
EBK CHEMISTRY FOR CHANGING TIMES
14th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663482
Author: MCCREARY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 4, Problem 54P
(a)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The bonds in 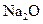 should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
Concept Introduction:
- Valence electron: The electrons which are present in the outer most energy level are known as valence electron. This can be calculated by the group number of the element. Generally, the group number is same as the valence electrons of any elements.
- Octet rule: Generally, all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electron configuration of the nearest noble element.
- The covalent bond is a type of bond which formed by sharing of electrons between atoms. It forms between two non-metals.
- The ionic bond is a type of bond which formed between positive and negative ions or one metal and one non-metal.
(b)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The bond in 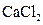 should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
Concept Introduction:
- Valence electron: The electrons which are present in the outer most energy level are known as valence electron. This can be calculated by the group number of the element. Generally, the group number is same as the valence electrons of any elements.
- Octet rule: Generally, all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electron configuration of the nearest noble element.
- The covalent bond is a type of bond which formed by sharing of electrons between atoms. It forms between two non-metals.
- The ionic bond is a type of bond which formed between positive and negative ions or one metal and one non-metal.
(c)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The bonds in 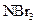 should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
Concept Introduction:
- Valence electron: The electrons which are present in the outer most energy level are known as valence electron. This can be calculated by the group number of the element. Generally, the group number is same as the valence electrons of any elements.
- Octet rule: Generally, all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electron configuration of the nearest noble element.
- The covalent bond is a type of bond which formed by sharing of electrons between atoms. It forms between two non-metals.
- The ionic bond is a type of bond which formed between positive and negative ions or one metal and one non-metal.
(d)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The bonds in 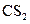 should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
should be classified as ionic, polar covalent or non-polar covalent.
Concept Introduction:
- Valence electron: The electrons which are present in the outer most energy level are known as valence electron. This can be calculated by the group number of the element. Generally, the group number is same as the valence electrons of any elements.
- Octet rule: Generally, all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electron configuration of the nearest noble element.
- The covalent bond is a type of bond which formed by sharing of electrons between atoms. It forms between two non-metals.
- The ionic bond is a type of bond which formed between positive and negative ions or one metal and one non-metal.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule?
Br
Br
Write the answer below.
Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H
atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red.
Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal.
Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum.
For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to
the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red.
If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right.
No additional Hs to color in top
molecule
For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will
contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red.
If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right.
No additional Hs to color in bottom
molecule
In the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction:
1. NaOH
?
2. CH3Br
If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area
instead.
No reaction.
Click and drag to start drawing a
structure.
☐ : A
ค
Predict the major products of the following organic reaction:
NC
Δ
?
Some important Notes:
• Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below.
• If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead.
• Be sure to draw bonds carefully to show important geometric relationships between substituents.
Note: if your answer contains a complicated ring structure, you must use one of the molecular fragment stamps (available in the menu at right) to enter the
ring structure. You can add any substituents using the pencil tool in the usual way.
Click and drag to start drawing a
structure.
Х
а
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY FOR CHANGING TIMES
Ch. 4 - Prob. 1RQCh. 4 - Prob. 2RQCh. 4 - What are the structural differences among chlorine...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4RQCh. 4 - What are the charges on simple ions formed from...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6RQCh. 4 - In what group of the periodic table would elements...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8RQCh. 4 - Prob. 9RQCh. 4 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 4 - 11. Write Lewis symbols for each of the following...Ch. 4 - Write the Lewis symbol for each species in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 13PCh. 4 - Prob. 14PCh. 4 - Prob. 15PCh. 4 - Prob. 16PCh. 4 - Prob. 17PCh. 4 - Prob. 18PCh. 4 - Prob. 19PCh. 4 - Prob. 20PCh. 4 - Prob. 21PCh. 4 - Prob. 22PCh. 4 - Prob. 23PCh. 4 - Prob. 24PCh. 4 - There are two common binary ionic compounds formed...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26PCh. 4 - Prob. 27PCh. 4 - Prob. 28PCh. 4 - Prob. 29PCh. 4 - Prob. 30PCh. 4 - Prob. 31PCh. 4 - Prob. 32PCh. 4 - Use Lewis dot symbols to show the sharing of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 34PCh. 4 - Prob. 35PCh. 4 - Prob. 36PCh. 4 - Prob. 37PCh. 4 - Prob. 38PCh. 4 - 39. Supply a formula for the name or a name for...Ch. 4 - Prob. 40PCh. 4 - Prob. 41PCh. 4 - Prob. 42PCh. 4 - Prob. 43PCh. 4 - Prob. 44PCh. 4 - Prob. 45PCh. 4 - Prob. 46PCh. 4 - Prob. 47PCh. 4 - Prob. 48PCh. 4 - Prob. 49PCh. 4 - Prob. 50PCh. 4 - Prob. 51PCh. 4 - Prob. 52PCh. 4 - Classify the bonds in the following as ionic or...Ch. 4 - Prob. 54PCh. 4 - Prob. 55PCh. 4 - Prob. 56PCh. 4 - Prob. 57PCh. 4 - Prob. 58PCh. 4 - Prob. 59PCh. 4 - Prob. 60PCh. 4 - Prob. 61PCh. 4 - Prob. 62PCh. 4 - Prob. 63PCh. 4 - Prob. 64PCh. 4 - Prob. 65PCh. 4 - Prob. 66PCh. 4 - Prob. 67PCh. 4 - Prob. 68PCh. 4 - Prob. 69PCh. 4 - Prob. 70PCh. 4 - Prob. 71PCh. 4 - Prob. 72APCh. 4 - Prob. 73APCh. 4 - Prob. 74APCh. 4 - Prob. 75APCh. 4 - Prob. 76APCh. 4 - Prob. 77APCh. 4 - Prob. 78APCh. 4 - Prob. 79APCh. 4 - Prob. 80APCh. 4 - Prob. 81APCh. 4 - Prob. 82APCh. 4 - Prob. 83APCh. 4 - Prob. 84APCh. 4 - Prob. 85APCh. 4 - Prob. 86APCh. 4 - Prob. 87APCh. 4 - Prob. 88APCh. 4 - Prob. 89APCh. 4 - Prob. 90APCh. 4 - Prob. 91APCh. 4 - Prob. 92APCh. 4 - Prob. 93APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.1CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.2CTECh. 4 - 4.3 Sodium chloride (NaCI) is a metal-nonmetal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.4CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.5CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.6CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.7CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.8CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.9CTECh. 4 - Prob. 4.10CTECh. 4 - Prob. 1CGPCh. 4 - Prob. 2CGPCh. 4 - Prepare a PowerPoint, poster, or other...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4CGPCh. 4 - Prob. 5CGPCh. 4 - Prob. 1CHQCh. 4 - Prob. 2CHQCh. 4 - Prob. 3CHQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use dash and wedge bonds to show stereochemistry where it's important. + ☑ OH 1. TsCl, py .... 文 P 2. t-BuO K Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ( Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : а ค 1arrow_forwardIn the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. 1. NaH 2. CH3Br ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. No reaction. : ☐ Narrow_forward
- + Predict the major product of the following reaction. : ☐ + ☑ ค OH H₂SO4 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ... OH CI Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ☐ No Reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : аarrow_forwardConsider the following reactants: Br Would elimination take place at a significant rate between these reactants? Note for advanced students: by significant, we mean that the rate of elimination would be greater than the rate of competing substitution reactions. yes O no If you said elimination would take place, draw the major products in the upper drawing area. If you said elimination would take place, also draw the complete mechanism for one of the major products in the lower drawing area. If there is more than one major product, you may draw the mechanism that leads to any of them. Major Products:arrow_forward
- Draw one product of an elimination reaction between the molecules below. Note: There may be several correct answers. You only need to draw one of them. You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction. OH + ! : ☐ + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFind one pertinent analytical procedure for each of following questions relating to food safety analysis. Question 1: The presence of lead, mercury and cadmium in canned tuna Question 2: Correct use of food labellingarrow_forwardFormulate TWO key questions that are are specifically in relation to food safety. In addition to this, convert these questions into a requirement for chemical analysis.arrow_forward
- What are the retrosynthesis and forward synthesis of these reactions?arrow_forwardWhich of the given reactions would form meso product? H₂O, H2SO4 III m CH3 CH₂ONa CH3OH || H₂O, H2SO4 CH3 1. LiAlH4, THF 2. H₂O CH3 IVarrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O IV III HCI D = III ა IVarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Calorimetry Concept, Examples and Thermochemistry | How to Pass Chemistry; Author: Melissa Maribel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSh29lUGj00;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY