
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781260562620
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 88CP
Cocaine is a widely abused, addicting drug. Cocaine is usually obtained as its hydrochloride salt (cocaine hydrochloride, an ionic salt). This salt can be converted to crack (a neutral molecule) by treatment with base.
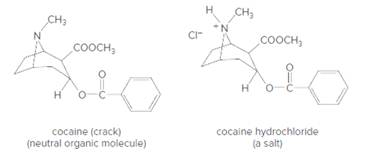
- Identify the
functional groups in cocaine. - Given what you have learned about ionic and covalent bonding, which of the two compounds—crack or cocaine hydrochloride—has a higher boiling point?
- Which compound is more soluble in water?
- Can you use the relative solubility to explain why crack is usually smoked but cocaine hydrochloride is injected directly into the bloodstream?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In terms of organic chemistry how do you know if an atom has ionic bonds or covalent bonds and how do you know if it has just one of these or if it has both? Could you provide some examples of what an ionic bond looks like, covalent bond looks like, and what an atom would look like with both of these?
"Cyclohexene is a linear
molecule with 6 carbon
Describe the molecule cyclohexene and provide
the chemical formula.
atoms and 12 hydrogen
atoms. There is a triple
bond because it ends in -
# 4 (Glycerina)
ene. The chemical formula
is C6H12"
Which two functional groups are in the molecule
shown below? Use the terms left and right to
distinguish them.
"The left functional group
is a carboxylic acid. The
right functional group is an
#5 (Trinitress)
alcohol."
H
The molecular formula of N-methylacrylamide is C4H7ON. How many valence electrons are needed to draw the Lewis structure of this molecule? Also, Draw the Lewis structure of N-methylacrylamide based on the skeleton above. Which is/are the intermolecular force(s) present between molecules of N-methylacrylamide?
Chapter 11 Solutions
CONNECT IA GENERAL ORGANIC&BIO CHEMISTRY
Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 11.1PCh. 11.2 - Fill in all H's and lone pairs in each compound.Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.2PPCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.2PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.3PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.3PPCh. 11.3 - How many lone pairs are present in lidocaine, the...Ch. 11.4 - Convert each compound to a condensed formula.Ch. 11.4 - Convert each condensed formula to a complete...Ch. 11.4 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...
Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.5PCh. 11.4 - How many H’s are bonded to each indicated carbon...Ch. 11.4 - Using the skeletal structure, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.7PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.8PCh. 11.5 - For each compound. [1] Identify the functional...Ch. 11.5 - How do a carboxylic acid and an alcohol differ?...Ch. 11.5 - Label each of the following condensed structures...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.11PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.12PCh. 11.5 - Identify all of the functional groups in atenolol,...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.13PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.10PPCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.14PCh. 11.6 - Indicate the polar bonds in each compound. Label...Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 11.11PPCh. 11.6 - Prob. 11.16PCh. 11.6 - Predict the water solubility of each compound.Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 11.17PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.18PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.19PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 11.20PCh. 11 - Prob. 21PCh. 11 - Prob. 22PCh. 11 - Complete each structure by filling in all H’s and...Ch. 11 - Complete the structure of mepivacaine by filling...Ch. 11 - Prob. 25PCh. 11 - Prob. 26PCh. 11 - Prob. 27PCh. 11 - Prob. 28PCh. 11 - “Ecstasy” is a widely used illegal stimulant....Ch. 11 - Prob. 30PCh. 11 - Explain why each C—C—C bond angle in benzene...Ch. 11 - Prob. 32PCh. 11 - Convert each compound to a condensed structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each compound to a condensed structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each compound to a skeletal structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each compound to a skeletal structure.Ch. 11 - Convert each shorthand structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - Convert each shorthand structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...Ch. 11 - A and B are ball-and-stick models of two compounds...Ch. 11 - Prob. 42PCh. 11 - What is wrong in each of the following shorthand...Ch. 11 - Prob. 44PCh. 11 - Prob. 45PCh. 11 - Albuterol (trade names Proventil and Ventolin) is...Ch. 11 - Prob. 47PCh. 11 - Prob. 48PCh. 11 - Prob. 49PCh. 11 - (a) Identify the functional groups in donepezil,...Ch. 11 - Prob. 51PCh. 11 - GHB is an addictive, illegal recreational drug...Ch. 11 - Prob. 53PCh. 11 - Prob. 54PCh. 11 - Prob. 55PCh. 11 - Prob. 56PCh. 11 - Prob. 57PCh. 11 - (a) Identify the functional groups in venlafaxine,...Ch. 11 - You are given two unlabeled bottles of solids, one...Ch. 11 - State how potassium iodide (KI) and pentane...Ch. 11 - The given beaker contains 100 mL of the organic...Ch. 11 - Prob. 62PCh. 11 - Why do we need to know the shape of a molecule...Ch. 11 - 1,1-Dichloroethylene (CH2=CCl2) is a starting...Ch. 11 - Indicate the polar bonds in each molecule. Label...Ch. 11 - Indicate the polar bonds in each molecule. Label...Ch. 11 - Classify each molecule as polar or nonpolar.Ch. 11 - Classify each molecule as polar or nonpolar. a....Ch. 11 - Which molecule is more water soluble? Explain.Ch. 11 - Explain why pantothenic acid, vitamin B5, is water...Ch. 11 - Prob. 71PCh. 11 - Prob. 72PCh. 11 - Explain why regularly taking a large excess of a...Ch. 11 - You can obtain the minimum daily requirement of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 75PCh. 11 - Vitamin B6 is obtained by eating a diet that...Ch. 11 - Prob. 77PCh. 11 - Can an oxygen-containing organic compound, have...Ch. 11 - Prob. 79PCh. 11 - Prob. 80PCh. 11 - Benzocaine is the active ingredient in topical...Ch. 11 - Methyl salicylate is responsible for the...Ch. 11 - Answer the following questions about aldosterone,...Ch. 11 - Answer the following questions about...Ch. 11 - Prob. 85PCh. 11 - Skin moisturizers come in two types, (a) One type...Ch. 11 - THC is the active component in marijuana (Section...Ch. 11 - Cocaine is a widely abused, addicting drug....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many electron pairs are shared when a triple bond exists between two carbon atoms? What must he the geometric arrangement around the carbon atoms in a triple bond? Draw the Lewis structure of a simple molecule that contains a triple bond.arrow_forward* Question Completion Status: A Moving to the next question prevents changes to this answer. Question 2 Identify the functional group HO NH₂ ester amine amide alcohol phenol alkene ketone sulfide A Moving to the next question prevents changes to this answer. ✓, and in the following compound.arrow_forwardwhy Acetanilide after cooling back at room temperature forms a crystal?arrow_forward
- Amines and amides both contain nitrogen. What are the differences in the structures of amines and amides in terms of the functional groups?arrow_forwardIn the structure of Methamphetamine. What functional groups are in the molecule?arrow_forwardHow does the structure of an alcohol differ from an ether? Describe how an aldehyde differs in structure from a ketone. Thiols are compounds which resemble alcohols, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. Draw the analogous thiol for the four carbon alcohol in Table 1. Describe the structural difference between carboxylic acids and esters. Are ethers polar molecules? Would you expect ethers to have higher or lower boiling points than alkanes (circle one)? Explain. Pentane (an alkane) has a boiling point of 36 °C. Does the data agree with your prediction? explain why this could be the casearrow_forward
- 23. Suppose that you are working with four unknown compounds in a chemistry laboratory. Your teacher tells you that these compounds are alkane, alcohol, ester and organic acid. Use the table of physical properties shown below to identify each unknown compound. Compound A is Compound C is Compound Boiling point A B C D -89°C 77°C Odour 118°C Odourless Sweet 78°C Sharp, antiseptic Very polar smell Molecular polarity Non-polar Polar Sharp, vinegar smell Very polar Compound B is Compound D isarrow_forwardIdentify the functional grouparrow_forwardFor each compound, consider whether or not H-bonding can occur between its molecules. Use a dashed line to show any H-bonding.Which compounds are polar? Which compounds are nonpolar? Explain your reasoningarrow_forward
- Describe the functional group similarities and differences among the four molecules shown below. Compare their polarities; explain your answer. H. H. H. H. H. H. H. HIIarrow_forwardWhich of the following is TRUE of hydrophobic molecules? They have limited solubility in water. Water forms a cage-like structure around them. Dissolving in water decreases the entropy of the mixture. All of the abovearrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true about a soap molecule? The carbon chain is polar and it attracts grease particles, while the carboxylate salt is nonpolar and it attracts water. The carbon chain is nonpolar and it attracts grease particles, while the carboxylate salt is polar and it attracts water. The carbon chain is nonpolar and it attracts water while the carboxylate salt is polar and it attracts grease particles. O Both, carbon chain and carboxylate salt are polar and attract only water.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY