
Concept explainers
Methyl salicylate is responsible for the characteristic odor of the oil Wintergreen.
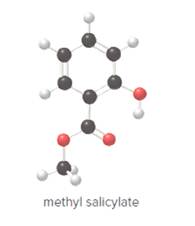
- Give the molecular formula for methyl salicylate.
- Draw in all lone pairs on heteroatoms using a skeletal structure.
- How many trigonal planar carbons does methyl salicylate contain?
- Predict the water solubility of methyl salicylate.
- Label all polar bonds.
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the molecular formula of methyl salicylate from the ball and stick model.
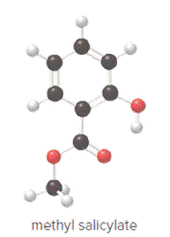
Concept Introduction:
In ball and stick model, black color ball represents carbon atom, white color ball represents hydrogen atom, red color ball represents oxygen atom and blue color ball represents nitrogen atom. To determine the molecular formula, convert the ball and stick model to complete structure.
Answer to Problem 82P
Molecular formula of methyl salicylate is
Explanation of Solution
Ball and stick model of methyl salicylate is as follows:
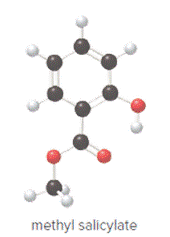
Convert ball and stick model to normal structure. Replace black balls by carbon atoms, red balls by oxygen atoms and white balls by hydrogen atom. But all the bonds between atoms are same.
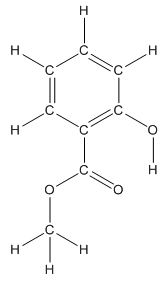
In methyl salicylate, eight carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms and three oxygen atoms present. Hence, molecular formula of methyl salicylate is
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw all lone pairs on heteroatoms of methyl salicylate using a skeletal structure.
Concept Introduction:
Heteroatoms are those atoms in an organic compound other than carbon and hydrogen atom like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. Lone pairs are pair of electrons available on an atom after bond formation.
Answer to Problem 82P
The structure having all lone pairs on heteroatoms is represented as follows:
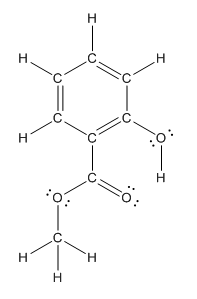
Explanation of Solution
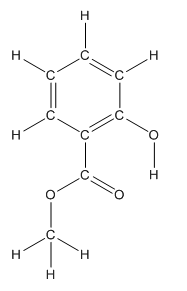
Structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
The heteroatoms present in benzocaine are oxygen atoms. Oxygen has six valence electrons. In double bonded oxygen atom, two electrons are used for making double bond. Remaining four electrons present as two lone pairs. Both the single bonded oxygen atom has two bonds. So, remaining four electrons present as two lone pairs in both the oxygen atom. So, the structure having all lone pairs on heteroatoms is represented as follows:
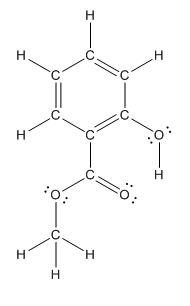
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the number of carbon atoms having trigonal planar shape in methyl salicylate.
Concept Introduction:
The following table should be used while determining shape around an atom.
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
If an atom is surrounded by three groups, then the shape around that particular atom is trigonal planar.
Answer to Problem 82P
Seven carbon atoms in methyl salicylate have trigonal planar structure.
Explanation of Solution
If an atom is surrounded by three groups, then the shape around that particular atom is trigonal planar.
Structure ofmethyl salicylate is as follows:
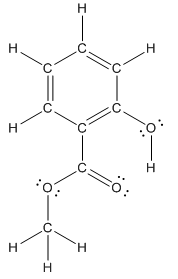
To find the number of carbon atoms having trigonal planar shape in methyl salicylate, observe the carbon atoms and find which carbon atom has three groups surround it.
All the carbon atoms in the benzene ring have three atoms around them also the carbon bonded to the benzene ring has three groups surround it. So, seven carbon atoms in methyl salicylatehave trigonal planar structure represented as follows:
The bold carbon atoms in the above structure have trigonal planar structure.
(d)
Interpretation:
To predict the solubility of methyl salicyate in water.
Concept Introduction:
Water is a polar solvent. To dissolve in water the compound must be polar. Polar compound is that compound in which polar bonds are present. The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 82P
Methyl salicylate is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
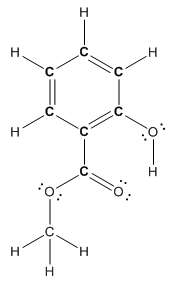
Structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
In methyl salicylate, three heteroatoms present that is, three oxygen atoms. These heteroatoms can form hydrogen bond with water. The presence of heteroatoms make the compound polar and a polar compound will dissolve in polar compound. So, methyl salicylate is soluble in water.
(e)
Interpretation:
To label all the polar bonds in methyl salicylate.
Concept Introduction:
The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 82P
The structure of methyl salicylate with all polar bonds labeled is as follows:
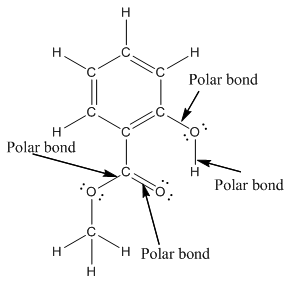
Explanation of Solution
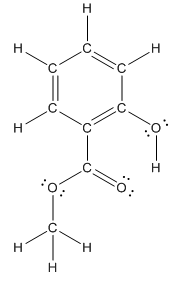
Structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
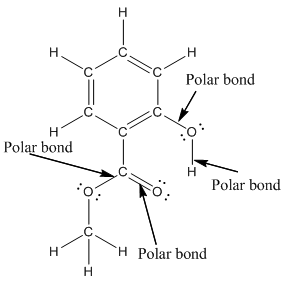
In organic compound, most of the polar bonds formed between carbon and heteroatoms like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. In methyl salicylate, four polar bonds present that is, three polar bond between carbon and oxygen (oxygen is more electronegative than carbon) and one polar bond between oxygen and hydrogen (oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- How many electron pairs are shared when a triple bond exists between two carbon atoms? What must he the geometric arrangement around the carbon atoms in a triple bond? Draw the Lewis structure of a simple molecule that contains a triple bond.arrow_forwardFor the following molecule, give, according to IUPAC standards, it's name. Follow the rules for commas, spaces and dashes.arrow_forwardFrom the condensed structural formulas,draw out the expanded structural formula for each in the table below(include all hydrogen). Name the organic compound using International union of pure and applied chemistry rules.arrow_forward
- Can you help me to solve this Provide an explanation for why carbon-carbon bond lengths are different.arrow_forwardIV. Fill up the numbered spaces (only) in the table below. Type your answer for the functional group. For the chemical formula, draw it manually, scan copy or shot a picture and paste in the answer sheets. Functional Structural Formula (SF) Condensed SF Condensed Formula Bond-line or Line-angle Group Formula 10 CH3 -(CH2),-C-O-CH(CH3)-CH3 11 12arrow_forward||| O NAMING AND DRAWING ORGANIC MOLECULES Interpreting condensed chemical structures Use this condensed chemical structure to complete the table below. 0 NH₂ - CH — C — OH | CH3 The condensed chemical structure of alanine Some facts about the alanine molecule: number of carbon-carbon single (C - C) bonds: number of carbon-hydrogen single (C-H) bonds: number of oxygen-hydrogen single (O - H) bonds: number of nitrogen-hydrogen single (N - H) bonds: number of lone pairs: X Ś 0 ☐ 1 D 503 Jessarrow_forward
- How many lone pairs of electrons are in 1-hexanolarrow_forwardDetermine whether the statement is true or false. Defend your answer with a MAXIMUM of 3 sentences. 1.Carboxyl groups are one of the most polar functional groups. Acetic acid (vinegar) has carboxyl group, so it has the most solubility with water.arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis Structure 1. CH3CHOHCH3, isopropyl alcohol 2. CH3CH2CH2CO2H, butyric acid 3. CH3COOCH2CH3, ethyl acetatearrow_forward
- Write the common (not systematic) name of each organic molecule. structure CH3 CH3-CH2-N-CH2-CH3 name CH2-CH3 ☐ CH3-CH2-CH2-N-CH2-CH3 CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-N-CH2-CH2-CH3 Xarrow_forwardthe carbon that the arrow is pointing to is valent mono di tetra triarrow_forwardI am studying for an o-chem exam and practicing name structures but there isn't an answer key. What is the correct name of these structures?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHERChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHERChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




