
Concept explainers
A soccer goal is subjected to gravity loads (in the - z direction, w = 73 N/m for DG, BG, and BC; w = 29 N/m for all other members; see figure) and a force F = 200 N applied eccentrically at the mid-height of member DG. Find reactions at sup ports C, D, and H.
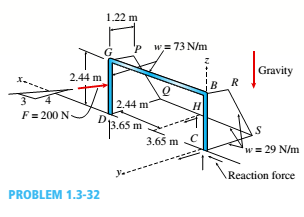
The reactions at support
The reaction at support
The reaction at support
Answer to Problem 1.3.32P
The reactions at support
The reactions at support
The reactions at support
Explanation of Solution
The weight per unit length in the members
The following figure shows the forces on the goal post.
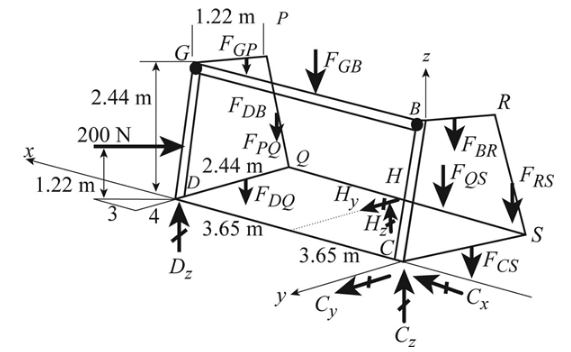
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the length of the members
Here, the length of member
Write the expression for horizontal component of force on member
Here the horizontal component of force is
Write the expression for the vertical component of force on member
Here, the vertical component of force is
Write the expression for moment about x axis.
Here, the force along the member
Write the expression for moment about Y axis.
Here, the length of member
Write the expression for moment about Z axis and equate it to zero.
Here, the reaction of Y axis about
Write the expression for the sum of forces about x axis.
Write the expression for the sum of forces about Y axis.
Write the expression for the sum of forces about Z axis.
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The following figure shows the free body diagram of forces along y and z axes.
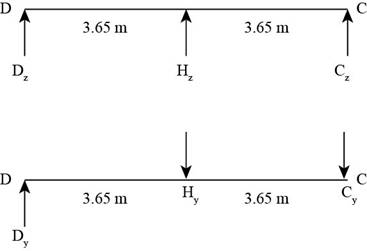
Figure-(2)
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reactions at support
The reactions at support
The reactions at support
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- Find support reactions at A and D and then calculate the axial force N, shear force V, and bending moment M at mid-span of AB. Let L = 14 ft, q0 = 12 lb/ft, P = 50 lb. and = 300 lb-ft.arrow_forwardFind support reactions at 4 and Band then use the method of joints to find all member forces. Let b = 3 m and P = 80 kN.arrow_forward1.3-15 A space truss is restrained at joints A, B, and C, as shown in the figure. Load 2P is applied at in the -x direction at joint A, load 3P acts in the + - direction at joint B. and load P is applied in the + r direction al joint C. Coordinates of all joints are given in terms of dimension variable L (see figure). (a) Find reaction force components Ayand Azin terms of load variable P. (b) Find the axial force in truss member AB in terms of load variable P.arrow_forward
- A plane Frame is restrained at joints A and D, as shown in the figure. Members AB and BCD are pin connected at B. A triangularly distributed lateral load with peak intensity of SO N/m acts on CD. An inclined concentrated force of 200 N acts at the mid-span of BC. (a) Find reactions at supports A and D. (b) Find resultant forces in the pins at B and C.arrow_forwardA space truss is restrained at joints O, A. B. and C, as shown in the figure. Load P is applied at joint A and load IP acts downward at joint C. (a) Find reaction force components Ax, By, and B. in terms of load variable P. (b) Find the axial force in truss member AB in terms of load variable P.arrow_forwardA space truss has three-dimensional pin supports at joints 0, B, and C, Load P is applied at joint A and acts toward point Q. Coordinates of all joints arc given in feet (see figure). (a) Find reaction force components B x, B z, and Oz (b) Find the axial force in truss member AC.arrow_forward
- A plane frame is restrained al joints A and C, as shown in the figure. Members AB and BC are pin connected at B. A triangularly distributed lateral load with a peak intensity or 90 lb/ft acts on AB. A concentrated moment is applied at joint C. (a) Find reactions at supports A and C. (b) Find internal stress resultants A', V, and \f at x = 3 ft on column AB.arrow_forwardA 150-lb rigid bar AB. with friction less rollers al each end. is held in the position shown in the figure by a continuous cable CAD. The cable is pinned at C and D and runs over a pulley at A. (a) Find reactions at supports A and B. (b) Find the force in the cable.arrow_forwardConsider the plane truss with a pin support at joint 3 and a crtica1 roller support at joint 5 (see figure). (a) Find reactions at support joints 3 and 5. (b) Find axial forces in truss members 11 and 13.arrow_forward
- Space frame A BCD is clamped at A, except it is Free to translate in the .v direction. There is also a roller support at D, which is normal to line CDE. A triangularly distributed Force with peak intensity q0 = 75 N/m acts along AB in the positive - direction. Forces Px= 60 N and Pz = = 45 N are applied at joint C, and a concentrated moment My = 120 N . m acts at the mid-span of member BC. (a) Find reactions at supports A and I). (b) Find internal stress resultants N. E’I T, and .11 at the mid-height of segment AB.arrow_forwardA long, slender bar in the shape of a right circular cone with length L and base diameter d hangs vertically under the action of its own weight (see figure). The weight of the cone is W and the modulus of elasticity of the material is E. Derive a formula for the increase S in the length of the bar due to its own weight. (Assume that the angle of taper of the cone is small.)arrow_forward,3-23 A 200-lb trap door (AD) is supported by a strut (BC) which is pin connected to the door at B (see figure). (a) Find reactions at supports A and C. (b) Find internal stress resultants N, V, and M on the trap door at 20 in. from A.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
