
(a)
Interpretation: The formula of an ionic compound formed when potassium reacts with iodine needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Electron dot structures of an element represent the number of electron/s present in its valance electron shell. In the electron dot structure, a symbol of an atom of an element is written and the number of valance electrons is arranged in pairs represented as dots around the symbol.
For example, the number of valance electrons in a bromine atom is 7; thus, its electron dot structure is represented as follows:
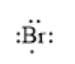
(a)
Answer to Problem 10SP
Explanation of Solution
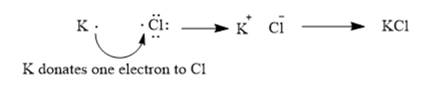
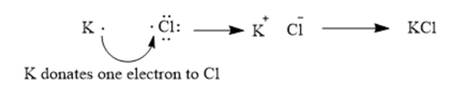
The given elements are potassium and iodine. Here, potassium is metal and belongs to group 1. It has 1 valance electron which can be easily donated to form potassium cation. Similarly, iodine belongs to group 17. It has 7 valence electrons. It requires 1 electron to complete its octet. It can easily gain one electron from potassium to form a chloride ion. The ionic compound so formed will be potassium chloride or KCl.
This can be explained using electron dot structures as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The formula forthe ionic compound formed when aluminum reacts with oxygen needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:The electron dot structure of an element represents the number of electron/s present in its valance electron shell. In the electron dot structure, a symbol of an atom of an element is written and the number of valance electrons is arranged in pairs represented as dots around the symbol.
For example, the number of valance electrons in a bromine atom is 7; thus, its electron dot structure is represented as follows:
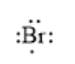
(b)
Answer to Problem 10SP
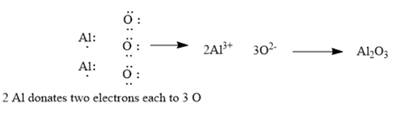
Explanation of Solution
The given elements are aluminum and oxygen. Here, aluminum is a metal and belongs to group 13. It has 3 valance electrons which can be easily donated to form an aluminumcation. Similarly, oxygen belongs to group 16. It has 6 valence electrons. It requires 2 electrons to complete its octet and form oxide. The ionic compound so formed will be aluminum oxide. Since ionic compounds are electrically neutral; thus, 2 Al ions combine with 3 O ions to form y1
This can be explained using electron dot structures as follows:
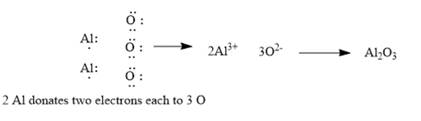
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- Using iodometry I want to titrate a sodium thiosulfate solution and I use 15 mL. If I have 50 mL of a 0.90 M copper solution and KI, what will be the molarity of sodium thiosulfate?arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when the following pair of compounds is treated with NaOEt in ethanol. + i CNarrow_forwardI need help with the followingarrow_forward
- I need help with the followingarrow_forwardFor Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





