
Concept explainers
For each pair of ions, determine which will have the greater number of unpaired electrons: (a) Fe2+, Fe3+; (b) P3+, P5+: (c) Cr2+, Cr3+.
(a)
Interpretation: Ground-state electronic configuration of the given set of ions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
- Aufbau Principle tells that the orbital with the lower energy is filled with electrons first and then the filling of higher energy orbital follows. By using this valence orbital diagram can be drawn for any atoms or ions.
- Electronic configuration is the arrangement of the electrons of atoms in the orbital. For atoms and ions, the electronic configuration is written by using Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule.
- According to Pauli Exclusion Principle, no two electrons having the same spin can occupy the same orbital.
- According to Hund’s rule, the orbital in the subshell is filled singly by one electron before the same orbital is doubly filled. When the orbital is singly filled, all the electrons have same spin. In a doubly filled orbital, there are two electrons with opposite spin.
To identify: The ion which has greater number of unpaired electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.78QP
Answer
In (a)
Explanation of Solution
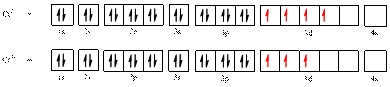
Electronic configuration of
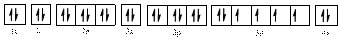
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
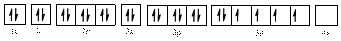
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
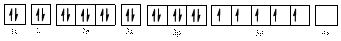
The electronic configuration of
Comparing the unpaired electrons in
By looking at the valence-orbital diagram we can see that in
(b)
Interpretation: Ground-state electronic configuration of the given set of ions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
- Aufbau Principle tells that the orbital with the lower energy is filled with electrons first and then the filling of higher energy orbital follows. By using this valence orbital diagram can be drawn for any atoms or ions.
- Electronic configuration is the arrangement of the electrons of atoms in the orbital. For atoms and ions, the electronic configuration is written by using Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule.
- According to Pauli Exclusion Principle, no two electrons having the same spin can occupy the same orbital.
- According to Hund’s rule, the orbital in the subshell is filled singly by one electron before the same orbital is doubly filled. When the orbital is singly filled, all the electrons have same spin. In a doubly filled orbital, there are two electrons with opposite spin.
To identify: The ion which has greater number of unpaired electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.78QP
Answer
In (b)
Explanation of Solution
Electronic configuration of
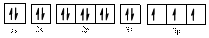
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
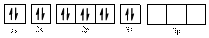
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
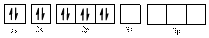
The electronic configuration of
Comparing the unpaired electrons in
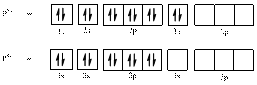
By looking at the valence-orbital diagram we can see that both electrons in
(c)
Interpretation: Ground-state electronic configuration of the given set of ions has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
- Aufbau Principle tells that the orbital with the lower energy is filled with electrons first and then the filling of higher energy orbital follows. By using this valence orbital diagram can be drawn for any atoms or ions.
- Electronic configuration is the arrangement of the electrons of atoms in the orbital. For atoms and ions, the electronic configuration is written by using Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule.
- According to Pauli Exclusion Principle, no two electrons having the same spin can occupy the same orbital.
- According to Hund’s rule, the orbital in the subshell is filled singly by one electron before the same orbital is doubly filled. When the orbital is singly filled, all the electrons have same spin. In a doubly filled orbital, there are two electrons with opposite spin.
To identify: The ion which has greater number of unpaired electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.78QP
Answer
In (c)
Explanation of Solution
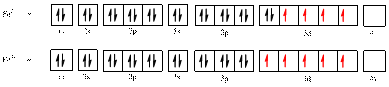
Electronic configuration of
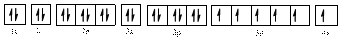
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
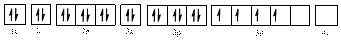
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
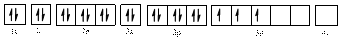
The electronic configuration of
Comparing the unpaired electrons in
By looking at the valence-orbital diagram we can see that in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- Why are normal electrode potentials also called relative electrode potentials?arrow_forwardEasily differentiate between electrochemical potential and Galvani potential.arrow_forwardConstruct a molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Identify the relevant point group,include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Make sure toaccount for the difference in electronegativity between C and O. Hint: CO is substantiallyisoelectronic to N2. (PLEASE DRAW THE ENTIRE MO DIAGRAM!!!)arrow_forward
 Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



