Concept explainers
Repeat Problem 1.47 if the reverse−saturation current for each diode isy
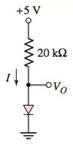
a.
The voltage across diode.
Answer to Problem 1.48P
The diode voltage,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The circuit diagram is given as:
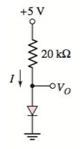
The reverse saturation current for each diode is
Calculation:
The expression for the diode current is given as:
From the given circuit, evaluating the diode current:
From the circuit, the output voltage is same as the diode voltage.
Solving equation 1 and 2 by using the hit and trial method:
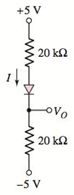
b.
The voltage across diode.
Answer to Problem 1.48P
The diode voltage,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The circuit diagram is given as:
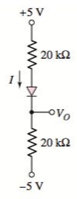
The reverse saturation current for each diode is
Calculation:
The expression for the diode current is given as:
From the given circuit, evaluating the diode current:
Applying the Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the circuit from top to bottom:
Assuming the voltage across diode vD, then applying the Kirchhoff’s voltage law from top to the output voltage:
From the circuit, the diode current is same as the current flowing in the circuit:
Solving equation 1, 2 and 3 by using the hit and trial method:
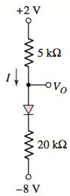
c.
The voltage across diode.
Answer to Problem 1.48P
The diode voltage,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The circuit diagram is given as:
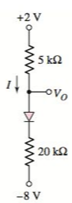
The reverse saturation current for each diode is
Calculation:
The expression for the diode current is given as:
From the given circuit, evaluating the diode current:
Applying the Kirchhoff’s voltage law to the circuit from top to bottom:
Then applying the Kirchhoff’s voltage law from top to the output voltage:
From the circuit, the diode current is same as the current flowing in the circuit:
Solving equation 1, 2 and 3 by using the hit and trial method:
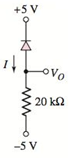
d.
The voltage across diode.
Answer to Problem 1.48P
The diode voltage,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The circuit diagram is given as:
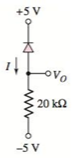
The reverse saturation current for each diode is
Calculation:
Referring the given circuit, here the diode current is flowing in the reverse direction.
Hence, the reverse saturation current will be the diode current in this case.
Since the value of the reverse saturation current is given in the question.
Therefore,
Now evaluating the diode voltage:
Since, due to reverse direction of the current, no current will flow through the resistor. Hence the drop across the resistor will be zero.
Therefore, the value of the diode voltage will be same as the output voltage:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- In thinkercad can you make a parallel circuit with a resistors and a voltage source explain how the voltage and current moves through the circuit, and explaining all the components, and if you were to break the circuit to find the current how would you do that? Please show visuals if possiblearrow_forwardQ1arrow_forward2-2 -Draw V-curves for synchronous motor at no load, half load, and full load? 2-List the advantages of damper bars in synchronous machines? 3-Draw phasor diagram for alternator at unity power factor, and derive EMF equation from it?arrow_forward
- conduit bending techniques and the most common anglesarrow_forwardQuestion 1 Draw and complex CMOS logic and design the width-to-length ratios (W/L) of the transistors needed to implement the CMOS circuit for the following function (asuume Wp: W₁ = 2:1) n f=AB+CD+E+AD Question 2 Implement the following function using CMOS technology. f = x1(x2x3 + x4) Design the width-to-length ratios (W/L) of the transistors needed to implement the CMOS circuuit for the following function (asuume Wp: W₁ = 2:1) n Question 3 Consider the following three-pole feedback amplifier with a loop gain function: 6000× B T (jf) = 1+j f 2×10³ 1+ j f 3×104 f 1+ j 4×105 If ẞ=38.66×10³ determine the phase margin and the gain margin of this system (if it is stable).arrow_forwardhow to bend conduit in exact angles. and bending angles stepsarrow_forward
- ¡ you need to connect a three phase alternator B (incoming generator) in parallel with alternator A which is connected to an infinite bus bar, what are the necessary conditions to make this connection appen properly? Explain how you can use a three lamps to achieve this connection?arrow_forwardQ2arrow_forwardexplain the operation of matched filter receiver I we discussed in class, and from your background in Signal and Systems, 16. (10pts) A M-ary QAM system transmits 4.8Kbps with an error rate of less than 10^-6. The center frequency is 1 GHZ and the channel has a bandwidth of 4 KHz. The channel attenuates the signal by 10 dB. The noise in the channel can be modeled as AWGN with a power spectral density of 10^-7 (watts/Hz). Estimate the required transmit signal power, Pt cts) The modulation format is DAMarrow_forward
- MacBook Air e 15. From w 12. A communication system uses QAM modulation. The Eb/No is fixed at 15 dB. The application requires a BER of less than 10^-4. What is the maximum number of symbols that could be used? F12 } 1 13: Estimate the bandwidth of a Double Sideband Plus Carrier modulated signal with an amplitude sensitivity (k) of 0.75 and a message bandwidth of 15KHz.arrow_forwardShort answers, 3pts each 11: Estimate the bandwidth of an FM modulated wave given: deviation ratio of 5 and the maximum frequency of the message is 15KHz.arrow_forwardMacBook Air J GE F11 + "/ F12 (25) Determine how 20. (45pts) A battery operated sensor transmits to a receiver that is plugged in to a power outlet. The device is continuously operated. The battery is a commercially available 9 V battery with a 1.1 AmpHr capacity. The application requires a bit rate of 120 Mbps and an error rate of less than 10^-5. The channel has a center frequency of 5.8 GHz, a bandwidth of 20 MHz and a noise power spectral density of 10^-12 W/Hz. The maximum distance is 50 meters and the losses in the channel attenuates the signal by 0.05 dB/meter. M-ary FSK is not possible due to bandwidth limitations. a) (5pts) To maximize battery life, what modulation scheme would you use?arrow_forward