
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781260562620
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 11, Problem 26P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The shape around the indicated atoms in ethambutol should be determined and the lone pairs should be added to the heteroatoms:
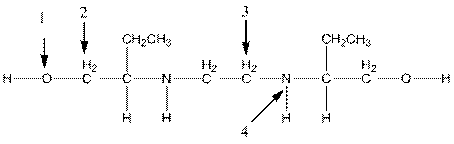
Concept introduction:
To add lone pair to an atom, first find the valence electron of the particular atom. After that find how many electrons are used in bond formation and then put the remaining valence electron on that particular atom.
The following table should be used while determining the shape around a carbon atom.
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear |
|
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
|
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
|
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
|
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
|
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please draw the major product of this reaction.
Draw the major product of this reaction.
identify the carbonyl compound that is incapable of forming an enolate ion
Chapter 11 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 11.1PCh. 11.2 - Fill in all H's and lone pairs in each compound.Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.2PPCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.2PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.3PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.3PPCh. 11.3 - How many lone pairs are present in lidocaine, the...Ch. 11.4 - Convert each compound to a condensed formula.Ch. 11.4 - Convert each condensed formula to a complete...Ch. 11.4 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...
Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.5PCh. 11.4 - How many H’s are bonded to each indicated carbon...Ch. 11.4 - Using the skeletal structure, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.7PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.8PCh. 11.5 - For each compound. [1] Identify the functional...Ch. 11.5 - How do a carboxylic acid and an alcohol differ?...Ch. 11.5 - Label each of the following condensed structures...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.11PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.12PCh. 11.5 - Identify all of the functional groups in atenolol,...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.13PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.10PPCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.14PCh. 11.6 - Indicate the polar bonds in each compound. Label...Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 11.11PPCh. 11.6 - Prob. 11.16PCh. 11.6 - Predict the water solubility of each compound.Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 11.17PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.18PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.19PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.20PCh. 11 - Prob. 21PCh. 11 - Prob. 22PCh. 11 - Complete each structure by filling in all H’s and...Ch. 11 - Complete the structure of mepivacaine by filling...Ch. 11 - Prob. 25PCh. 11 - Prob. 26PCh. 11 - Prob. 27PCh. 11 - Prob. 28PCh. 11 - “Ecstasy” is a widely used illegal stimulant....Ch. 11 - Prob. 30PCh. 11 - Explain why each C—C—C bond angle in benzene...Ch. 11 - Prob. 32PCh. 11 - Convert each compound to a condensed structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each compound to a condensed structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each compound to a skeletal structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each compound to a skeletal structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each shorthand structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - Convert each shorthand structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - A and B are ball-and-stick models of two compounds...Ch. 11 - Prob. 42PCh. 11 - What is wrong in each of the following shorthand...Ch. 11 - Prob. 44PCh. 11 - Prob. 45PCh. 11 - Albuterol (trade names Proventil and Ventolin) is...Ch. 11 - Prob. 47PCh. 11 - Prob. 48PCh. 11 - Prob. 49PCh. 11 - (a) Identify the functional groups in donepezil,...Ch. 11 - Prob. 51PCh. 11 - GHB is an addictive, illegal recreational drug...Ch. 11 - Prob. 53PCh. 11 - Prob. 54PCh. 11 - Prob. 55PCh. 11 - Prob. 56PCh. 11 - Prob. 57PCh. 11 - (a) Identify the functional groups in venlafaxine,...Ch. 11 - You are given two unlabeled bottles of solids, one...Ch. 11 - State how potassium iodide (KI) and pentane...Ch. 11 - The given beaker contains 100 mL of the organic...Ch. 11 - Prob. 62PCh. 11 - Why do we need to know the shape of a molecule...Ch. 11 - 1,1-Dichloroethylene (CH2=CCl2) is a starting...Ch. 11 - Indicate the polar bonds in each molecule. Label...Ch. 11 - Indicate the polar bonds in each molecule. Label...Ch. 11 - Classify each molecule as polar or nonpolar.Ch. 11 - Classify each molecule as polar or nonpolar. a....Ch. 11 - Which molecule is more water soluble? Explain.Ch. 11 - Explain why pantothenic acid, vitamin B5, is water...Ch. 11 - Prob. 71PCh. 11 - Prob. 72PCh. 11 - Explain why regularly taking a large excess of a...Ch. 11 - You can obtain the minimum daily requirement of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 75PCh. 11 - Vitamin B6 is obtained by eating a diet that...Ch. 11 - Prob. 77PCh. 11 - Can an oxygen-containing organic compound, have...Ch. 11 - Prob. 79PCh. 11 - Prob. 80PCh. 11 - Benzocaine is the active ingredient in topical...Ch. 11 - Methyl salicylate is responsible for the...Ch. 11 - Answer the following questions about aldosterone,...Ch. 11 - Answer the following questions about...Ch. 11 - Prob. 85PCh. 11 - Skin moisturizers come in two types, (a) One type...Ch. 11 - THC is the active component in marijuana (Section...Ch. 11 - Cocaine is a widely abused, addicting drug....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- predict the product formed by the reaction of one mole each of cyclohex-2-en-1-one and lithium diethylcuprate. Assume a hydrolysis step follows the additionarrow_forwardPlease handwriting for questions 1 and 3arrow_forwardIs (CH3)3NHBr an acidic or basic salt? What happens when dissolved in aqueous solution? Doesn't it lose a Br-? Does it interact with the water? Please advise.arrow_forward
- © Macmilla Finish resonance structure 3 Select Draw Templates More C H N 0 H H S Erase Which structure is the most stable (lowest energy) resonance contributor? The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and sulfur. All structures are equal in stability. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on sulfur and carbon. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and carbon. Q2Qarrow_forwardThree pure compounds are formed when 1.00 g samples of element x combine with, respectively, 0.472 g, 0.630 g, and 0.789 g of element z. The first compound has the formula x2Z3. find the empricial formula of the other two compoundsarrow_forwardDraw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forward
- In reactions whose kinetic equation is v = k[A]m, the rate coefficient k is always positive. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of A decreases exponentially with time, what is the rate equation? (A). -d[A] (B). dt d[A] = k[A] e-kt dtarrow_forwardGiven the first-order reaction: aA → products. State its kinetic equation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning