
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron configuration of elements with two unpaired electrons and with an
Concept Introduction:
The electronic configuration is defined as the distribution of electrons in various atomic orbitals of the atom. The electrons that are present in an outermost orbital are known as valence electrons whereas those present in the orbitals with lower quantum numbers are called core electrons. The general outer electronic configuration of
Electrons are filled in orbitals in accordance with three rules: Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Aufbau principle states that electrons are filled in the orbitals from lower to higher energy level as follows:
Hund’s rule states that initially each orbital is singly occupied and then pairing occurs and Pauli’s exclusion principle states that the spin of two electrons in one orbital is always different.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
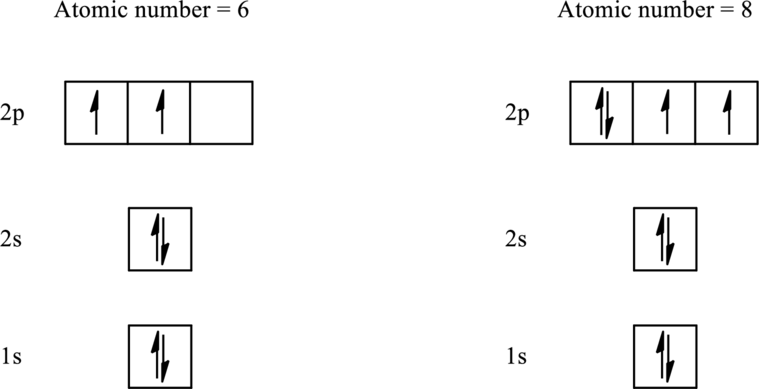
The electronic configuration for elements with an atomic number less than 10 is as follows:
According to Hund’s rule, initially each orbital is singly occupied and then pairing occurs in the filling of an electron in same subshell.
Therefore, the two unpaired electrons are present in
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron configuration of element with the largest number of unpaired electrons and with an atomic number less than 10 has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
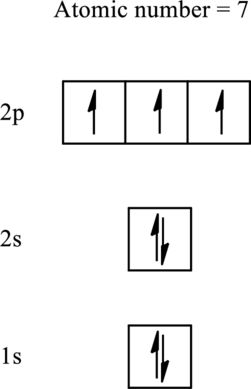
The electronic configuration for elements with an atomic number less than 10 is as follows:
According to Hund’s rule, initially each orbital is singly occupied and then pairing occurs in the filling of an electron in same subshell.
Therefore, the most unpaired electrons are contained by an element that has atomic number 7. The number of unpaired electrons is 3 and it is represented as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron configuration for those elements that have only two occupied subshells with an atomic number less than 10 has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration for elements with an atomic number less than 10 is as follows:
The elements that have occupied only two subshells are the elements with atomic number 3and 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward9arrow_forwardalekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward
- 0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forwardS: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





