
Concept explainers
Benzocaine is the active ingredient in topical pain relievers such as Orajel and Anbesol. Give the molecular formula for benzocaine.
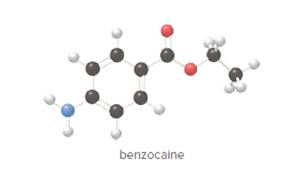
- Give the molecular formula for benzocaine.
- Draw in all lone pairs on heteroatoms using a skeletal structure.
- How many trigonal planar carbons does benzocaine contain?
- Predict the water solubility of benzocaine.
- Label all polar bonds.
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the molecular formula of benzocaine from the ball and stick model.
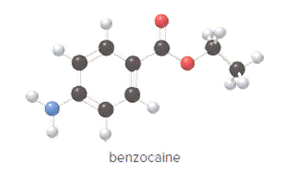
Concept Introduction:
In ball and stick model, black color ball represents carbon atom, white color ball represents hydrogen atom, red color ball represents oxygen atom and blue color ball represents nitrogen atom. To determine the molecular formula, convert the ball and stick model to complete structure.
Answer to Problem 81P
Molecular formula of benzocaine is
Explanation of Solution
The compound is as follows:
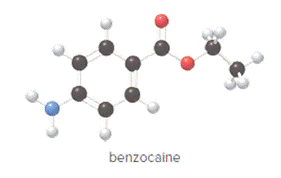
Convert ball and stick model to normal structure. Replace black balls by carbon atoms, red balls by oxygen atoms, blue ball by nitrogen atom and whit balls by hydrogen atom. But, all the bonds between atoms are same.
In benzocaine, nine carbon atoms, eleven hydrogen atoms, two oxygen atoms and one nitrogen atom present. Hence, molecular formula of benzocaine is
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw all lone pairs on heteroatoms of benzocaine using a skeletal structure.
Concept Introduction:
Heteroatoms are those atoms in an organic compound other than carbon and hydrogen atom like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. Lone pairs are pair of electrons available on an atom after bond formation.
Answer to Problem 81P
The structure of benzocaine having all lone pairs on heteroatoms is as follows:
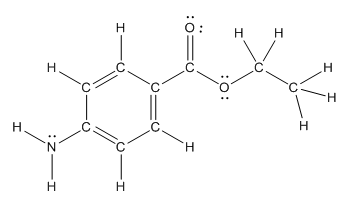
Explanation of Solution
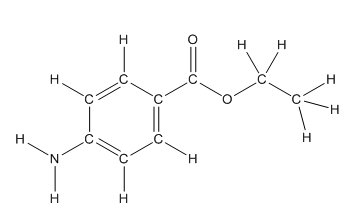
Skeletal structure of benzocaine is as follows:
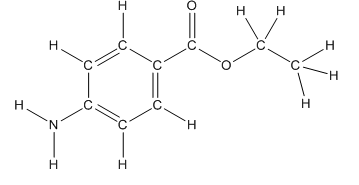
The heteroatoms present in benzocaine are nitrogen atom and two oxygen atoms. Nitrogen has five valence electrons. Out of five electrons, two electrons are used for making two (N-H) bonds, one electron is used for making one N-C bond. Remaining two electrons forms a lone pair. Oxygen has six valence electrons. For double bonded oxygen atom, two electrons are used for making the double bond. Remaining four electrons forms two lone pair. Other oxygen atom forms two bonds with carbon atoms means two electrons are used in bond formation. So, two pairs of lone pair present. Hence, the structure having all lone pairs on heteroatoms is as follows:
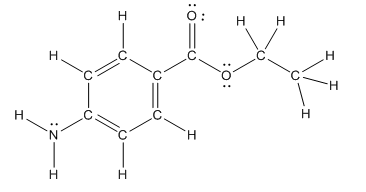
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the number of carbon atoms having trigonal planar shape in benzocaine.
Concept Introduction:
The following table should be used while determining shape around an atom.
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
If an atom is surrounded by three groups, then the shape around that particular atom is trigonal planar.
Answer to Problem 81P
In benzocaine, seven carbon atoms have trigonal planar structure.
Explanation of Solution
If an atom is surrounded by three groups, then the shape around that particular atom is trigonal planar.
Structure of benzocaine is as follows:
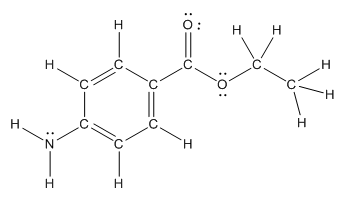
To find the number of carbon atoms having trigonal planar shape in benzocaine, observe the carbon atoms and find which carbon atom has three groups surround it.
All the carbon atoms in the benzene ring have three atoms around them also the carbon bonded to the benzene ring has three groups surround it. So, seven carbon atoms in benzocaine have trigonal planar structure.
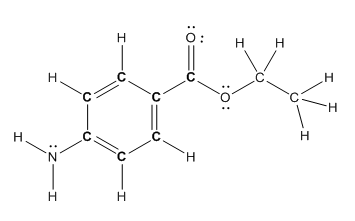
The bold carbon atoms have trigonal planar structure.
(d)
Interpretation:
To predict the solubility of benzocaine in water.
Concept Introduction:
Water is a polar solvent. To dissolve in water the compound must be polar. Polar compound is that compound in which polar bonds are present. The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 81P
Benzocaine is water soluble compound.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzocaine is as follows:
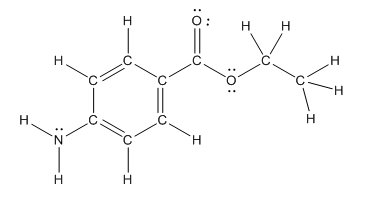
As the compound contains heteroatoms like nitrogen, oxygen the compound is polar that is, they can form hydrogen bonds with water. So, benzocaine is water soluble compound.
(e)
Interpretation:
To label all the polar bonds in benzocaine.
Concept Introduction:
The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 81P
Polar bond in benzocaine are as follows:
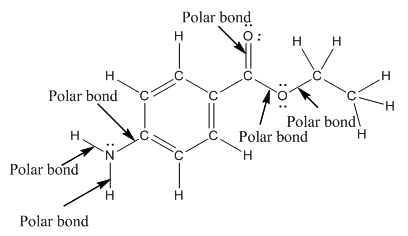
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzocaine is as follows:
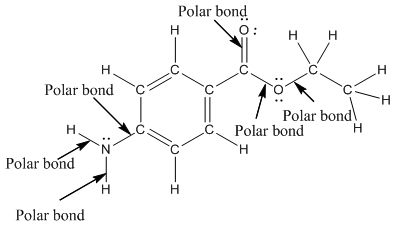
In organic compound, most of the polar bonds formed between carbon and heteroatoms like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. In benzocaine six polar bonds present that is, three polar bond between carbon and oxygen (oxygen is more electronegative than carbon), two polar bond between nitrogen and hydrogen (nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen) and on polar bond between carbon and nitrogen (nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
- Choose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. What is the half-life for this reaction?arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 1. PhNa A 2. H3O+ 1. PhCH2MgBr B 2. H3O+ хё 1. PhMgBr C 2. H3O+ 00 HO Q E D 1. H3O+ 2. PhMgBr PhMgBrarrow_forward
- Please answer all of the questions and provide detailed explanations and include a drawing to show the different signals on the molecule and include which ones should be highlighted.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ Q OH ☑ Select to Drawarrow_forwardHow should I graph my data for the Absorbance of Pb and Fe for each mushroom? I want to compare the results to the known standard curve. Software: Excel Spreadsheets Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/Eb2PfHdfEtBJiWh0ipHZ_kkBW4idWWwvpLPPtqoq2WkgbQ?rtime=HxrF0_tR3Ugarrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly, but do not use italics in Canvas.arrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. How many minutes will it take for the concentration of A to reach 0.144 Marrow_forwardWhat is the rate for the second order reaction A → Products when [A] = 0.256 M? (k = 0.761 M⁻¹s⁻¹)arrow_forward
- For reaction N2(g) + O2(g) --> 2NO(g) Write the rate of the reaction in terms of change of NO.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardThe reaction of 2-oxacyclopentanone with hydrochloric acid in water (i.e., "excess") produces which of the following carboxylic acids?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning



