
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation: Conjugate base for each below acid should be determined. Also, rank of conjugate bases from strongest to weakest P.E. should be determined.
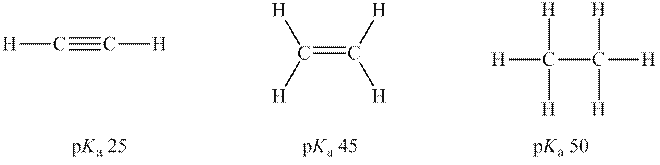
Concept introduction: According to the Bronsted-Lowry concept, a substance that donates proton is termed as acid while that accepts or gains protons is called a base. Species formed after loss of protons from acids are known as their respective conjugate bases whereas conjugate acid is produced by the addition of protons to base. The strength of conjugate acids and conjugate bases are inversely related to strengths of their respective bases and acids.
According to Lewis's concept, a substance that donates electron pair is termed as a base while that accepts or gains electron pair is called acid. For example,
According to the Arrhenius concept, substances that donate hydrogen ions in solutions are known as acids while bases are substances that release hydroxide ions in solutions.
b)
Interpretation: Type of orbital that has a lone pair of electrons in the below conjugate base should be drawn.
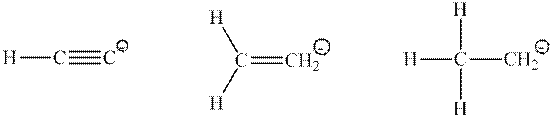
Concept introduction: Hybridization is processed to intermix atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals. It can be determined by the calculation of the number of hybrid orbitals
Type of hybridization that corresponds to the different number of hybrid orbitals is described in the following table:
c)
Interpretation: Percent
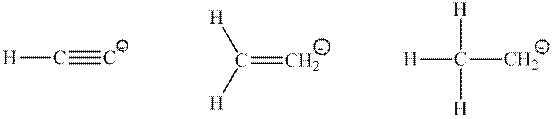
Concept introduction: Hybridization is processed to intermix atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals. It can be determined by the calculation of the number of hybrid orbitals
Type of hybridization that corresponds to a different number of hybrid orbitals is described in the following table:
d)
Interpretation: Whether
Concept introduction: Orbitals are defined as regions around atomic nucleus where electrons are found. Atomic orbitals help to form covalent bonds. Atomic orbitals can be
e)
Interpretation: Reason for pattern in
Concept introduction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
