
Concept explainers
(a) To Explain:
That Light rays from stars (including our sun)always bend towards the vertical direction as they pass through the Earth’s atmosphere
Answer to Problem 19Q
Solution:
When light rays from stars (including our sun)enter from vacuum (lower refractive index medium)to our atmosphere (higher refractive index medium), then
Explanation of Solution
The light rays, coming from the stars and sun travelling through the vacuum and enter the Earth atmosphere. The refractive index of the vacuum is lower than the refractive index of the Earth Atmosphere.
From the Snell’s law
The velocity of the light is slower and hence the refractive index of the medium is high, as given by the equation
Where
Also from the equation,
Where
At the boundary of the Earth atmosphere, as the light rays enter the Earth atmosphere of high refractive index, the angle of refraction is low and so the rays are bent toward the normal and the refracted rays are only observed by the observers at Earth.
(b) To determine:
The apparent positions of stars as viewed from Earth if Light rays from stars (including our sun)always bend toward the vertical direction as they pass through the Earth’s atmosphere
Answer to Problem 19Q
Solution:
When light rays enter from vacuum (lower refractive index medium)to our atmosphere (higher refractive index medium), as per Snell's law the light rays are bent towards the vertical direction.
As the observers sitting on Earth can see the refracted light rays, they interpret that they are seeing the image of the Sun and the stars appear to come from the apparent position as depicted by the figure.
As light rays come from very far away distance and the distances of the objects are too high, the apparent position of the Sun and stars cannot be practically predicted.
Explanation of Solution
The Sun and the stars that are viewed by the observers on Earth are the apparent position of the Sun and the stars. Because, the observer can see the refracted light rays from the Sun and the Star
As the light rays are come from the vacuum and enters the air atmosphere and it undergo refraction at the boundary of the earth atmosphere.
These refracted rays are viewed by the earth observer and hence they are viewing the image of the Sun and the stars, which are the apparent position.
The situation is depicted by the figure below.
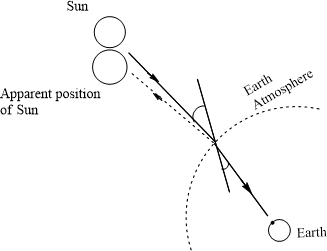
But, the apparent location of the Sun and star, cannot determined as the object are situated at very far distance, the observe cannot predict that the position of the Sun and the star, whether it is above or below or sideways of the real objects, that the position with respect to the real object is beyond the knowledge of the observer.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Formant Freqmcy The horizontal dotted lines represent the formants. The first box represents the schwa sound. The second box is a different vowel. The scale is the same on each of these two vowels. Use the two formant contours to answer questions 12-16 SCHWA VOWEL 2 0.179362213 Time (s) 0.92125285 0.0299637119 4000 1079 Time(s) unknown 0.6843 13. Please describe what the tongue is doing to shift from the schwa to vowel 2? 14. Is vowel 2 a rounded or unrounded vowel? 15. Is vowel 2 a front or back vowel? 16. What vowel is vowel 2 (00, ee, ah) 0684285714arrow_forwardmicrowavearrow_forward4) Consider the pulley (Mass = 20kg, Radius 0.3m) shown in the picture. Model this pulley as a uniform solid disk (1 = (1/2) MR2) that is hinged at its center of mass. If the hanging mass is 30 kg, and is released, (a) compute the angular acceleration of the pulley (b) calculate the acceleration of the hanging mass. A o 0.3 3019 20KSarrow_forward
- Refer to the image attachedarrow_forwardShrinking Loop. A circular loop of flexible iron wire has an initial circumference of 161 cm , but its circumference is decreasing at a constant rate of 15.0 cm/s due to a tangential pull on the wire. The loop is in a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.00 T , which is oriented perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Assume that you are facing the loop and that the magnetic field points into the loop. Find the magnitude of the emf E induced in the loop after exactly time 9.00 s has passed since the circumference of the loop started to decrease. Find the direction of the induced current in the loop as viewed looking along the direction of the magnetic field. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardMake up an application physics principle problem that provides three (3) significant equations based on the concepts of capacitors and ohm's law.arrow_forward
- A straight horizontal garden hose 38.0 m long with an interior diameter of 1.50 cm is used to deliver 20oC water at the rate of 0.590 liters/s. Assuming that Poiseuille's Law applies, estimate the pressure drop (in Pa) from one end of the hose to the other.arrow_forwardA rectangle measuring 30.0 cm by 40.0 cm is located inside a region of a spatially uniform magnetic field of 1.70 T , with the field perpendicular to the plane of the coil (the figure (Figure 1)). The coil is pulled out at a steady rate of 2.00 cm/s traveling perpendicular to the field lines. The region of the field ends abruptly as shown. Find the emf induced in this coil when it is all inside the field, when it is partly in the field, and when it is fully outside. Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA rectangular circuit is moved at a constant velocity of 3.00 m/s into, through, and then out of a uniform 1.25 T magnetic field, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The magnetic field region is considerably wider than 50.0 cm . Find the direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the current induced in the circuit as it is going into the magnetic field (the first case), totally within the magnetic field but still moving (the second case), and moving out of the field (the third case). Find the magnitude of the current induced in the circuit as it is going into the magnetic field . Find the magnitude of the current induced in the circuit as it is totally within the magnetic field but still moving. Find the magnitude of the current induced in the circuit as it is moving out of the field. Please show all stepsarrow_forward
- Shrinking Loop. A circular loop of flexible iron wire has an initial circumference of 161 cm , but its circumference is decreasing at a constant rate of 15.0 cm/s due to a tangential pull on the wire. The loop is in a constant uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.00 T , which is oriented perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Assume that you are facing the loop and that the magnetic field points into the loop. Find the magnitude of the emf E induced in the loop after exactly time 9.00 s has passed since the circumference of the loop started to decrease. Find the direction of the induced current in the loop as viewed looking along the direction of the magnetic field. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA circular loop of wire with radius 0.0480 m and resistance 0.163 Ω is in a region of spatially uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure (Figure 1). The magnetic field is directed out of the plane of the figure. The magnetic field has an initial value of 7.88 T and is decreasing at a rate of -0.696 T/s . Is the induced current in the loop clockwise or counterclockwise? What is the rate at which electrical energy is being dissipated by the resistance of the loop? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA 0.333 m long metal bar is pulled to the left by an applied force F and moves to the left at a constant speed of 5.90 m/s. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 46.7 Ω resistor, as shown in (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. You can ignore the resistance of the bar and rails. The circuit is in a uniform 0.625 T magnetic field that is directed out of the plane of the figure. Is the induced current in the circuit clockwise or counterclockwise? What is the rate at which the applied force is doing work on the bar? Please explain all stepsarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





