
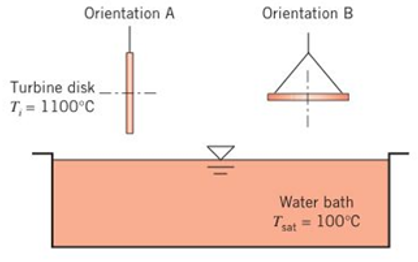
A disk-shaped turbine rotor is heat-treated by quenching in water at
(a) Assuming lumped-capacitance behavior and constant properties for the rotor, carefully plot the rotor temperature versus time, pointing out important features of your
(b) If the rotor is reoriented so that its large surfaces are horizontal (Orientation B), would the rotor temperature decrease more rapidly or less rapidly relative to Orientation A?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- 1.7 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.23 using two beam elements. A. E. I constant M₂ T + FIGURE 1.23 A fixed-pinned beam subjected to a momentarrow_forward42 PART 1 Introduction A. E. I constant FIGURE 1.22 A fixed-pinned beam. 1.6 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.22 using two beam elements.arrow_forward1.4 Using a one-beam element idealization, find the stress distribution under a load of P for the uniform cantilever beam shown in Fig. 1.20. A, E, I constant L FIGURE 1.20 A uniform cantilever beamarrow_forward
- Mechanical engineering,FBD required.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardPlease Please use MATLAB with codes and graph. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure is attached below.arrow_forward
- Please only step 6 (last time I asked it was cut off at that point)arrow_forwardPlease Please use a MATLAB with codes and grap. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure attached below.arrow_forwardI REPEAT!!!!! I NEED HANDDRAWING!!!!! NOT A USELESS EXPLANATION!!!! I REPEAT SUBMIT A HANDDRAWING IF YOU CANNOT UNDERSTAND THIS SKIP IT ! I need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forward
- I need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forwardAn elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + b(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = Edx du Hooke's law (1) b(x) = gp= body force per unit volume where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the axial stress in the rod. g * I u(x) L 2arrow_forwardAn elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + b(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = Edx du Hooke's law (1) b(x) = gp= body force per unit volume where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the axial stress in the rod. g * I u(x) L 2arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
