
(a)
Interpretation:
The shape of silane (SiH4) should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of molecule depends upon the number of bonded pair of electron and lone pair of electron on central atom
- If there are two bonded groups the shape will be linear (AX)
- If there are three bonded groups the shape will be trigonal planar, with zero lone pair of electrons (AX2). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be V (AXE).
- If there are four bonded groups the shape will be tetrahedral, with no lone pair of electrons (AX4). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be trigonal pyramidal (AX3E). And if two lone pair of electrons the shape will be bent (AX2E2).
(b)
Interpretation:
The shape of hydrogen selenide (H2Se) should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of molecule depends upon the number of bonded pair of electron and lone pair of electron on central atom
- If there are two bonded groups the shape will be linear (AX)
- If there are three bonded groups the shape will be trigonal planar, with zero lone pair of electrons (AX2). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be V (AXE).
- If there are four bonded groups the shape will be tetrahedral, with no lone pair of electrons (AX4). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be trigonal pyramidal (AX3E). And if two lone pair of electrons the shape will be bent (AX2E2).
(c)
Interpretation:
The shape of phosphine 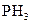 should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of molecule depends upon the number of bonded pair of electron and lone pair of electron on central atom
- If there are two bonded groups the shape will be linear (AX)
- If there are three bonded groups the shape will be trigonal planar, with zero lone pair of electrons (AX2). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be V (AXE).
- If there are four bonded groups the shape will be tetrahedral, with no lone pair of electrons (AX4). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be trigonal pyramidal (AX3E). And if two lone pair of electrons the shape will be bent (AX2E2).
Interpretation:
The shape of silicon tetrafluoride (SiF4) should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of molecule depends upon the number of bonded pair of electron and lone pair of electron on central atom
- If there are two bonded groups the shape will be linear (AX)
- If there are three bonded groups the shape will be trigonal planar, with zero lone pair of electrons (AX2). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be V (AXE).
- If there are four bonded groups the shape will be tetrahedral, with no lone pair of electrons (AX4). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be trigonal pyramidal (AX3E). And if two lone pair of electrons the shape will be bent (AX2E2).
(e)
Interpretation:
The shape of oxygen diflouride (OF2) should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of molecule depends upon the number of bonded pair of electron and lone pair of electron on central atom
- If there are two bonded groups the shape will be linear (AX)
- If there are three bonded groups the shape will be trigonal planar, with zero lone pair of electrons (AX2). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be V (AXE).
- If there are four bonded groups the shape will be tetrahedral, with no lone pair of electrons (AX4). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be trigonal pyramidal (AX3E). And if two lone pair of electrons the shape will be bent (AX2E2).
(f)
Interpretation:
The shape of formaldehyde (H2CO) should be identified on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of molecule depends upon the number of bonded pair of electron and lone pair of electron on central atom
- If there are two bonded groups the shape will be linear (AX)
- If there are three bonded groups the shape will be trigonal planar, with zero lone pair of electrons (AX2). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be V (AXE).
- If there are four bonded groups the shape will be tetrahedral, with no lone pair of electrons (AX4). If there is one lone pair of electrons the shape will be trigonal pyramidal (AX3E). And if two lone pair of electrons the shape will be bent (AX2E2).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY FOR CHANGING TIMES
- Match the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forwardCan you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward
- 2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forwardconsider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





