
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780073380643
Author: Donald A. Neamen
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Companies, The
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.49P
(a) In the circuit Shown in Figure P1.49, find the diode voltage
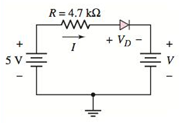
Figure P1.49
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
constants:
A (medium) single phase transmission line 100 km long has the following
Resistance/km = 0.25 2;
Susceptance/km = 14 × 10 siemen;
Reactance/km = 0.8
Receiving end line voltage = 66,000 V
Assuming that the total capacitance of the line is localised at the receiving end alone, determine
(i) the sending end current (ii) the sending end voltage (iii) regulation and (iv) supply power factor.
The line is delivering 15,000 kW at 0.8 power factor lagging. Draw the phasor diagram to illustrate
your calculations.
For the power system given below, the voltage at bus 2 is kept at 1.03 pu. The maximum power can be delivered by G2 is 35
MW. Obtain the load flow solution. Take the base power 100 MVA.
V₁ = 1.0520
G₁
0.02+j0.06
G2 V2=1.03
P2 = 35 MW
0.08+j0.24
SL2 20+j50 MVA
SL3
60+j25 MVA
0.06+j0.018
General Directions: Read the questions carefully and answer (3*10=30marks)
1. Design a summing amplifier by choosing appropriate values of resistors an so that
the output is 5 times the sum of the input voltages. (you are free to use any number
of inputs, the type of op-amp, any value of resistors)
2. Derive the equation for the closed loop gain of the inverting and non-inverting
Amplifier using appropriate circuit diagrams.
3. Determine the values read by the measuring devices using appropriate formulae
www
Voc
+8V
R₁
33 k
Rc
2.2 k
ww
WWW
Poc 200
R₁₂
RE
10 kn
1.0 kn
Chapter 1 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
Ch. 1 - Calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration in...Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate the majority and minority carrier...Ch. 1 - Consider ntype GaAs at T=300K doped to a...Ch. 1 - Consider silicon at T=300K . Assume the hole...Ch. 1 - Determine the intrinsic carrier concentration in...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider silicon at T=300K . Assume that...Ch. 1 - Using the results of TYU1.2, determine the drift...Ch. 1 - The electron and hole diffusion coefficients in...Ch. 1 - A sample of silicon at T=300K is doped to...Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate Vbi for a GaAs pn junction at T=300K...
Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction at T=300K is doped at...Ch. 1 - (a) A silicon pn junction at T=300K has a...Ch. 1 - (a) Determine Vbi for a silicon pn junction at...Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction diode at T=300K has a...Ch. 1 - Recall that the forwardbias diode voltage...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit in Figure 1.28. Let VPS=4V ,...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1.28. Let...Ch. 1 - The resistor parameter in the circuit shown in...Ch. 1 - Consider the diode and circuit in Exercise EX 1.8....Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit in Figure 1.28. Let R=4k and...Ch. 1 - The power supply (input) voltage in the circuit of...Ch. 1 - (a) The circuit and diode parameters for the...Ch. 1 - Determine the diffusion conductance of a pn...Ch. 1 - Determine the smallsignal diffusion resistance of...Ch. 1 - The diffusion resistance of a pn junction diode at...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode and a Schottky diode both have...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1.45....Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1.46. The...Ch. 1 - A Zener diode has an equivalent series resistance...Ch. 1 - The resistor in the circuit shown in Figure 1.45...Ch. 1 - Describe an intrinsic semiconductor material. What...Ch. 1 - Describe the concept of an electron and a hole as...Ch. 1 - Describe an extrinsic semiconductor material. What...Ch. 1 - Describe the concepts of drift current and...Ch. 1 - How is a pn junction formed? What is meant by a...Ch. 1 - How is a junction capacitance created in a...Ch. 1 - Write the ideal diode currentvoltage relationship....Ch. 1 - Describe the iteration method of analysis and when...Ch. 1 - Describe the piecewise linear model of a diode and...Ch. 1 - Define a load line in a simple diode circuit.Ch. 1 - Under what conditions is the smallsignal model of...Ch. 1 - Describe the operation of a simple solar cell...Ch. 1 - How do the i characteristics of a Schottky barrier...Ch. 1 - What characteristic of a Zener diode is used in...Ch. 1 - Describe the characteristics of a photodiode and a...Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration...Ch. 1 - (a) The intrinsic carrier concentration in silicon...Ch. 1 - Calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration in...Ch. 1 - (a) Find the concentration of electrons and holes...Ch. 1 - Gallium arsenide is doped with acceptor impurity...Ch. 1 - Silicon is doped with 51016 arsenic atoms/cm3 ....Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate the concentration of electrons and...Ch. 1 - A silicon sample is fabricated such that the hole...Ch. 1 - The electron concentration in silicon at T=300K is...Ch. 1 - (a) A silicon semiconductor material is to be...Ch. 1 - (a) The applied electric field in ptype silicon is...Ch. 1 - A drift current density of 120A/cm2 is established...Ch. 1 - An ntype silicon material has a resistivity of...Ch. 1 - (a) The applied conductivity of a silicon material...Ch. 1 - In GaAs, the mobilities are n=8500cm2/Vs and...Ch. 1 - The electron and hole concentrations in a sample...Ch. 1 - The hole concentration in silicon is given by...Ch. 1 - GaAs is doped to Na=1017cm3 . (a) Calculate no and...Ch. 1 - (a) Determine the builtin potential barrier Vbi in...Ch. 1 - Consider a silicon pn junction. The nregion is...Ch. 1 - The donor concentration in the nregion of a...Ch. 1 - Consider a uniformly doped GaAs pn junction with...Ch. 1 - The zerobiased junction capacitance of a silicon...Ch. 1 - The zerobias capacitance of a silicon pn junction...Ch. 1 - The doping concentrations in a silicon pn junction...Ch. 1 - (a) At what reversebias voltage does the...Ch. 1 - (a) The reversesaturation current of a pn junction...Ch. 1 - (a) The reversesaturation current of a pn junction...Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction diode has an emission...Ch. 1 - Plot log10ID versus VD over the range 0.1VD0.7V...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider a silicon pn junction diode operating...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode has IS=2nA . (a) Determine the...Ch. 1 - The reversebias saturation current for a set of...Ch. 1 - A germanium pn junction has a diode current of...Ch. 1 - (a)The reversesaturation current of a gallium...Ch. 1 - The reversesaturation current of a silicon pn...Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction diode has an applied...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode is in series with a 1M...Ch. 1 - Consider the diode circuit shown in Figure P1.39....Ch. 1 - The diode in the circuit shown in Figure P1.40 has...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.41PCh. 1 - (a) The reversesaturation current of each diode in...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.40....Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.44....Ch. 1 - The cutin voltage of the diode shown in the...Ch. 1 - Find I and VO in each circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - Repeat Problem 1.47 if the reversesaturation...Ch. 1 - (a) In the circuit Shown in Figure P1.49, find the...Ch. 1 - Assume each diode in the circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider a pn junction diode biased at IDQ=1mA...Ch. 1 - Determine the smallsignal diffusion resistancefor...Ch. 1 - The diode in the circuit shown in Figure P1.53 is...Ch. 1 - The forwardbias currents in a pn junction diode...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode and a Schottky diode have...Ch. 1 - The reversesaturation currents of a Schottky diode...Ch. 1 - Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - (a) The Zener diode in Figure P1.57 is ideal with...Ch. 1 - Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - The Output current of a pn junction diode used as...Ch. 1 - Using the currentvoltage characteristics of the...Ch. 1 - (a) Using the currentvoltage characteristics of...Ch. 1 - Use a computer simulation to generate the ideal...Ch. 1 - Use a computer simulation to find the diode...Ch. 1 - Design a diode circuit to produce the load line...Ch. 1 - Design a circuit to produce the characteristics...Ch. 1 - Design a circuit to produce the characteristics...Ch. 1 - Design a circuit to produce the characteristics...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 十 : + B 日 العنوان I need a detailed drawing with explanation ややハメPV+96252 4 Project Homework: Create a simulation for a tank when the flowrate inside and outside the tank must range between 0 and 10 lit/s: 1) The level should be controlled within a range between more than zero to 1000 lit. 2) An alarm must be launched when the level is out of range (less than 100 and more than 900 lit). 3) When the capacity reaches to the maximum the motor turns OFF. area=A Qout -20 solve in lab view X9.01 *175*1arrow_forwardProject Homework: Create a simulation for a tank when the flowrate inside and outside the tank must range between 0 and 10 lit/s: 1) The level should be controlled within a range between more than zero to 1000 lit. 2) An alarm must be launched when the level is out of range (less than 100 and more than 900 lit). 3) When the capacity reaches to the maximum the motor turns OFF. Qin h C Qout area=A solve in lab viewarrow_forwardQUESTION [3] A no-load and short-circuit test should be conducted on a 220V/110V, 280VA transformer. a. Draw the circuit diagram for the no-load test and include all measurements that should be made. Also write down the maximum voltage that you should apply to the primary winding and estimate the current drawn from the supply. (5) b. Draw a circuit diagram for the short-circuit test and include all measurements that should be made. Also write down the maximum current that should be allowed to flow in the primary winding and estimated the primary voltage that will cause this value of the current to flow. (5)arrow_forward
- A dc compound motor having a rating of 10 kW, 1150 r/min, 230 V, 50 A, has the following losses at full-load: bearing friction loss 40 W brush friction loss == 50 W windage loss = 200 W (1) total mechanical losses = 290 W (2) iron losses = 420 W (3) copper loss in the shunt field = 120 W copper losses at full-load: (4) a. in the armature b. in the series field c. in the commutating winding total copper loss in the 500 W 25 W 70 W armature circuit at full-load = 595 Warrow_forward4 What determines the power rating of a ma- chine? -5 If we cover up the vents in a motor, its out- put power must be reduced. Explain. -6 If a motor operates in a cold environment, may we load it above its rated power? Why?arrow_forwardAn electric motor driving a skip hoist with- draws 1.5 metric tons of minerals from a trench 20 m deep every 30 seconds. If the hoist has an overall efficiency of 94 percent, calculate the power output of the motor in horsepower and in kilowatts.arrow_forward
- The efficiency of a motor is always low when it operates at 10 percent of its nominal power rating. Explain.arrow_forwardA dc motor connected to a 240 V line pro- duces a mechanical output of 160 hp. Knowing that the losses are 12 kW, calculate the input power and the line current.arrow_forwardA 115 V dc generator delivers 120 A to a load. If the generator has an efficiency of 81 percent, calculate the mechanical power needed to drive it [hp].arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Diodes Explained - The basics how diodes work working principle pn junction; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fwj_d3uO5g8;License: Standard Youtube License