
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Valence shell electronic configuration of
Concept Introduction:
Molecular orbital diagram is a linear combination of atomic orbitals of similar energy and similar symmetry. It is formed by the proper overlap of the atomic orbitals.
There are 3 types of molecular orbitals as follows:
1. Bonding molecular orbital: They are formed by the constructive interference of atomic orbitals and electrons in it stabilize the molecule and are of lesser in energy.
2. Antibonding molecular orbital: This type of orbitals increases the energy of molecule and destabilizes it and weakens the bond between the atoms.
3. Non-bonding molecular orbital: These types of orbitals have energy similar to atomic orbitals that is addition or removal of electron does not change the energy of molecule.
The order of energy in molecular orbital follows two rules as follows:
1. For
2. For atomic number more than 14 order of energy is,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
For
The symbol for nitrogen is
One positive charge is added up in the total valence count.
Thus total valence electrons is sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
Hence, 9 electrons are to be arranged in each molecular orbital to obtain an electronic configuration. Since number of electrons in
Hence, the electronic configuration of
For
The symbol for nitrogen is
Two positive charges are subtracted from the total valence count.
Thus total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
Hence, 8 electrons are to be arranged in each molecular orbital to obtain an electronic configuration. Since number of electrons in
Hence, the electronic configuration of
For
The symbol for nitrogen is
Two negative charges are added up in total valence count.
Thus total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
Hence, 12 electrons are to be arranged in each molecular orbital to obtain an electronic configuration. Since number of electrons in
Hence, the electronic configuration of
(b)
Interpretation:
The bond order of
Concept Introduction:
Bond order
(b)
Explanation of Solution
For
The electronic configuration of
Substitute 7 for number of electrons in bonding orbitals and 2 for number of electrons in antibonding orbitals in equation (1) to calculate bond order.
Hence, the bond order of the molecule
For
The electronic configuration of
Substitute 6 for number of electrons in bonding orbitals and 2 for number of electrons in antibonding orbitals in equation (1) to calculate bond order.
Hence, the bond order of the molecule
For
The electronic configuration of
Substitute 8 for number of electrons in bonding orbitals and 4 for number of electrons in antibonding orbitals in equation (1) to calculate bond order.
Hence, the bond order of the molecule
(c)
Interpretation:
Molecular orbital diagram of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to (a)
(c)
Explanation of Solution
For
The electronic configuration of
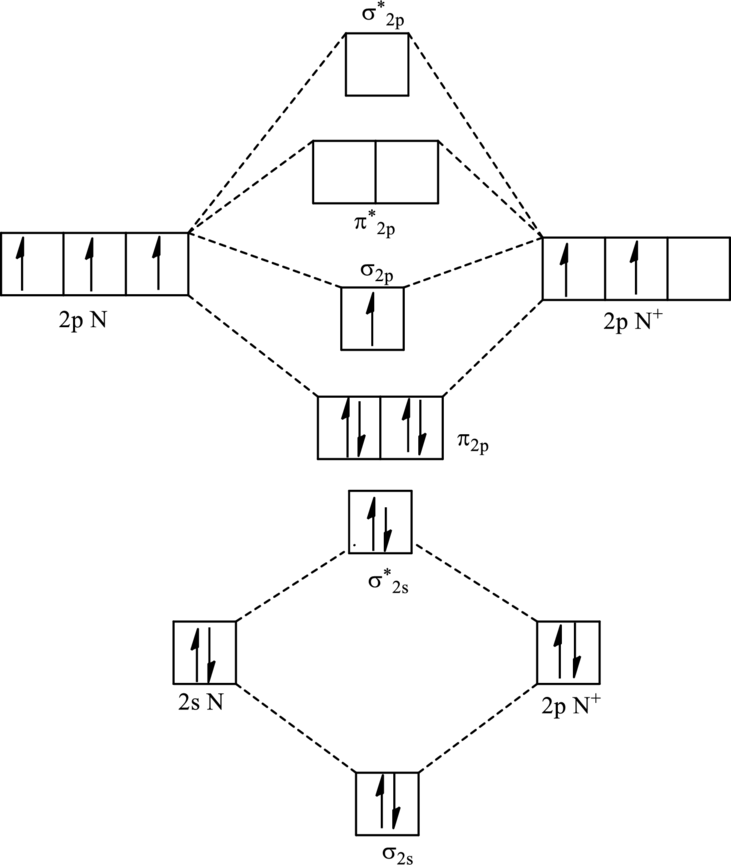
Since
For
The electronic configuration of
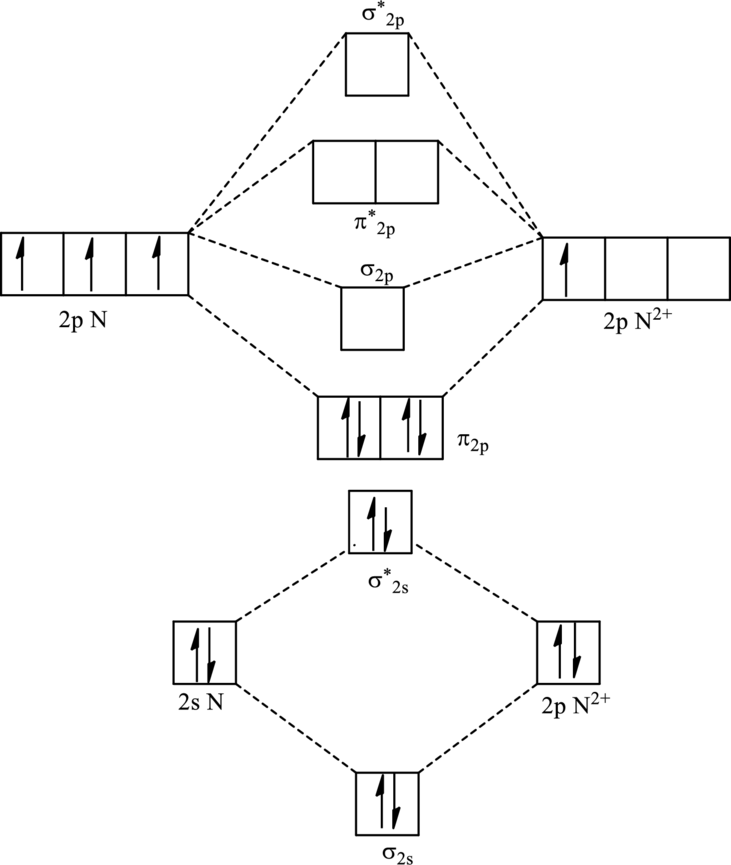
Since
For
The electronic configuration of
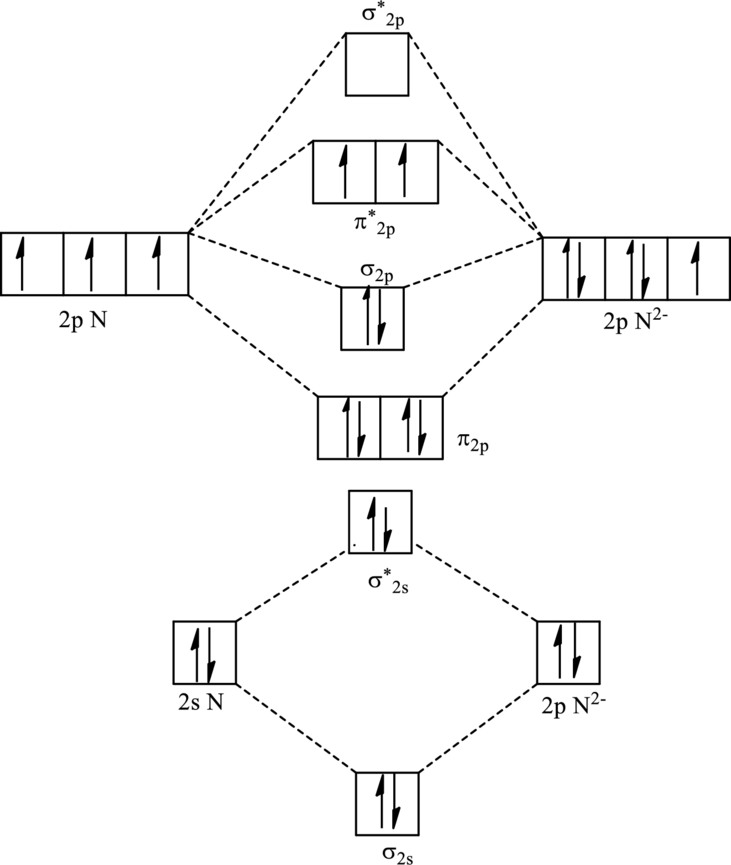
Since
(d)
Interpretation:
Character of highest energy orbital of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to (a)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
For
The electronic configuration of
For
The electronic configuration of
For
The electronic configuration of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 2TERM
- 4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

