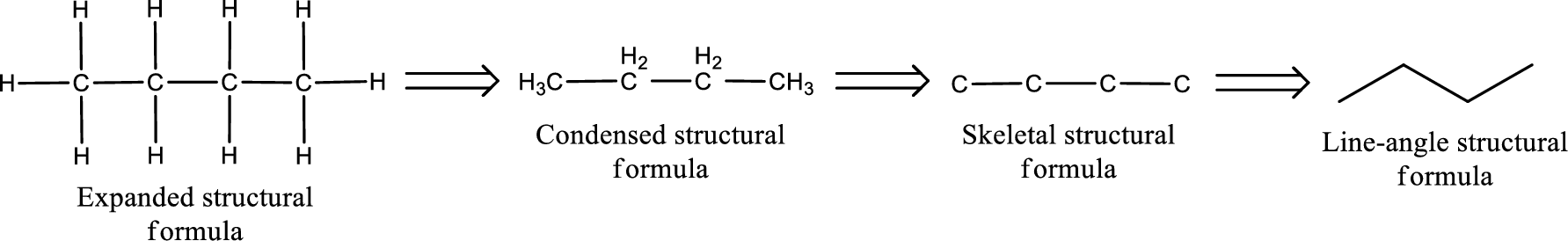
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the given aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(d)
Interpretation:
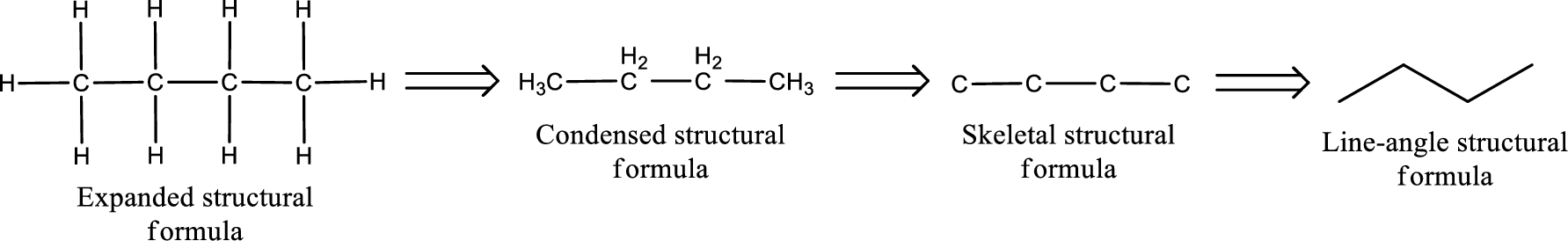
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the given aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 15 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- Outline the negative feedback loop that allows us to maintain a healthy water concentration in our blood. You may use diagram if you wisharrow_forwardGive examples of fat soluble and non-fat soluble hormonesarrow_forwardJust click view full document and register so you can see the whole document. how do i access this. following from the previous question; https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/hi-hi-with-this-unit-assessment-psy4406-tp4-report-assessment-material-case-stydu-ms-alecia-moore.-o/5e09906a-5101-4297-a8f7-49449b0bb5a7. on Google this image comes up and i have signed/ payed for the service and unable to access the full document. are you able to copy and past to this response. please see the screenshot from google page. unfortunality its not allowing me attch the image can you please show me the mathmetic calculation/ workout for the reult sectionarrow_forward
- Skryf n kortkuns van die Egyptians pyramids vertel ñ story. Maximum 500 woordearrow_forward1.)What cross will result in half homozygous dominant offspring and half heterozygous offspring? 2.) What cross will result in all heterozygous offspring?arrow_forward1.Steroids like testosterone and estrogen are nonpolar and large (~18 carbons). Steroids diffuse through membranes without transporters. Compare and contrast the remaining substances and circle the three substances that can diffuse through a membrane the fastest, without a transporter. Put a square around the other substance that can also diffuse through a membrane (1000x slower but also without a transporter). Molecule Steroid H+ CO₂ Glucose (C6H12O6) H₂O Na+ N₂ Size (Small/Big) Big Nonpolar/Polar/ Nonpolar lonizedarrow_forward
- what are the answer from the bookarrow_forwardwhat is lung cancer why plants removes liquid water intead water vapoursarrow_forward*Example 2: Tracing the path of an autosomal dominant trait Trait: Neurofibromatosis Forms of the trait: The dominant form is neurofibromatosis, caused by the production of an abnormal form of the protein neurofibromin. Affected individuals show spots of abnormal skin pigmentation and non-cancerous tumors that can interfere with the nervous system and cause blindness. Some tumors can convert to a cancerous form. i The recessive form is a normal protein - in other words, no neurofibromatosis.moovi A typical pedigree for a family that carries neurofibromatosis is shown below. Note that carriers are not indicated with half-colored shapes in this chart. Use the letter "N" to indicate the dominant neurofibromatosis allele, and the letter "n" for the normal allele. Nn nn nn 2 nn Nn A 3 N-arrow_forward
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage





