
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
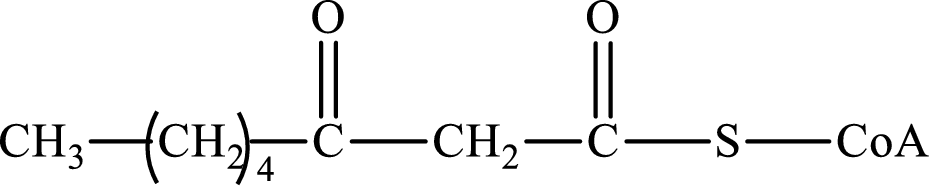
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
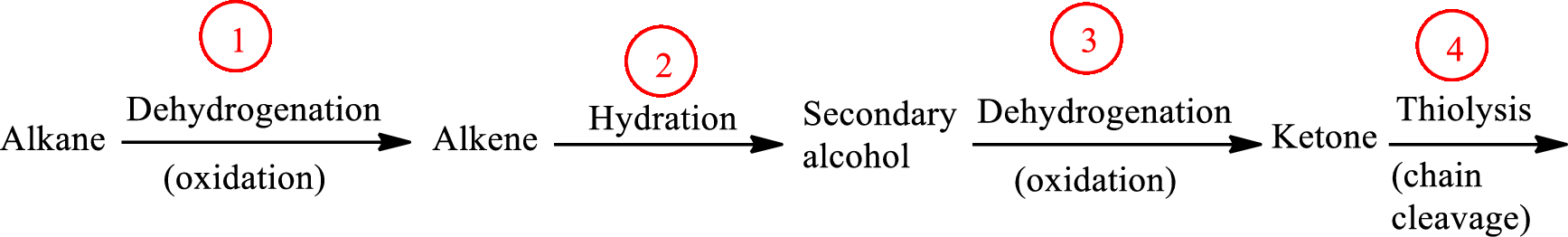
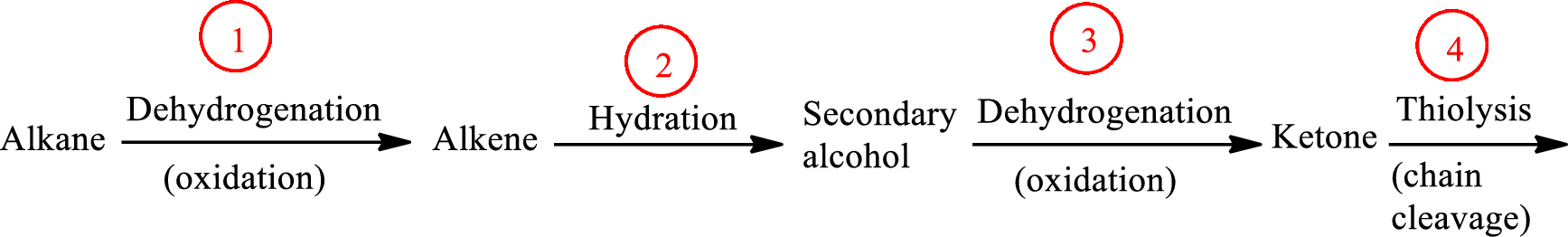
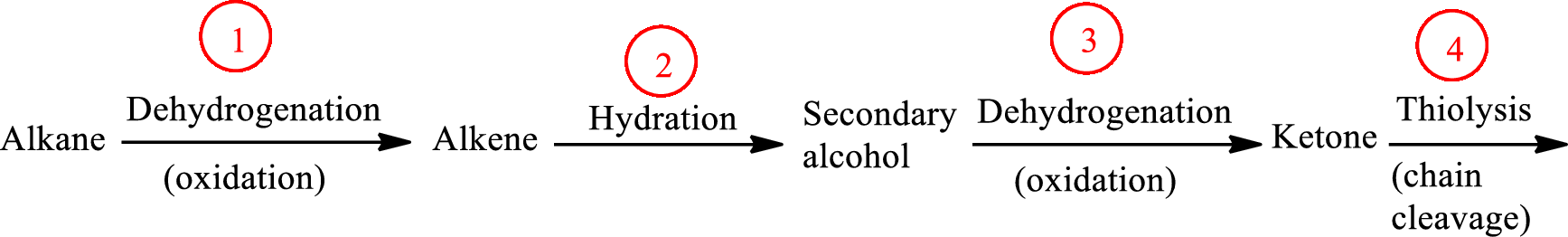
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
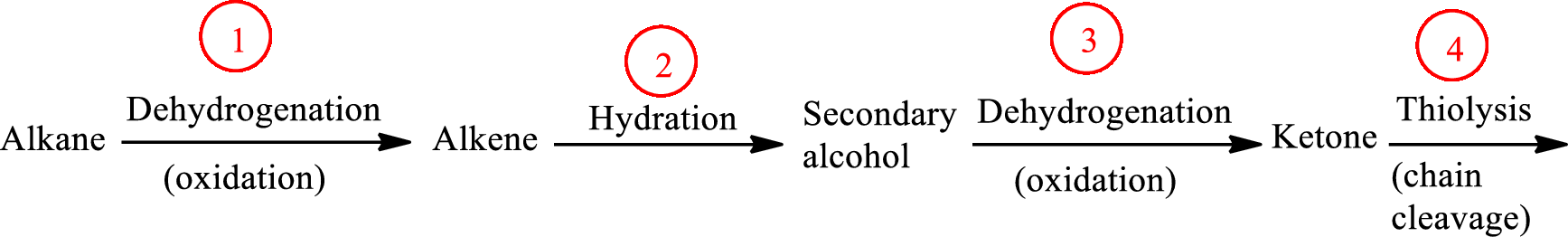
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In
(b)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
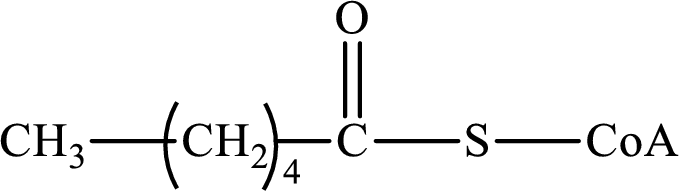
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
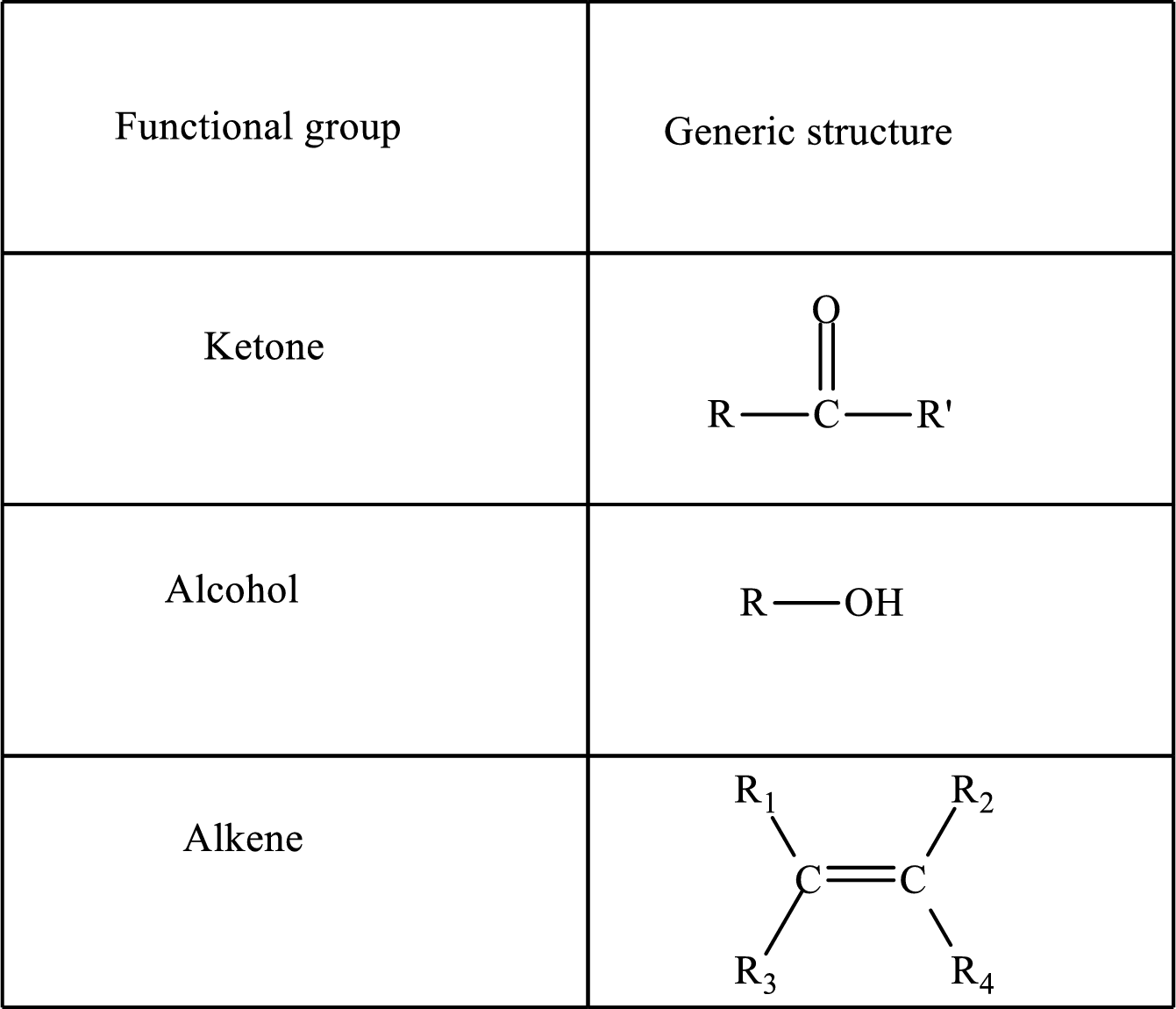
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
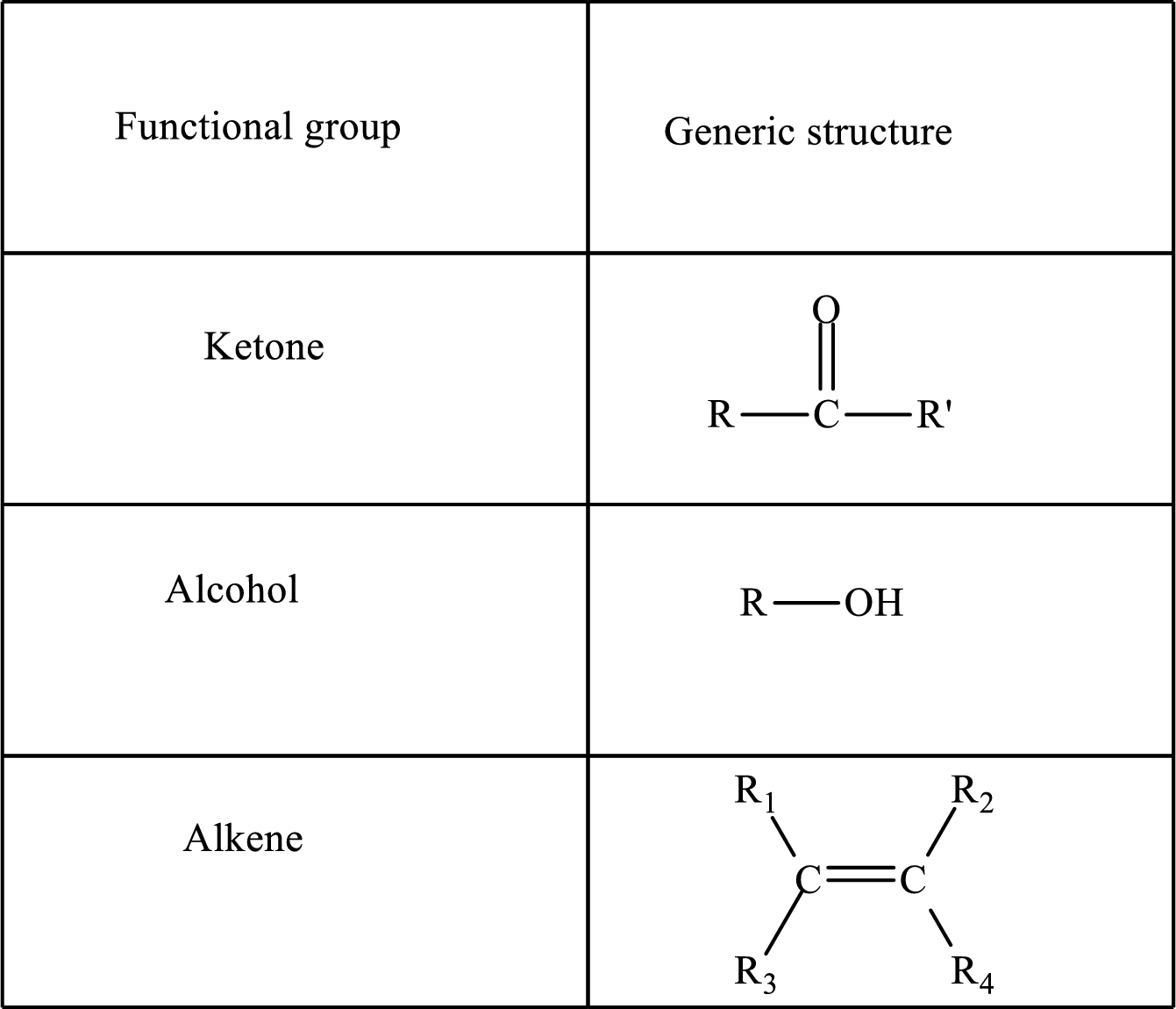
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
(c)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
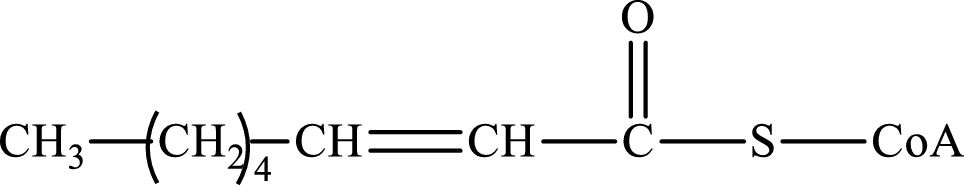
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
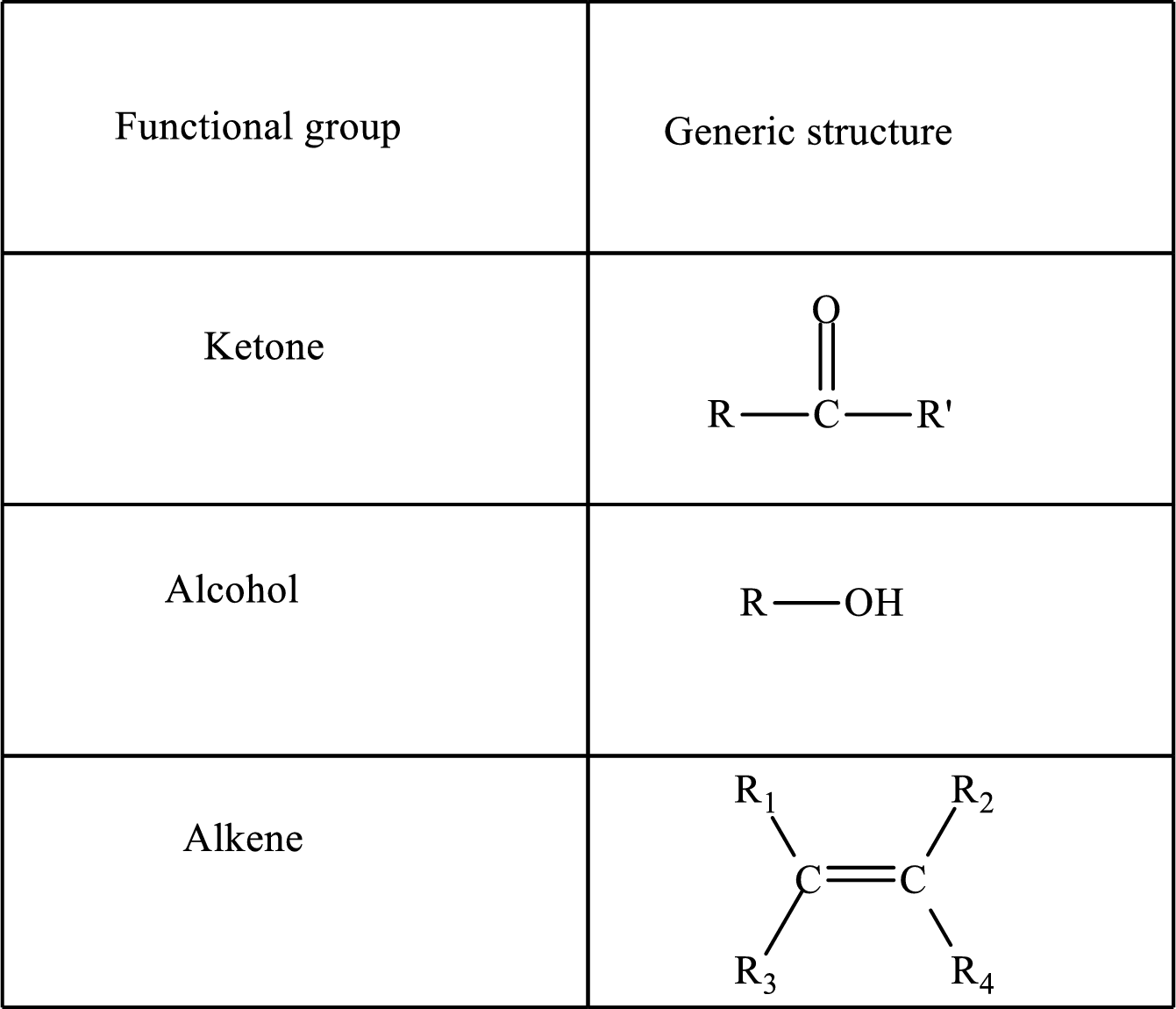
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
(d)
Interpretation:
The step (of steps 1 through 4) and turn (second or third) of the β-oxidation pathway in which the following compound is encountered as a reactant if the degraded fatty acid is decanoic acid has to be determined.
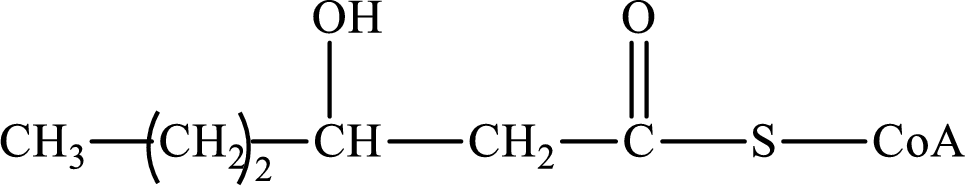
Concept introduction:
The β-oxidation pathway is defined as a repetitive series of four biochemical reactions in which acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA by the removal of two carbon atoms at a time. NADH and FADH2 are also produced in this pathway.
The functional group change in the β-oxidation pathway is as follows:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
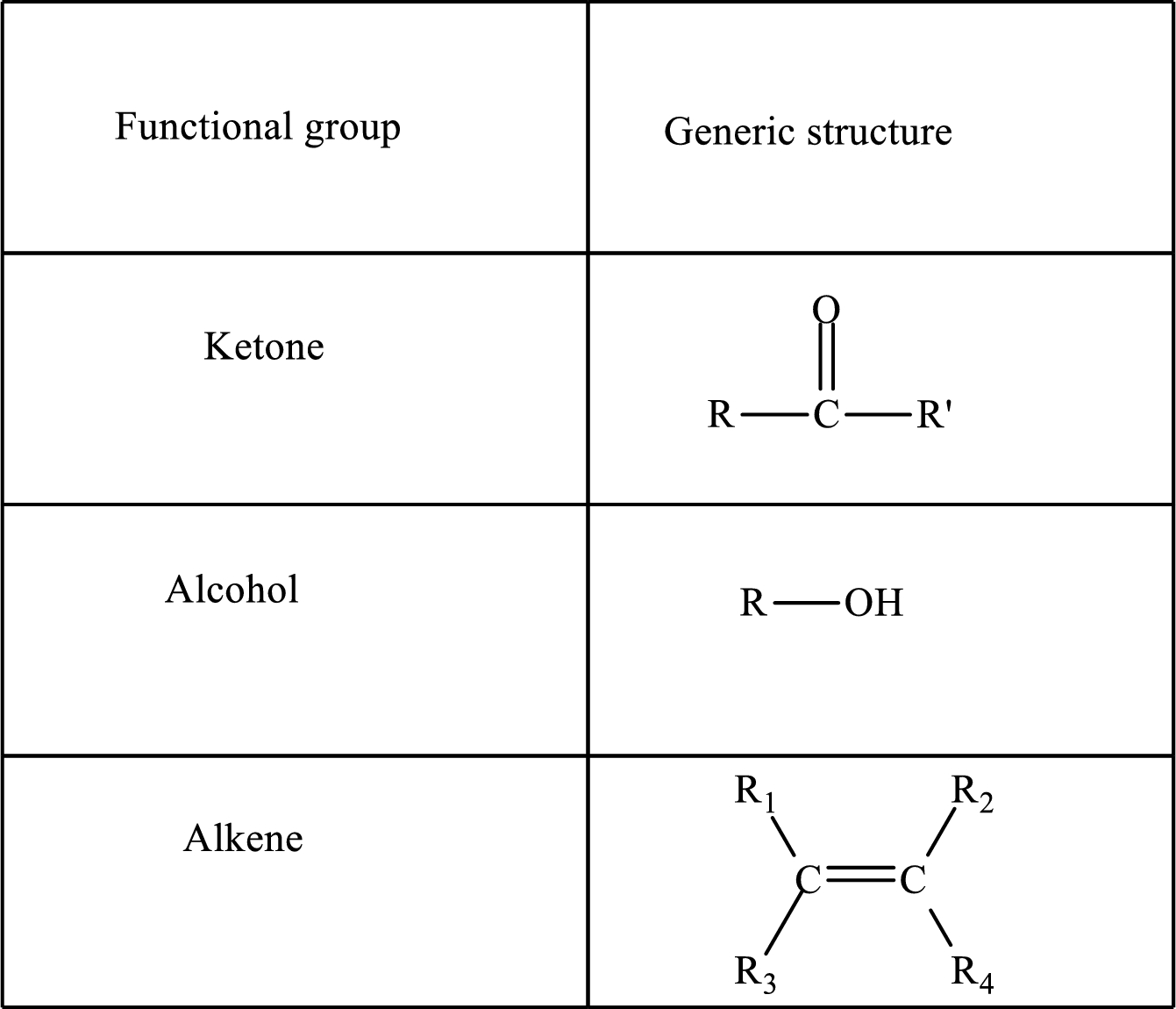
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward2,2-Dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Indicate the products obtained.arrow_forwardAdd conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





