
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Cyanide ion, carbonate ion, acetate ion can be considered as organic or not is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Compounds can be classified as organic and inorganic material on the basis of the material from which they are derived. The organic compound is the class of compound that has carbon-hydrogen bond or carbon-carbon long chains in their structure. They are derived from plants, animals and living organisms.
Inorganic compounds are those compounds that consist of other elements than carbon or have no carbon-carbon bond in their structure. They are derived from minerals.
Answer to Problem 1E
Acetate ion
Explanation of Solution
Cyanide ion
Acetate ion
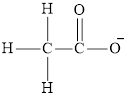
Acetate ion
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- In the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC name) can be represented by the letter OH OH HE > ' ÕH C B OH D A/ E OHarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardWhy is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forward
- In the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forwardFeedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: CN Δ + A ? NC Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. esc Check 80 MH F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 50 @ # C % 95 € Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C A DII F6 F7 F8 7 * 8 Λ & 6 F9 F10 9 0 4arrow_forwardIncorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Δ A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privaarrow_forwardesc 2 Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? A O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Check F1 ! @ X C Save For Later Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 80 et A ད 1 4 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 # $ 45 % A 6 87 & * 8 9 ) 0 + ||arrow_forwardCan the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ?A Δ O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilit ku F11arrow_forward
- १ eq ine teaching and × + rn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take [Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is In progress mit Answer Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support Save and Exitarrow_forwardDraw the molecules.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-hexan-2-ol with arrows please.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning





