
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780073380643
Author: Donald A. Neamen
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Companies, The
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.16P
The electron and hole concentrations in a sample of silicon are shown in Figure P1.16. Assume the electron and hole mobilities are the same as in Problem 1.12. Determine the total diffusion current density versus distance x for
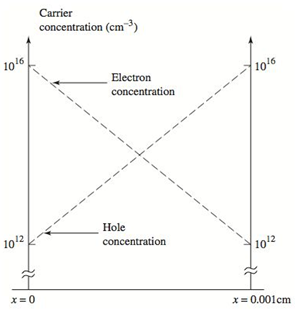
Figure P1.16
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve by Pen and Paper not using chatgpt
f. The figure below shows two stage RC coupled amplifier. If the input resistance Rin
of each stage is 1kN. (B = 100). Determine its overall voltage gain. (5 marks)
+15V
ΣΚΩ
kn
10kΩ
10ΚΩ
output
35 ΚΩ
2ΚΩ
5kЛ
2ΚΩ
NO AI PLEASE
Chapter 1 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
Ch. 1 - Calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration in...Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate the majority and minority carrier...Ch. 1 - Consider ntype GaAs at T=300K doped to a...Ch. 1 - Consider silicon at T=300K . Assume the hole...Ch. 1 - Determine the intrinsic carrier concentration in...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider silicon at T=300K . Assume that...Ch. 1 - Using the results of TYU1.2, determine the drift...Ch. 1 - The electron and hole diffusion coefficients in...Ch. 1 - A sample of silicon at T=300K is doped to...Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate Vbi for a GaAs pn junction at T=300K...
Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction at T=300K is doped at...Ch. 1 - (a) A silicon pn junction at T=300K has a...Ch. 1 - (a) Determine Vbi for a silicon pn junction at...Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction diode at T=300K has a...Ch. 1 - Recall that the forwardbias diode voltage...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit in Figure 1.28. Let VPS=4V ,...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1.28. Let...Ch. 1 - The resistor parameter in the circuit shown in...Ch. 1 - Consider the diode and circuit in Exercise EX 1.8....Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit in Figure 1.28. Let R=4k and...Ch. 1 - The power supply (input) voltage in the circuit of...Ch. 1 - (a) The circuit and diode parameters for the...Ch. 1 - Determine the diffusion conductance of a pn...Ch. 1 - Determine the smallsignal diffusion resistance of...Ch. 1 - The diffusion resistance of a pn junction diode at...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode and a Schottky diode both have...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1.45....Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1.46. The...Ch. 1 - A Zener diode has an equivalent series resistance...Ch. 1 - The resistor in the circuit shown in Figure 1.45...Ch. 1 - Describe an intrinsic semiconductor material. What...Ch. 1 - Describe the concept of an electron and a hole as...Ch. 1 - Describe an extrinsic semiconductor material. What...Ch. 1 - Describe the concepts of drift current and...Ch. 1 - How is a pn junction formed? What is meant by a...Ch. 1 - How is a junction capacitance created in a...Ch. 1 - Write the ideal diode currentvoltage relationship....Ch. 1 - Describe the iteration method of analysis and when...Ch. 1 - Describe the piecewise linear model of a diode and...Ch. 1 - Define a load line in a simple diode circuit.Ch. 1 - Under what conditions is the smallsignal model of...Ch. 1 - Describe the operation of a simple solar cell...Ch. 1 - How do the i characteristics of a Schottky barrier...Ch. 1 - What characteristic of a Zener diode is used in...Ch. 1 - Describe the characteristics of a photodiode and a...Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration...Ch. 1 - (a) The intrinsic carrier concentration in silicon...Ch. 1 - Calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration in...Ch. 1 - (a) Find the concentration of electrons and holes...Ch. 1 - Gallium arsenide is doped with acceptor impurity...Ch. 1 - Silicon is doped with 51016 arsenic atoms/cm3 ....Ch. 1 - (a) Calculate the concentration of electrons and...Ch. 1 - A silicon sample is fabricated such that the hole...Ch. 1 - The electron concentration in silicon at T=300K is...Ch. 1 - (a) A silicon semiconductor material is to be...Ch. 1 - (a) The applied electric field in ptype silicon is...Ch. 1 - A drift current density of 120A/cm2 is established...Ch. 1 - An ntype silicon material has a resistivity of...Ch. 1 - (a) The applied conductivity of a silicon material...Ch. 1 - In GaAs, the mobilities are n=8500cm2/Vs and...Ch. 1 - The electron and hole concentrations in a sample...Ch. 1 - The hole concentration in silicon is given by...Ch. 1 - GaAs is doped to Na=1017cm3 . (a) Calculate no and...Ch. 1 - (a) Determine the builtin potential barrier Vbi in...Ch. 1 - Consider a silicon pn junction. The nregion is...Ch. 1 - The donor concentration in the nregion of a...Ch. 1 - Consider a uniformly doped GaAs pn junction with...Ch. 1 - The zerobiased junction capacitance of a silicon...Ch. 1 - The zerobias capacitance of a silicon pn junction...Ch. 1 - The doping concentrations in a silicon pn junction...Ch. 1 - (a) At what reversebias voltage does the...Ch. 1 - (a) The reversesaturation current of a pn junction...Ch. 1 - (a) The reversesaturation current of a pn junction...Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction diode has an emission...Ch. 1 - Plot log10ID versus VD over the range 0.1VD0.7V...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider a silicon pn junction diode operating...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode has IS=2nA . (a) Determine the...Ch. 1 - The reversebias saturation current for a set of...Ch. 1 - A germanium pn junction has a diode current of...Ch. 1 - (a)The reversesaturation current of a gallium...Ch. 1 - The reversesaturation current of a silicon pn...Ch. 1 - A silicon pn junction diode has an applied...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode is in series with a 1M...Ch. 1 - Consider the diode circuit shown in Figure P1.39....Ch. 1 - The diode in the circuit shown in Figure P1.40 has...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.41PCh. 1 - (a) The reversesaturation current of each diode in...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.40....Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.44....Ch. 1 - The cutin voltage of the diode shown in the...Ch. 1 - Find I and VO in each circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - Repeat Problem 1.47 if the reversesaturation...Ch. 1 - (a) In the circuit Shown in Figure P1.49, find the...Ch. 1 - Assume each diode in the circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - (a) Consider a pn junction diode biased at IDQ=1mA...Ch. 1 - Determine the smallsignal diffusion resistancefor...Ch. 1 - The diode in the circuit shown in Figure P1.53 is...Ch. 1 - The forwardbias currents in a pn junction diode...Ch. 1 - A pn junction diode and a Schottky diode have...Ch. 1 - The reversesaturation currents of a Schottky diode...Ch. 1 - Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - (a) The Zener diode in Figure P1.57 is ideal with...Ch. 1 - Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - The Output current of a pn junction diode used as...Ch. 1 - Using the currentvoltage characteristics of the...Ch. 1 - (a) Using the currentvoltage characteristics of...Ch. 1 - Use a computer simulation to generate the ideal...Ch. 1 - Use a computer simulation to find the diode...Ch. 1 - Design a diode circuit to produce the load line...Ch. 1 - Design a circuit to produce the characteristics...Ch. 1 - Design a circuit to produce the characteristics...Ch. 1 - Design a circuit to produce the characteristics...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- solve by impedancearrow_forwardConsider the circuit diagram below. Compute a single equivalent impedance for this circuit for a source frequency of F = 60 Hz. Express your final answer as a complex impedance with rectangular coordinates. You must show your all your work for the complex math. Include a diagram of the equivalent circuit as part of your solution.arrow_forwardConsider the circuit diagram below. Compute a single equivalent impedance for this circuit for a source frequency of f = 165 Hz. Express your final answer as a phasor with polar coordinates. You must show your all your work for the complex math. Include a diagram of the equivalent circuit as part of your solution.arrow_forward
- Consider the circuit diagram below. Using mesh analysis, compute the currents (a) IR1, (b) IL1, and (c) IC1. Express your final answers as phasors using polar coordinates with phase angles measured in degrees. Your solution should include the circuit diagram redrawn to indicate these currents and their directions. You must solve the system of equations using MATLAB and include the code or commands you ran as part of your solution.arrow_forwarduse kvl to solvearrow_forwardR1 is 978 ohms R2 is 2150 ohms R3 is 4780 R1 is parallel to R2 and R2 is parallel to R3 and R1 and R3 are in seriesarrow_forward
- Q7 For the circuit shown in Fig. 2.20, the transistors are identical and have the following parameters: hfe = 50, hie = 1.1K, hre = 0, and hoe = 0. Calculate Auf, Rif and Rof. Ans: 45.4; 112 KQ; 129. 25 V 10k 47k 4.7k Vo 150k w Vs 47k 4.7k W 22 5μF 33k 50uF 50μF 4.7k 4.7k R₁ Rof Rif R1000 Fig. 2.20 Circuit for Q7.arrow_forwardQ6)) The transistors in the feedback amplifier shown are identical, and their h-parameters are.. hie = 1.1k, hfe = 50, hre=o, and hoe = 0. Calculate Auf, Rif and Rof. {Ans: 6031583; 4. Kor. Is 4 4.7 k www 4.7k 91k 4.7k 91k 10k 1k. 10k 21000 4.7k w 15k Fig. 2.19 Circuit for Q6.arrow_forwardQ5 For the circuit shown in Fig. 2.18, hie =1.1 KQ, hfe =50. Find Avf, Rif and Rof Ans: -3.2; 193 ; 728 N. Vcc Vs Rs=10kQ Re=4KQ RF - = 40ΚΩ www Fig. 2.18 Circuit for Qs.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Diodes Explained - The basics how diodes work working principle pn junction; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fwj_d3uO5g8;License: Standard Youtube License