
a)
To determine: The standard time for the operation.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
a)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
Formula:
Calculation of standard time of operation:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | Observed time | Normal time | Afjob | Standard time | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 | 1.198 | 1.317 | 1.15 | 1.52 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.83 | 0.954 | 1.15 | 1.10 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 | 0.564 | 0.592 | 1.15 | 0.68 |
| Standard time for operation | 3.29 | |||||||||||
Excel Worksheet:
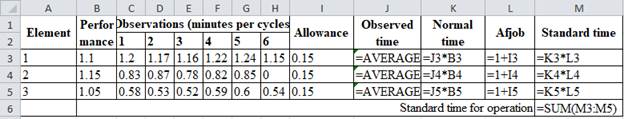
Element 1:
Observed time is calculated by taking mean for the 1.2, 1.17, 1.16, 1.22, 1.24 and 1.15 which gives 1.198.
Normal time is calculated by multiplying observed timing, 1.198 and performance rating, 1.1 which yields 1.317 minutes.
Allowance factor is calculated by adding 1 with the allowance factor 0.15 to give 1.15.
Standard time for element 1 is calculated by multiplying normal time of 1.317 minutes with allowance factor of 1.15 which gives 1.52 minutes.
Same process applies for element 2 and 3 which yields the standard times as 1.10 and 0.68. The standard time for operation is obtained by adding 1.52, 1.10 and 1.68 minutes which gives 3.29 minutes.
Hence, the standard time for the operation is 3.29 minutes.
b)
To determine: The number of observations for element 2.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
b)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
Confidence= 95.5%
1% of true value
Formula:
Calculation of number of observations for element A:
In the above formula the sample standard deviation is calculated by,
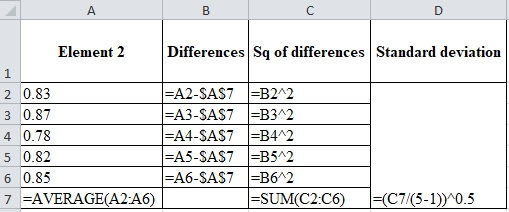
Calculation of standard deviation:
| Element 2 | Differences | Square of differences | Standard deviation |
| 0.83 | 0 | 0 | 0.0339 |
| 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.0016 | |
| 0.78 | -0.05 | 0.0025 | |
| 0.82 | -0.01 | 0.0001 | |
| 0.85 | 0.02 | 0.0004 | |
| Mean=0.83 | SSQ=0.0046 |
Excel worksheet:
Z value for confidence interval of 95.5% is 2.00.
The confidence interval
- Using z = 2.00:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5% is calculated by dividing the product of 2.00 and 0.0339 with product of 0.01 and 0.83 and squaring the resultant which gives 66.7272.
- Using z = 2.01:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5% is calculated by dividing the product of 2.01 and 0.0339 with product of 0.01 and 0.83 and squaring the resultant which gives 67.3962.
Hence, the number of observation is 68.
c)
To determine: The number of observations needed to estimate the mean time for element 2 within 0.01 minute of its true value.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
c)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.15 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
Confidence= 95.5%
0.10 minute of actual value.
Formula:
Calculation of number of observations for element C:
In the above formula the sample standard deviation is calculated by,
Z value for confidence interval of 95.5% is 2.00.
The confidence interval
- Using z = 2.00:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5 is calculated by dividing the product of 2.00 and 0.0339 with 0.01 and squaring the resultant which gives 45.9684.
- Using z = 2.00:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 95.5 is calculated by dividing the product of 2.01 and 0.0339 with 0.01 and squaring the resultant which gives 46.4292.
Hence, the number of observations needed to estimate the mean time for element 2 within 0.01 minute of its true value is 46.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Loose-leaf for Operations Management (The Mcgraw-hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- The binding constraints for this problem are the second and third constraints are binding. Min x1 + 2x2 s.t. x1 + x2 ≤ 300 2x1 + x2 ≥ 400 2x1 + 5x2 ≥750 X1, X220 (a) Keeping the second objective function coefficient fixed at 2, over what range can the first objective function coefficient vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point? The first objective coefficient can from a low of to a high of (b) Keeping the first objective function coefficient fixed at 1, over what range can the second objective function coefficient vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point? The second objective coefficient can from a low of to a high of (c) If the objective function becomes Min 1.5x₁ + 2x2, what will be the optimal values of x1 and x2? x1 = X2 = What is the value of the objective function at the minimum? (d) If the objective function becomes Min 7x₁ + 6x2, what constraints will be binding? (Select all that apply.) First Constraint Second Constraint Third Constraint…arrow_forward[-16.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES CAMMIMS16 4.E.008. 0/1 Submissions Used A linear programming computer package is needed. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER The Clark County Sheriff's Department schedules police officers for 8-hour shifts. The beginning times for the shifts are 8:00 a.m., noon, 4:00 p.m., 8:00 p.m., midnight, and 4:00 a.m. An officer beginning a shift at one of these times works for the next 8 hours. During normal weekday operations, the number of officers needed varies depending on the time of day. The department staffing guidelines require the following minimum number of officers on duty: Time of Day 8:00 A.M. Noon Noon - 4:00 P.M. Minimum Officers Time of Day on Duty 4 7 4:00 P.M. - 8:00 P.M. 11 8:00 P.M. Midnight 6 Midnight 4:00 A.M. 4:00 A.M. -8:00 A.M. 3 7 Determine the number of police officers that should be scheduled to begin the 8-hour shifts at each of the six times (8:00 a.m., noon, 4:00 p.m., 8:00 p.m., midnight, and 4:00 a.m.) to minimize the total number…arrow_forwarddiscuss in detail the benefits of working in a teamarrow_forward
- Learning Activity 6: Canadian Business This Year Read the following webpage: The Business Development Bank of Canada. (2023). Canadian economic outlook for 2024: Shifting into neutral. https://www.bdc.ca/en/articles- tools/blog/canadian-economic-outlook-for-2024- shifting-into-neutral "Despite persistently high inflation and rising. interest rates, the news was generally better than expected for the Canadian economy in 2023" (BDC Blog 2024). Discussion Question: In your view, what are the most pressing problems for Canadian companies or consumers in 2024? Explain your answer using current examples of companies or consumer concerns.arrow_forwardTravelling and working internationally can lead to a life of adventure and unique career experiences. For businesses, selecting the right candidates to take on foreign assignments can propel, delay, or deny the success of the international ventures. As an international manager, identify key competencies you would look for in choosing expatriates. What might be some of their concerns in taking on overseas assignments? What are some best practices in supporting expats during and after their assignments?arrow_forwardResearch proposal: The Investigation of Career Development and Job satisfaction atEskom Rotek Industries 1. Introduction (250 words) 2. Research Context: Background (Research Context: Background (250 words) 3. The Research Problem (The Research Problem) 4. Aim of the study (Maximum 50 words) 5. Research Objectives (3 in total) 6. Research Questions (3 in total) 7. Justification or rationale of the study (150 words) 8. Literature Review (2-3 pages / 1000-1500 words) 9. Research Design and Methodology (1 - 2 page in total, from 9.1 to 9.6) 9.1 Research Philosophy 9.2 Research Methodology 9.3 Target Population and Sampling strategy 9.4 Data Collection 9.5 Data Analysis (100 words) 9.6 Pilot Study 10. Ethical considerations 11. Referencearrow_forward
- With your experience and research, discuss;(a) what type of “Leadership Style” is used in communications services (Digicel Group Limited)?(b) whether the style used is successful or not and why. Justify your position with relevant citation and references ( Rubic is attached to guide the essay ) NOTE: NO AI RESPONSES PLEASEarrow_forwardby the end of 2013, the IPL port was operational and the naphtha was flowing to the Himachal Fertilizer Corporation (HFC) plant in Central India after being granted the port contract in Summer 2012. The plant was located in an industrial area that had several pipelines in the general geographic area including a crude oil pipeline leading to a refinery, and a pipeline carrying pesticides to be processed and redistributed to local farms in the area. In July 2014, Ajay Patel, the logistics general manager received notification that there were some minor leaks along the pipeline that were being fixed. Workers in the area had experienced sudden headaches and lightheadedness and the company immediately moved to investigate the leak and address faulty seams that had eroded and weakened. The flow of naphtha was temporarily stopped for 72 hours so two portions of the pipeline could be removed, and the eroded portions replaced. Patel put enormous pressure on the repair team to get the repair…arrow_forwardin the MABE: learning to be multinational case report, what is the reccomended course of action?arrow_forward
 Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,



