
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Bond angle at central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model predicts shape by inclusion of bond angles and most distant arrangement of atoms that leads to minimum repulsion. For the molecules that have no lone pairs around the central atom the bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement is decided by the table as follows:
In order to determine the shape the steps to be followed are indicated as follows:
- 1. Lewis structure of molecule should be written.
- 2. The type electron arrangement around the central atom should be identified around the central atom. This essentially refers to determination of bond pairs and unshared or lone pairs around central atoms.
- 3. Then bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement that can maximize the distance of electron pairs about central atom determines the shape.
For molecules that have lone pairs around central atom, lone pairs influence shape, because there are no atoms at the positions occupied by these lone pairs. The key rule that governs the molecular shape, in this case, is the extent of lone –lone pair repulsions are far greater than lone bond pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsions. The table that summarized the molecular shapes possible for various combinations of bonded and lone pairs are given as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E.18E
In
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 8 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
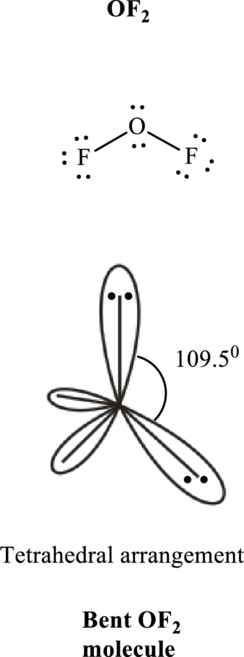
It is evident that
(b)
Interpretation:
Bond angle at central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 2E.18E
In
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 8 electron pairs are allotted as one multiple bond and rest as lone pairs to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
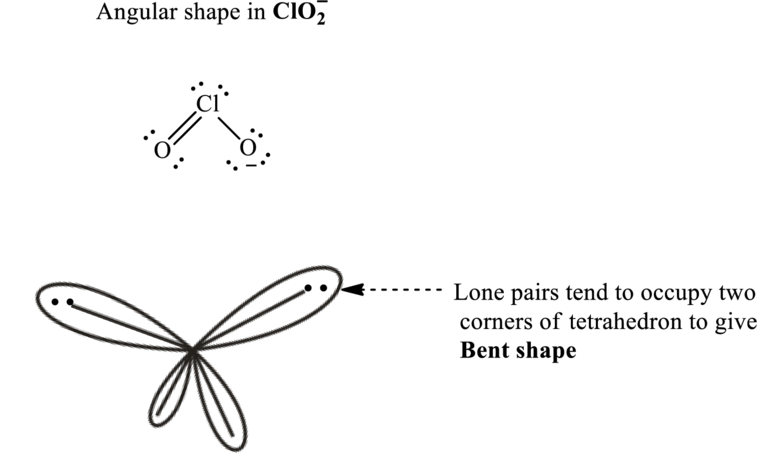
It is evident that
(c)
Interpretation:
Bond angle at central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.18E
In
Explanation of Solution
Thus total valence electrons is sum of the valence electrons on each atom along with charge in
The skeleton structure in
These 7 electron pairs are allotted multiple bonds or lone pairs to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure and bond angle in
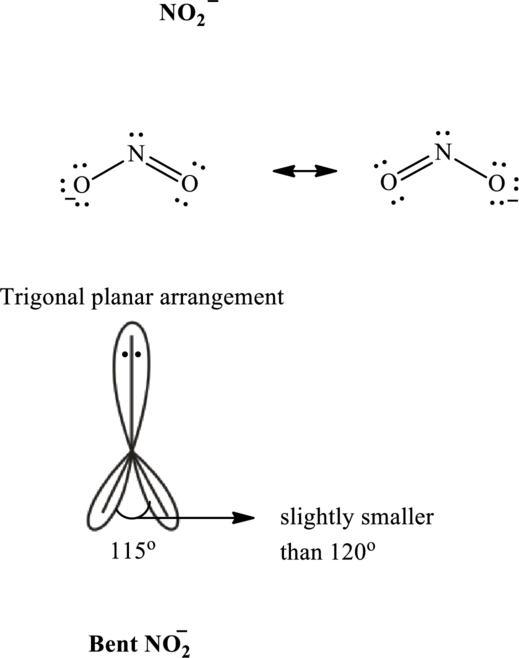
It is evident that
(d)
Interpretation:
Bond angle at central atom for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E.18E
Bond angle in
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 8 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to satisfy the respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
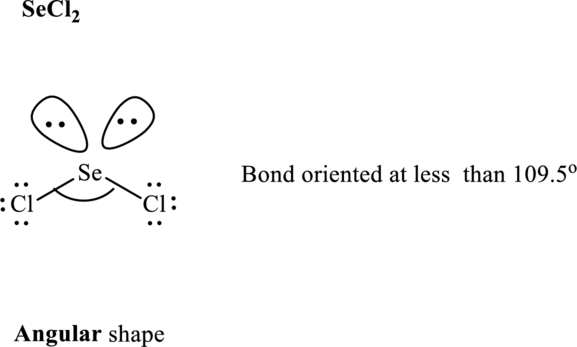
It is evident that in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 2TERM
- I need help with the followingarrow_forwardFor Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
- For CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning



