
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
HMG-CoA is encountered in the process (1) glycerol
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as β-oxidation pathway.
Ketogenesis is a metabolic process by which
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney where it is converted to
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.104EP
HMG-CoA is encountered in ketogenesis.
Explanation of Solution
HMG-CoA is produced in step 2 in ketogenesis.
Step 2 is a condensation reaction. In step 2, acetoacetyl CoA reacts with acetyl CoA and water to produce 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl (HMG-CoA) and CoA-SH. The reaction for step 2 is:
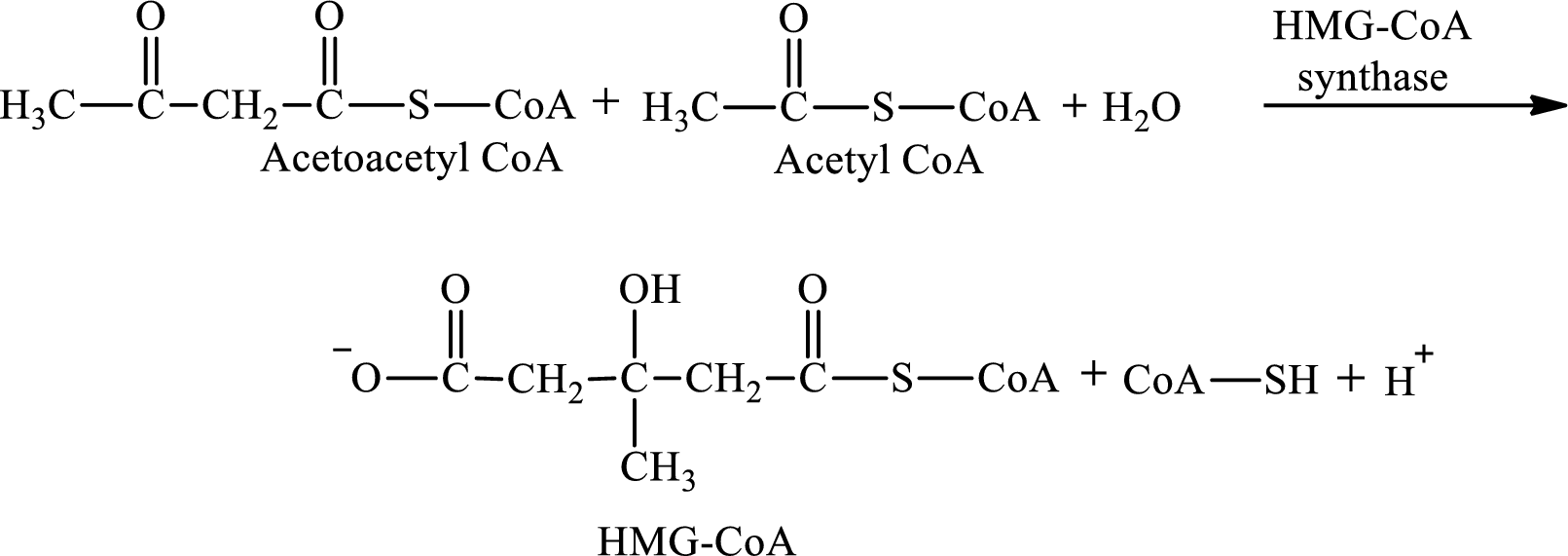
(b)
Interpretation:
NADPH is encountered in the process (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) β-oxidation pathway, (3) ketogenesis, and (4) lipogenesis has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as β-oxidation pathway.
Ketogenesis is a metabolic process by which ketone bodies are produced by the breakdown of fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids. This metabolic process supplies our organs with needed energy under certain circumstances such as starvation. Fatty acid molecules degrade into acetyl CoA which are utilized as reactants in the process of ketogenesis. These molecules of acetyl CoA undergo the process of condensation twice, followed by chain cleavage and hydrogenation to produce ketone bodies.
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney where it is converted to
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.104EP
NADPH is encountered in lipogenesis.
Explanation of Solution
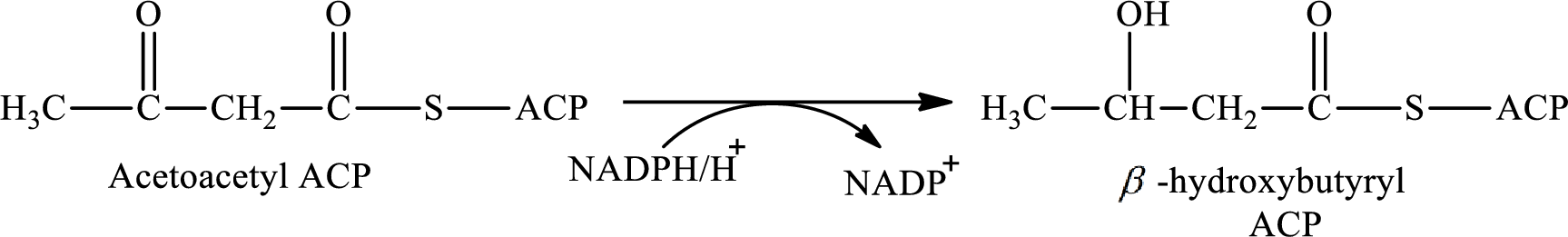
NADPH acts as the reducing agent in step 2 and 4 of the cyclic process of lipogenesis. NADPH gets oxidized to form NADP+.
Step 2 involves the hydrogenation of acetoacetyl ACP to synthesis β-hydroxybutyrylwith the help of reducing agent NADPH. The reaction of this step is:
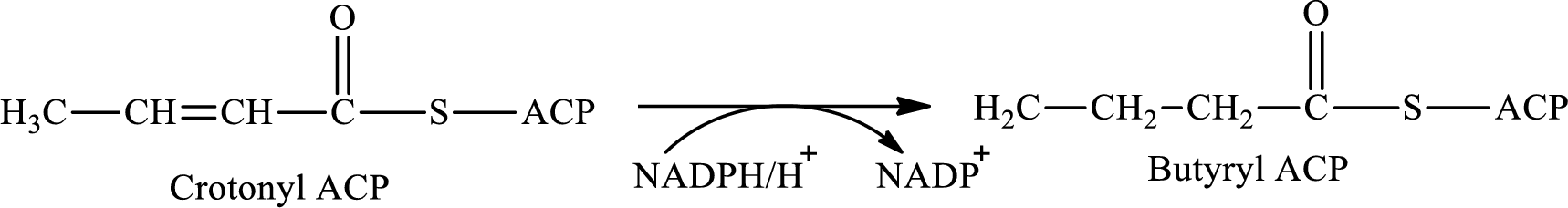
Step 4 again involves hydrogenation reaction. In this step, crotonyl ACP is converted to butyryl ACP with the help of reducing agent NADPH. The reaction of this step is:
(c)
Interpretation:
Malonyl ACP is encountered in the process (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) β-oxidation pathway, (3) ketogenesis, and (4) lipogenesis has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as β-oxidation pathway.
Ketogenesis is a metabolic process by which ketone bodies are produced by the breakdown of fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids. This metabolic process supplies our organs with needed energy under certain circumstances such as starvation. Fatty acid molecules degrade into acetyl CoA which are utilized as reactants in the process of ketogenesis. These molecules of acetyl CoA undergo the process of condensation twice, followed by chain cleavage and hydrogenation to produce ketone bodies.
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney where it is converted to
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.104EP
Malonyl ACP is encountered in lipogenesis.
Explanation of Solution
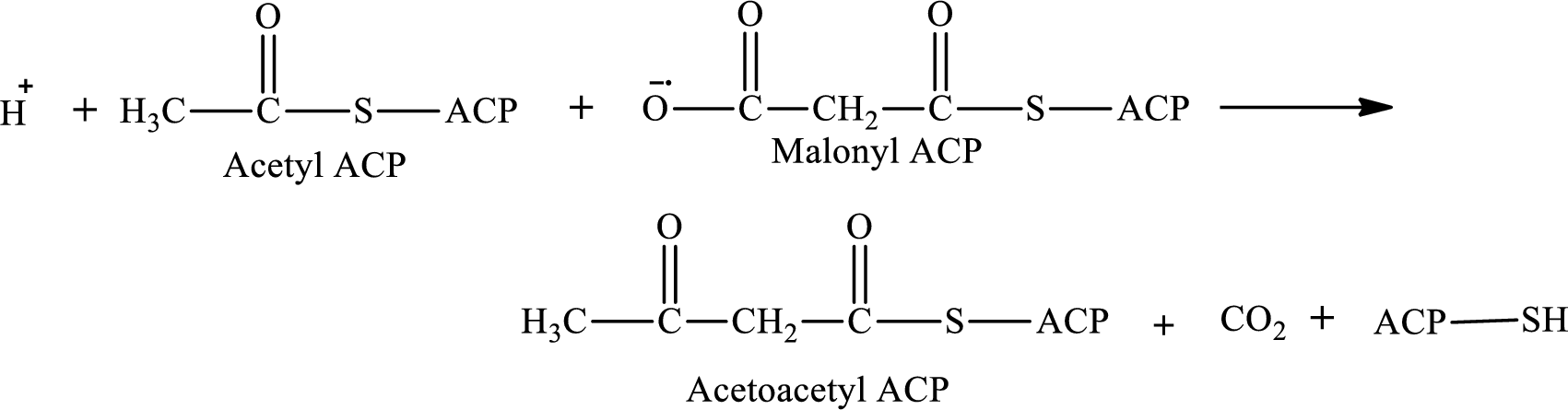
Malonyl ACP is the reactant in step 1 in the cyclic process in lipogenesis.
The first step involves the condensation reaction between acetyl ACP and malonyl ACP. The product formed in the first reaction is acetoacetyl ACP. The reaction of step 1 is:
(d)
Interpretation:
Acetoacetyl CoA is encountered in the process (1) glycerol metabolism to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, (2) β-oxidation pathway, (3) ketogenesis, and (4) lipogenesis has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The fatty acids are broken down to provide energy. The breakdown of fatty acids is a three parts process. In the first part, the fatty acid is activated. In the second part, the transportation of fatty acid into the mitochondrial matrix is facilitated by a shuttle mechanism. In the third part, the fatty acid is readily oxidized, cycling through a series of four reactions. In these series of reactions, acyl CoA is degraded to acetyl CoA. This pathway is termed as β-oxidation pathway.
Ketogenesis is a metabolic process by which ketone bodies are produced by the breakdown of fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids. This metabolic process supplies our organs with needed energy under certain circumstances such as starvation. Fatty acid molecules degrade into acetyl CoA which are utilized as reactants in the process of ketogenesis. These molecules of acetyl CoA undergo the process of condensation twice, followed by chain cleavage and hydrogenation to produce ketone bodies.
Triacylglycerol mobilization is an ongoing process in which triacylglycerols that are stored in the adipose tissue are hydrolyzed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the products of triacylglycerol mobilization. The products are released into the bloodstream.
After entering the bloodstream, the glycerol travels to the kidneys or liver. The first stage of glycerol metabolism occurs in the liver or kidney where it is converted to
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.104EP
Acetoacetyl CoA is encountered in ketogenesis.
Explanation of Solution
Step 2 is a condensation reaction. In step 2, acetoacetyl CoA reacts with acetyl CoA and water to produce 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl (HMG-CoA) and CoA-SH. The reaction for step 2 is:
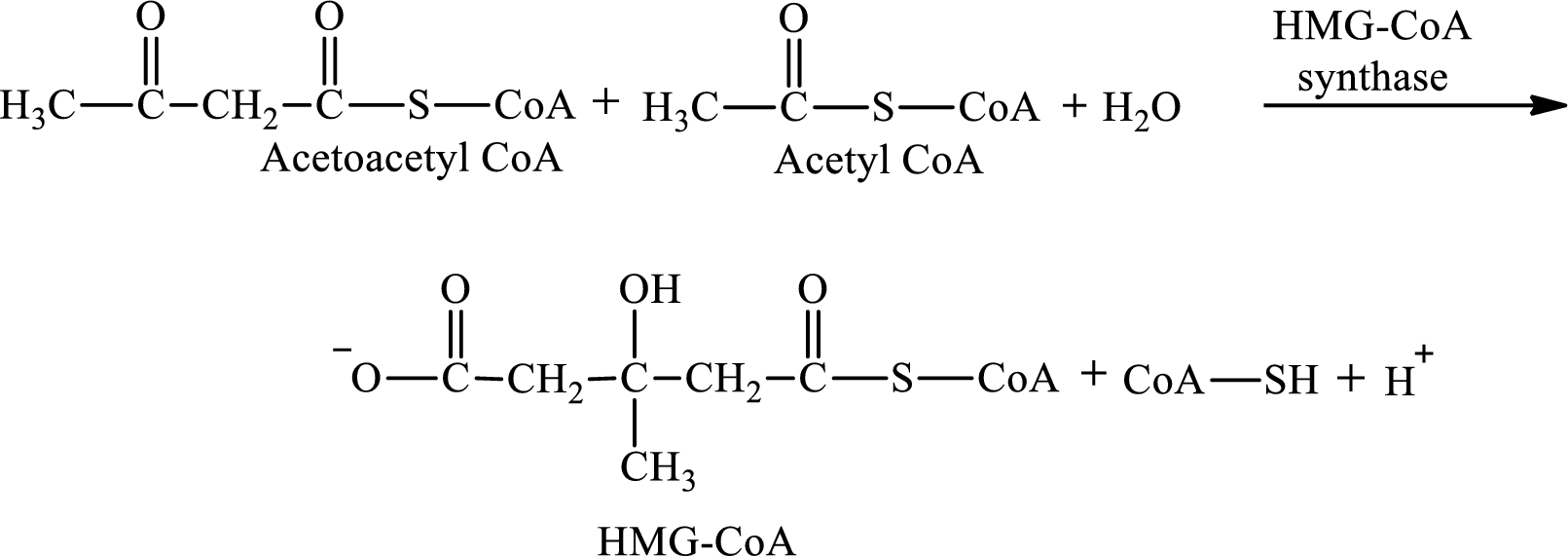
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Indicate the differences between the spectra of 1-methyl-benzimidazole and benzimidazole.arrow_forwardProvide reasons as to why appropriate sampling is important in relation to food?arrow_forwardWhat is the significance of selecting a "representative" sample for chemical analysis, and how does this practice ensure accurate and reliable results with respect to chemical analyses?arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation of the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous sampling in the context of sampling methods.arrow_forwardГ C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.0 b.092 0.797 1.088 1.813 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =13 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:09:52 CH PKNO TIME 1 2 0.797 3 1.088 4 1.813 AREA 1508566 4625442 2180060 HEIGHT 207739 701206 V 287554 V MK IDNO CONC NAME 18.1447 55.6339 26.2213 TOTAL 8314067 1196500 100 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0. 0 087 337. 0.841 1.150 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =14 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:12:40 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA 1 3 0.841 1099933 41.15 4039778 HEIGHT MK IDNO 170372 649997¯¯¯ CONC NAME 21.4007 78.5993 TOTAL 5139711 820369 100 3 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.100 0:652 5.856 3 1.165 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH-1 Report No. =15 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:15:26 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA HEIGHT MK IDNO CONC NAME 1 3 3 0.856 4 1.165 TOTAL 1253386 4838738 175481 708024 V 20.5739 79.4261 6092124…arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate please.arrow_forward
- Relative Abundance 20- Problems 501 (b) The infrared spectrum has a medium-intensity peak at about 1650 cm. There is also a C-H out-of-plane bending peak near 880 cm. 100- 80- 56 41 69 M(84) LL 15 20 25 30 35 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 m/zarrow_forwardPolyethylene furanoate is a polymer made from plant-based sources; it is used for packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardPhenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



