
Concept explainers
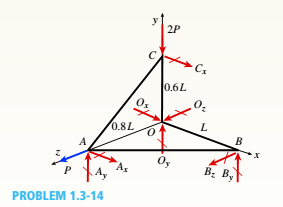
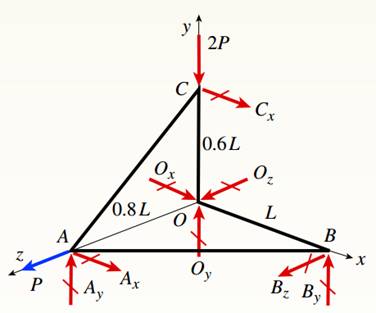
A space truss is restrained at joints O, A. B. and C, as shown in the figure. Load P is applied at joint A and load IP acts downward at joint C.
(a) Find reaction force components Ax, By, and B. in terms of load variable P.
(b) Find the axial force in truss member AB in terms of load variable P.
(a)
You need to determine the force components
Answer to Problem 1.3.14P
The correct answers are:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
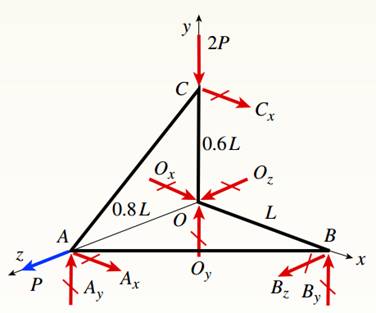
You have following figure with all relevant information,
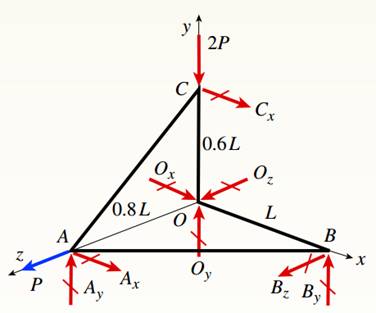
Draw free body diagram of joints and use equilibrium of forces to determine the unknowns.
Calculation:
Draw free body diagram as shown in the following figure,
Joint C :
The forces at joint C are,
Take equilibrium of forces at joint C in vector form,
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below,
Solve the three equations to get
Joint A :
The forces at joint A are,
Take equilibrium of forces at joint A in vector form,
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below,
Solve the three equations to get
Joint B :
The forces at joint B are,
Take equilibrium of forces at joint B in vector form,
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below,
Solve the three equations to get
Conclusion:
Thus the forces are:
(b)
You need to determine the member force
Answer to Problem 1.3.14P
The correct answers are:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
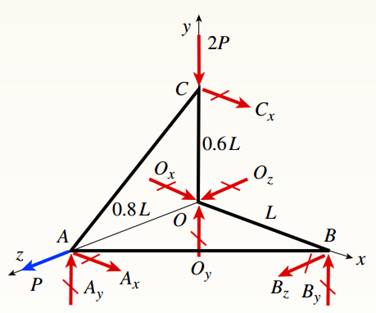
You have following figure with all relevant information,
Draw free body diagram of joints and use equilibrium of forces to determine the unknowns.
Calculation:
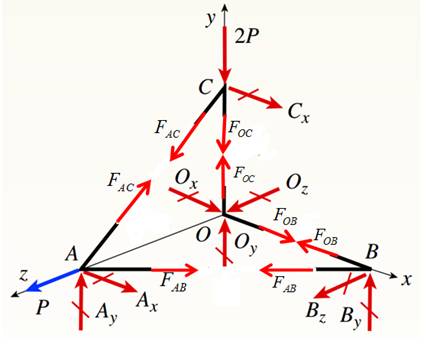
Draw free body diagram as shown in the following figure,
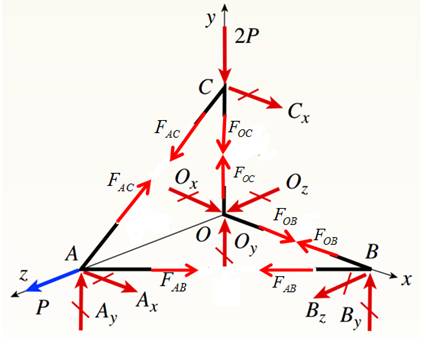
Joint C :
The forces at joint C are,
Take equilibrium of forces at joint C in vector form,
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below,
Solve the three equations to get
Joint A :
The forces at joint A are,
Take equilibrium of forces at joint A in vector form,
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below,
Solve the three equations to get
Conclusion:
Thus the forces are:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- My ID#016948724 please solve this problems and show me every step clear to follow pleasearrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forward
- can you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forwardhi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
