
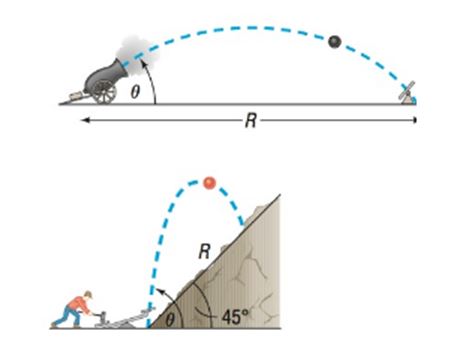
Projectile Motion The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity feet per second and at an angle to the horizontal at the end of seconds is given by the parametric equations
See the illustration.
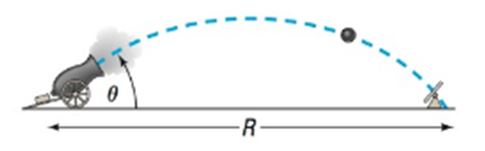
a. Obtain the rectangular equation of the trajectory and identify the curve.
b. Show that the projectile hits the ground when .
c. How far has the projectile traveled (horizontally) when it strikes the ground? In other words, find the range .
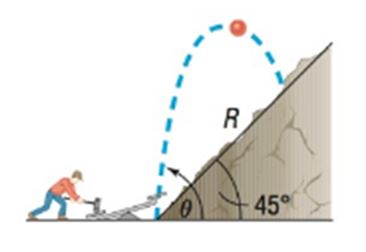
d. Find the time when . Then find the horizontal distance and the vertical distance traveled by the projectile in this time. Then compute . This is the distance , the range, that the projectile travels up a plane inclined at to the horizontal . See the following illustration. (See also Problem 99 in Section 7.6.)
To find:
a. The rectangular equation of the trajectory and identify the curve.
Answer to Problem 60AYU
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity feet per second and at an angle to the horizontal at the end of seconds is given by the parametric equations.
,
Formula used:
,
Calculation:
a. ,
is a quadratic function of and it represents the graph of a parabola where , and .
To find:
b. To show that the projectile hits the ground when .
Answer to Problem 60AYU
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity feet per second and at an angle to the horizontal at the end of seconds is given by the parametric equations.
,

Formula used:
,
Calculation:
b.
To find:
c. How far has the projectile traveled (horizontally) when it strikes the ground? In other words, find the range R.
Answer to Problem 60AYU
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity feet per second and at an angle to the horizontal at the end of seconds is given by the parametric equations.
,

Formula used:
,
Calculation:
c. To find R
We substitute in
To find:
d. Find the time when . Then find the horizontal distance and the vertical distance traveled by the projectile in this time. Then compute . This is the distance R, the range, that the projectile travels up a plane inclined at to the horizontal .
Answer to Problem 60AYU
d. as
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The position of a projectile fired with an initial velocity feet per second and at an angle to the horizontal at the end of seconds is given by the parametric equations.
,

Formula used:
,
Calculation:
d.
;
At
hence,
as
Chapter 10 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- Draw the triangle and show all the workarrow_forwardsolve these pleasearrow_forwardA factorization A = PDP 1 is not unique. For A= 7 2 -4 1 1 1 5 0 2 1 one factorization is P = D= and P-1 30 = Use this information with D₁ = to find a matrix P₁ such that - -1 -2 0 3 1 - - 1 05 A-P,D,P P1 (Type an integer or simplified fraction for each matrix element.)arrow_forward
- Matrix A is factored in the form PDP 1. Use the Diagonalization Theorem to find the eigenvalues of A and a basis for each eigenspace. 30 -1 - 1 0 -1 400 0 0 1 A= 3 4 3 0 1 3 040 3 1 3 0 0 4 1 0 0 003 -1 0 -1 Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Use a comma to separate vectors as needed.) A basis for the corresponding eigenspace is { A. There is one distinct eigenvalue, λ = B. In ascending order, the two distinct eigenvalues are λ₁ ... = and 2 = Bases for the corresponding eigenspaces are { and ( ), respectively. C. In ascending order, the three distinct eigenvalues are λ₁ = = 12/2 = and 3 = Bases for the corresponding eigenspaces are {}, }, and { respectively.arrow_forwardN Page 0.6. 0.4. 0.2- -0.2- -0.4- -6.6 -5 W 10arrow_forwardDiagonalize the following matrix, if possible. 8 0 6 - 8 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. 8 0 OA. For P= D= 0 3 6 0 B. For P = D= 0 -6 8 0 C. For P = D= 0 - 8 D. The matrix cannot be diagonalized.arrow_forward
- 4 In the integral dxf1dy (7)², make the change of variables x = ½(r− s), y = ½(r + s), and evaluate the integral. Hint: Find the limits on r and s by sketching the area of integration in the (x, y) plane along with the r and s axes, and then show that the same area can be covered by s from 0 to r and r from 0 to 1.arrow_forward7. What are all values of 0, for 0≤0<2л, where 2 sin² 0=-sin? - 5π 6 π (A) 0, л, and 6 7π (B) 0,л, 11π , and 6 6 π 3π π (C) 5π 2 2 3 , and π 3π 2π (D) 2' 2'3 , and 3 4元 3 1 די } I -2m 3 1 -3 บ 1 # 1 I 3# 3m 8. The graph of g is shown above. Which of the following is an expression for g(x)? (A) 1+ tan(x) (B) 1-tan (x) (C) 1-tan (2x) (D) 1-tan + X - 9. The function j is given by j(x)=2(sin x)(cos x)-cos x. Solve j(x) = 0 for values of x in the interval Quiz A: Topic 3.10 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities Created by Bryan Passwaterarrow_forwardcan you solve this question using the right triangle method and explain the steps used along the wayarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





