
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model predicts shape by inclusion of bond angles and most distant arrangement of atoms that leads to minimum repulsion.
For molecules that have lone pairs around central atom, lone pairs influence shape, because there are no atoms at the positions occupied by these lone pairs. The key rule that governs the molecular shape, in this case, is the extent of lone pair–lone pair repulsions are far greater than lone bond pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsions. The table that summarized the molecular shapes possible for various combinations of bonded and lone pairs are given as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E.20E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 15 electron pairs are assigned as lone pairs of each of the
Hence, the Lewis structure
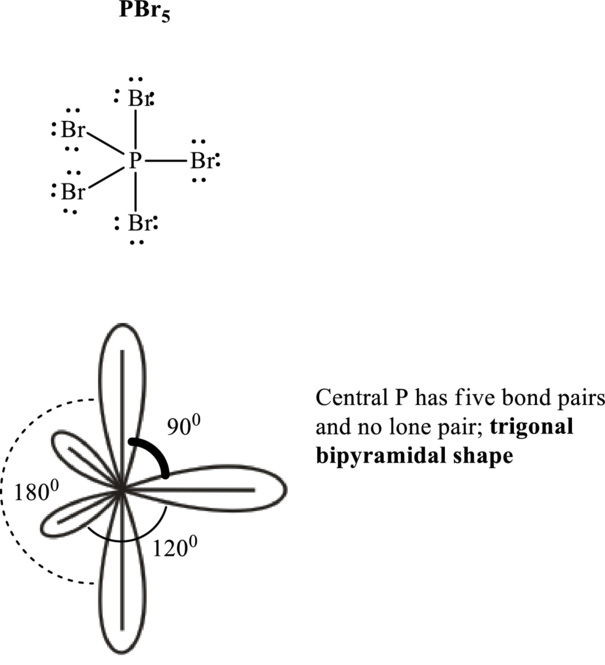
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any trigonal pyramidal geometry the VSEPR formula is predicted as
It is evident that in
The bond angles are
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 2E.20E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 11 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the fluorine, oxygen atoms and central xenon to satisfy respective octets. Thus, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSEPR geometry

It is evident that in
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.20E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each chlorine and central iodine in
The skeleton structure in
These 15 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to each of the
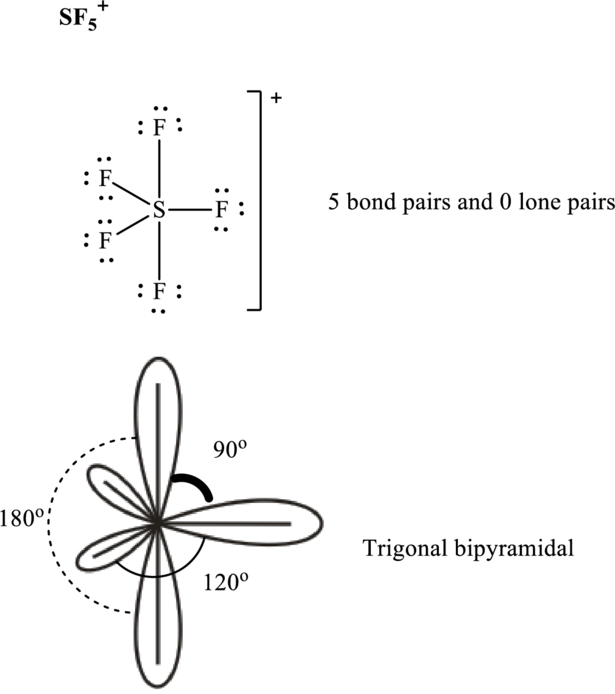
It is evident that in
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E.20E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each
The skeleton structure in
These 11 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the fluorine atoms and central iodine to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSPER geometry in
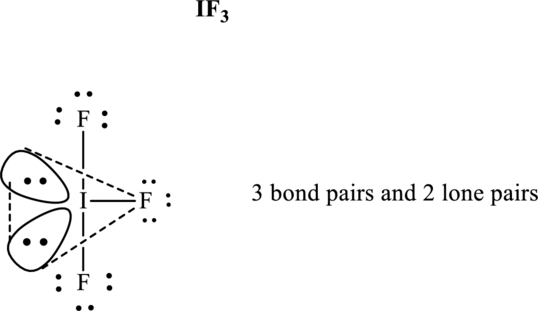
It is evident that in
Lone pairs tend to occupy the equatorial locations of trigonal plane so that they are
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Answer to Problem 2E.20E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 10 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs or multiple bonds to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSPER geometry in
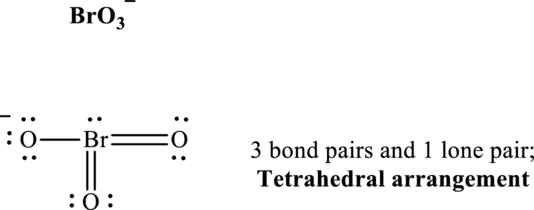
It is evident that in
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any see-saw species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
The bond pairs in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 2TERM
- NAME: 1. Draw the major product of the following E2 reaction. Make sure you pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. To get credit for this question, you must EXPLAIN how you got your answer using STRUCTURES and WORDS. Br NaOCH3 acetone F2 reaction To get credit for thisarrow_forward3. Reactions! Fill in the information missing below. Make sure to pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Br2 CH3OH + 4. Mechanism! Show the complete arrow pushing mechanism, including all steps and intermediates for the following reactions. To get credit for this, you MUST show how ALL bonds are broken and formed, using arrows to show the movement of electrons. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardPlease provide a synthesis for the Ester using proponoic acid, thank you!arrow_forward
- Please help with the curved arrow mechanism of this reaction, thank youarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 Question: Determine the regression equation (a and b coefficients) from first principlesarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 You have been asked to determine the concentration of citral in a highly valued magnolia essential oil. QUESTION: Calculate the concentration of citral in your highly valued magnolia essential oil which returns a peak area of 41658arrow_forward
- Need help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- 6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forwardDraw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning




