
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Provide the formula of potassium hydroxide.
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
(b)
Interpretation:
Provide the name of 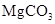
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
Interpretation:
Provide the formula of iron (III) cyanide.
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
(d)
Interpretation:
Provide the formula of iron (II) oxalate
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
(e)
Interpretation:
Provide the name of
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
Interpretation:
Provide the name of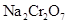
Concept introduction:
An ion is a group of atoms and atoms where the number of the proton is different from the number of electrons. A positive ion or a cation is known as where the proton’s numbers are greater than the electrons. A negative ion or anion is known as where a number of electrons are more than the number of protons.
When an atom donates an electron, it has a positive charge and when an atom accepts the negative charge then it has a negative charge.
Binary ionic compounds comprise two elements only in which one is cation and another is an anion. It is vital to know that while writing the name of a binary ionic compound always cation comes first.
Polyatomic ions are the ions which contain more than one atom. Like NO3- contain one nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. In the polyatomic ions, the atoms are generally bonded covalently to each other and thus stay together as a one charged unit.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY FOR CHANGING TIMES
- Calculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbonsarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseeearrow_forward
- Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward
- III O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forward
- What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. Br Br₂, light D Br Br Br Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





